Shenton’s line is normal on the left (red line). If this line is followed on the right a clear breach in the cortex is seen along the neck of the femur. A fracture line passes across the femoral neck from this point (arrowheads)
24.2 Osteoarthritis: AP view
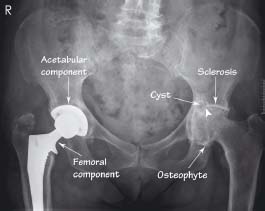
The left hip shows joint space narrowing (arrowhead), articular surface sclerosis, subchondral cyst formation, and an osteophyte of the head-neck junction. The right hip has already been replaced
24.3 Paget’s disease: left hip AP view
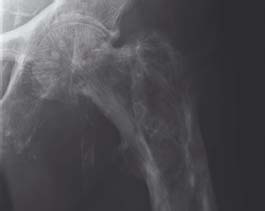
Coarsening of the trabecular markings and thickening of the cortex are typical features of Paget’s disease
24.4 Slipped upper femoral epiphysis: ‘frog-leg’ view
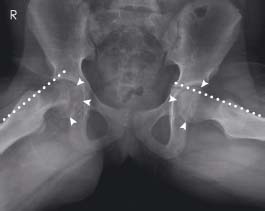
On the right (R) the ‘line of Klein’ (dotted line) no longer passes through the femoral capital epiphysis (arrowheads). Normal appearances are shown on the left
24.5 Perthes’ disease: AP and ‘frog-leg’ views
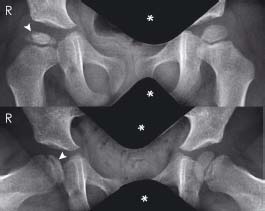
The right femoral epiphysis is small and flattened compared with the left side. Sclerosis of the epiphysis (arrowheads) and joint space widening are also demonstrated. Shielding (*) is used to protect the genitals from radiation exposure
24.6 Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH): AP view
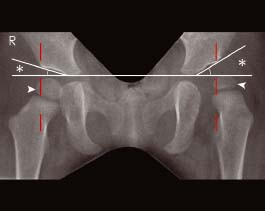
On the left the femoral epiphysis (arrowhead) lies almost entirely outside Perkins’ line (red dotted line). The acetabular angle (*) is also increased on the left. Normal appearances are shown on the right
Neck of femur fracture (NOFF)
These are common injuries, often sustained by the elderly. The patient classically presents unable to weight-bear on a shortened and externally rotated leg (due to the unopposed action of the iliopsoas muscle on the femur). NOFFs are clinically classified into:
- Intracapsular NOFF – these are high transcervical or subcapital fractures within the joint capsule and disrupt the major blood supply to the femoral head. This predisposes the femoral head to avascular necrosis (AVN) or fracture nonunion. These fractures require hemiarthroplasty or total hip replacement.
- Extracapsular NOFF – the fracture lies outside the joint capsule (lower third of the neck) and so the vascular supply to the femoral head is uninterrupted. These can be treated with dynamic hip or can-nulated screws, thereby preserving the femoral head.
- Trochanteric NOFF

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree