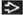Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, Acute-Subcute
Jud W. Gurney, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Diffuse granulomatous interstitial lung disease caused by inhalation of various antigenic particles (microbes, animal proteins, and low-molecular weight chemicals)
Imaging Findings
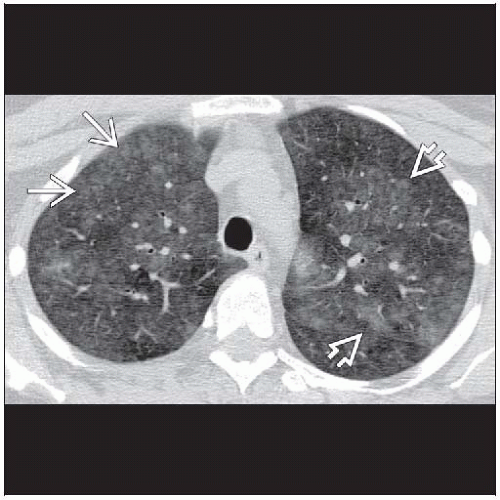
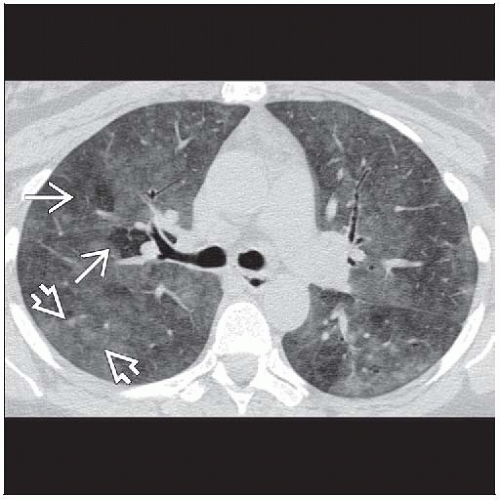
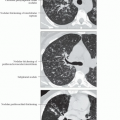
Ground-glass centrilobular nodules & mosaic perfusion
Geographic ground-glass attenuation + normal lung + mosaic perfusion + air-trapping = head cheese sign
Air-trapping expiratory scan (95%)
Tree-in-bud pattern rare
Lung cysts (10%), always seen in conjunction with diffuse ground-glass opacities
Top Differential Diagnoses
Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia (NSIP)
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Vasculitis, includes Churg-Strauss, microscopic polyangiitis, lupus erythematosus
Sarcoidosis
Clinical Issues
Diagnosis often delayed more than 1 year
Depends largely on avoiding antigen and removal from offending environment
Nonspecific symptoms in acute disease often mistaken as pneumonia
Since disease self-limited, antibiotics may appear to improve patient’s condition
Diagnostic Checklist
Normal chest radiograph and strikingly diffuse abnormal CT commonly seen with HP
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Extrinsic allergic alveolitis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP), farmer’s lung
Definitions
Diffuse granulomatous interstitial lung disease caused by inhalation of various antigenic particles (microbes, animal proteins, and low-molecular weight chemicals)
Farmer’s lung and bird fancier’s lung are most common forms
“Hot tub” lung latest source
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue: Ground-glass centrilobular nodules & mosaic perfusion (or lobular air-trapping)
Patient position/location: Diffuse mid lung most common, typically spares costophrenic angles
Morphology: Predominant ground-glass opacities forming small ill-defined centrilobular nodules
CT Findings
More sensitive than chest radiography but may be normal
Sensitivity in 1 population-based study that used 1990’s technology, only 50% (sensitivity of chest radiographs even worse at 10%)
CT signs
Ground-glass opacities (100%)
Geographic distribution in central and peripheral portions of lung, nonspecific
Centrilobular nodules (70%)
Ground-glass density with ill-defined edges usually < 5 mm in diameter
Pleural surfaces usually spared
Mosaic perfusion (80%) (usually from air-trapping)
Air-trapping expiratory scan (95%)
Individual signs nonspecific, combined signs more specific
Distribution of disease
Most prominent mid to lower lungs, commonly spares (or less severe) costophrenic angles
Acute stage
Diffuse ground-glass opacities
Small ill-defined centrilobular nodules, nearly always in conjunction with ground-glass opacities
Centrilobular nodules more likely to be found in less severely involved lung
Air-trapping common, usually at lobular level
Tree-in-bud pattern rare
Subacute stage
Ground-glass opacities (patchy distribution) to mosaic perfusion
Ill-defined centrilobular nodules (< 5 mm diameter) more common than in acute stage
Lung cysts (10%), nearly always seen in conjunction with diffuse ground-glass opacities
Thin-walled 3-25 mm diameter
Mean number 4 cysts per patient (range 1-15)
Associated findings
Mediastinal adenopathy (50%), nodes < 20 mm short axis diameter
Pleural effusion rare
Resolution: Lung may return to normal with avoidance of antigen or steroid therapy
Radiographic Findings
Radiography
Acute stage
Chest radiography abnormal in only about 10%
Nonspecific fine nodular or reticulonodular pattern, consolidation rare (usually signifies community acquired pneumonia)
Subacute stage
Chest radiograph more often abnormal (90%) (but may be subtle)
Poorly defined small nodules (miliary pattern) or areas of ground-glass opacities
Imaging Recommendations
Best imaging tool: 1 clue to diagnosis of HP is marked disparity between normal chest radiograph and striking diffuse abnormal CT
Protocol advice: Expiratory scanning may be useful to show air-trapping
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia (NSIP)
Ground-glass opacities > reticulation
Traction bronchiectasis usually out of proportion to degree of reticulation
Peripheral &/or peribronchovascular distribution
Air-trapping not a feature as it is in HP
Centrilobular nodules uncommon
Metastatic Pulmonary Calcification
Ill-defined centrilobular nodules similar to HP
Nodules may have calcific attenuation, not seen with HP
Usually upper lung zone in distribution
Seen in patients with disorders of calcium metabolism, most commonly renal failure
Vasculitis
Includes Church-Strauss syndrome and
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Anemia with hemorrhage, not seen with HP
Air-trapping uncommon
Often have renal disease
Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia
Similar CT findings: Ground-glass opacities, centrilobular nodules and cysts
Air-trapping not a feature
Often have dysproteinemias or Sjögren syndrome
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Centrilobular nodules, may cavitate as they get larger
Usually seen in smokers (smoking less common in HP)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree