Stage
Areas involved
I
One lymph node region or lymphoid structure
II
≥2 lymph node regions on the same side of the diaphragm
III
Lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm
IV
Extranodal sites other than one contiguous or proximal extranodal site or bone marrow
Qualifier
Clinical features
A
No systemic symptoms present
B
Unexplained fevers >38 °C; drenching night sweats; or weight loss >10% of body weight (within 6 months prior to diagnosis)
X
Bulky disease (mediastinal mass larger than a third of thoracic diameter, or any nodal mass >10 cm in diameter)
E
Involvement of one contiguous or proximal extranodal site
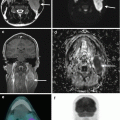
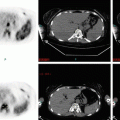
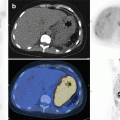
The Lugano Classification also incorporates CT neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis combined with functional imaging with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-PET (PET/CT) as the optimal staging modality in Hodgkin lymphoma. PET/CT upstages 13–24% of cases compared to CT only. PET/CT may however be positive in sites of infection or inflammation and careful interpretation is required.
PET/CT is highly sensitive for focal bone marrow infiltration, and non-targeted pelvic bone marrow biopsy for staging is now rarely performed. Diffuse bone marrow uptake on PET/CT usually reflects a reactive process, while focal lesions are usually due to disease. Where there is uncertainty, a bone marrow biopsy is advisable.
1.6 Prognostic Factors at Baseline
At diagnosis, cHL is sub-classified into three main prognostic categories (Box 1.1), namely, early favourable, early unfavourable, and advanced, according to the modified Ann-Arbor stage and, for early stage cHL, the presence of clinical risk factors. The treatment and outcomes are in turn influenced by the prognostic category the patient falls into. The precise definition of the risk factors differs somewhat among study groups. The German Hodgkin Study Group risk factors are widely used in early stage disease. Bulky disease has been shown to be an independent adverse prognostic marker in early stage cHL, as is extranodal extension, presence of 3 or more nodal sites (see Fig 1.1) and a raised ESR.
German Hodgkin Study Group Risk Factors for early stage cHL
Large mediastinal mass ≥one third of the maximum thorax diameter
Involvement of one contiguous or proximal extranodal site
Involvement of three or more nodal areas (see Fig. 1.1)
Elevated ESR (>50 mm/h in stages I–IIA and >30 mm/h in stages I–IIB)
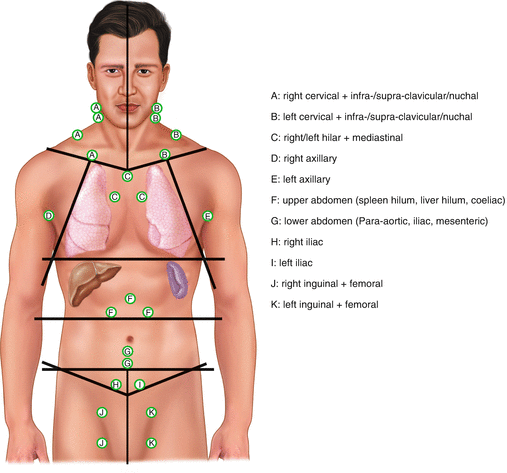
Fig. 1.1
Definition of main lymph node areas (German Hodgkin Study Group)
Box 1.1 Prognostic Categories in cHL
Early favourable
Stages I–IIA/B without any risk factors
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree