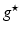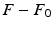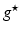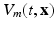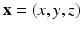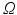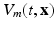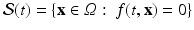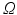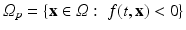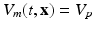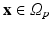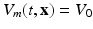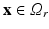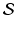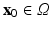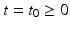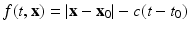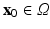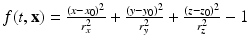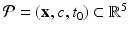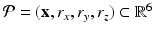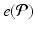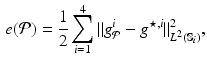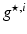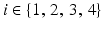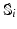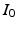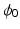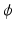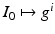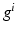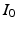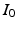) recorded when the tissue is at rest. Fluxes captured during an AP are denoted by F. The signal due only to the AP itself is 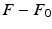 . We shall rather use the usual renormalization:
. We shall rather use the usual renormalization:
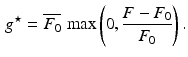
(1)
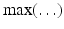 amounts to ignore negative, physically irrelevant, optical signals (due to noise). The multiplication by the average
amounts to ignore negative, physically irrelevant, optical signals (due to noise). The multiplication by the average 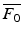 of the background signal is a way to retrieve the correct amplitude of the signal. Our main goal is to reconstruct the 3D front of the AP from these 2D optical data.
of the background signal is a way to retrieve the correct amplitude of the signal. Our main goal is to reconstruct the 3D front of the AP from these 2D optical data.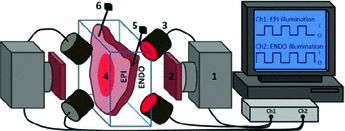
Fig. 1.
The optical imaging setup: (1) CCD camera, (2) emission filter, (3) LED illumination, (4) tissue sample, (5) ECG electrode, (6) bipolar stimulating electrode.
3 Model
3.1 Forward Problem
In order to write the mathematical model of these observations, we assume the following: the cameras record photon fluxes through the surfaces, the light interacts with the tissue material in the diffusive regime [2], and a Robin boundary condition can be used to model the interaction between the tissue and its environment. Hence the illumination light is described by its photon density 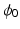 that solves the diffusion equation
that solves the diffusion equation
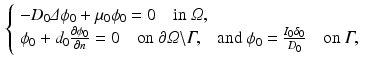
where  represents the slab of tissue,
represents the slab of tissue, 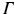 is the illuminated surface, and n is the unit normal to
is the illuminated surface, and n is the unit normal to 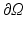 , outward of
, outward of 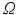 . The fluorescent light is assumed to be proportional to the TMP and the illumination light (multiplicative factor
. The fluorescent light is assumed to be proportional to the TMP and the illumination light (multiplicative factor 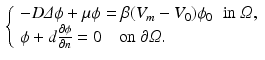
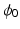 that solves the diffusion equation
that solves the diffusion equation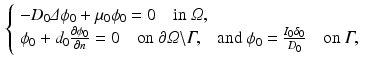
(2)
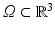 represents the slab of tissue,
represents the slab of tissue, 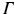 is the illuminated surface, and n is the unit normal to
is the illuminated surface, and n is the unit normal to 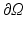 , outward of
, outward of 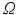 . The fluorescent light is assumed to be proportional to the TMP and the illumination light (multiplicative factor
. The fluorescent light is assumed to be proportional to the TMP and the illumination light (multiplicative factor 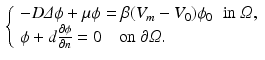
(3)
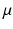 , d stand respectively for diffusion coefficient, absorption coefficient and extrapolation distance. The attenuation length is the parameter
, d stand respectively for diffusion coefficient, absorption coefficient and extrapolation distance. The attenuation length is the parameter 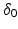 defined by
defined by 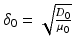 . The intensity of the illumination, assumed uniform, is the parameter
. The intensity of the illumination, assumed uniform, is the parameter 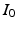 . The multiplicative factor
. The multiplicative factor