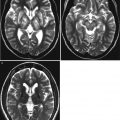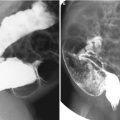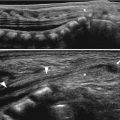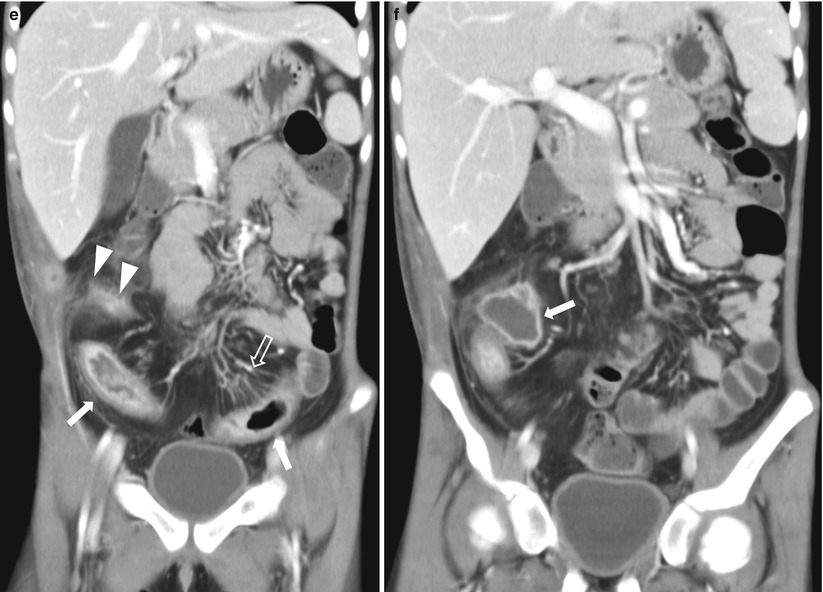
Fig. 21.1
Crohn disease. (a) Small bowel series in an 8-year-old girl with Crohn disease shows irregular loops of the distal ileum with nodular thickening of the mucosal folds and speculated borders (arrows). (b) Ultrasound of the same patient shows diffuse bowel wall thickening with submucosal low echogenicity in the distal ileum (arrows). (c) Color Doppler ultrasound shows increased vascularity of the involved distal small bowel loops. (d) Ultrasound of the same patient 6 years later shows diffuse thickening of the bowel loops with loss of normal mucosal layering (arrows) and diffuse echogenicity along the bowel loops suggesting fatty proliferation. (e) Coronal view of contrast-enhanced CT of the same patient demonstrates mucosal hyperenhancement (arrows) wall thickening and multiple mesenteric LNS in the RLQ. Note the engorged vasa recta suggesting comb sign in the LLQ (open arrow) and enhancing fistulous tract in the RLQ (arrowheads). (f) An abscess with irregular enhancing wall (arrow) is also seen in RLQ
21.4.2 Crohn Disease: MR Enterography
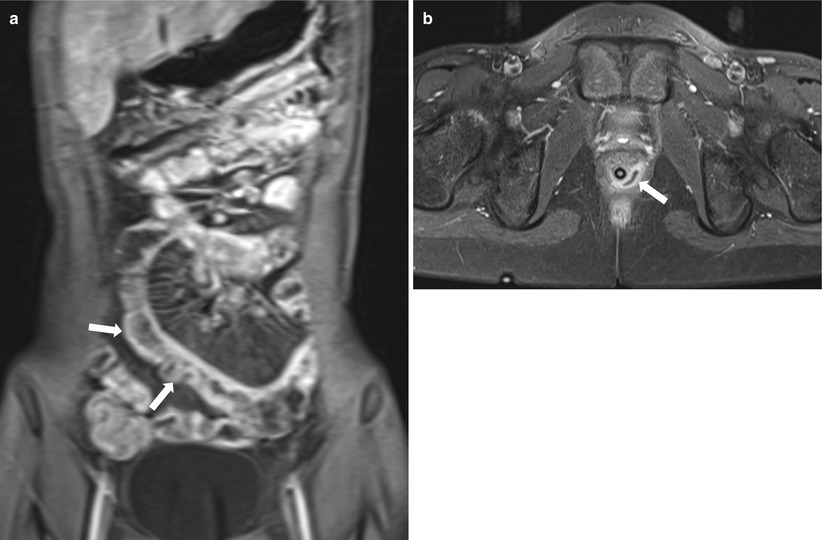
Fig. 21.2
Crohn disease: MR enterography. (a) Coronal view of contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image of a 19-year-old male demonstrates mucosal hyperenhancement and engorged vasa recta of the small bowel segments indicating active inflammation. Note the pseudosacculation of the distal small bowel loops (arrows). (b) Axial view of contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image of a 10-year-old boy shows peripheral-enhancing perianal abscess from 3 to 6 o’clock direction (arrow)
21.4.3 Ulcerative Colitis
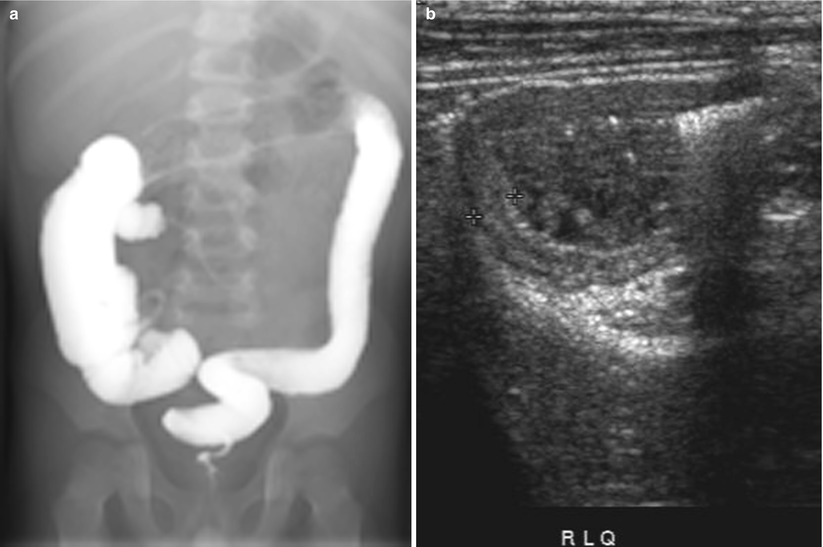
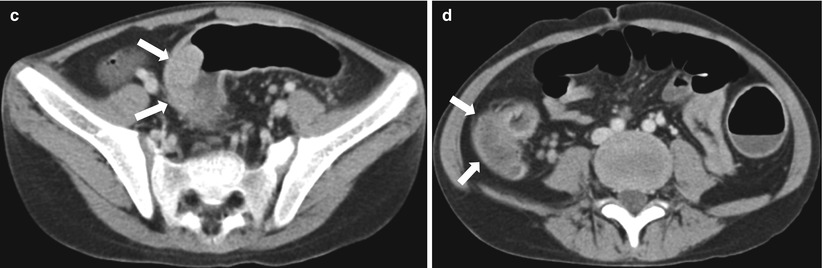
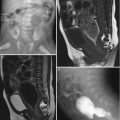
Fig. 21.3
Ulcerative colitis. (a) Barium enema of a 5-year-old boy shows loss of haustra and fine nodularities in the descending colon and transverse colon. (b) Ultrasound demonstrates diffuse bowel wall thickening in the entire colon. (c, d) Follow-up CT obtained 10 years later shows a polypoid mass (c, arrows) in the sigmoid colon and diffuse bowel wall thickening in the ascending colon (d, arrows). Total proctocolectomy was performed and the sigmoid mass was confirmed as adenocarcinoma
21.4.4 Chronic Granulomatous Disease
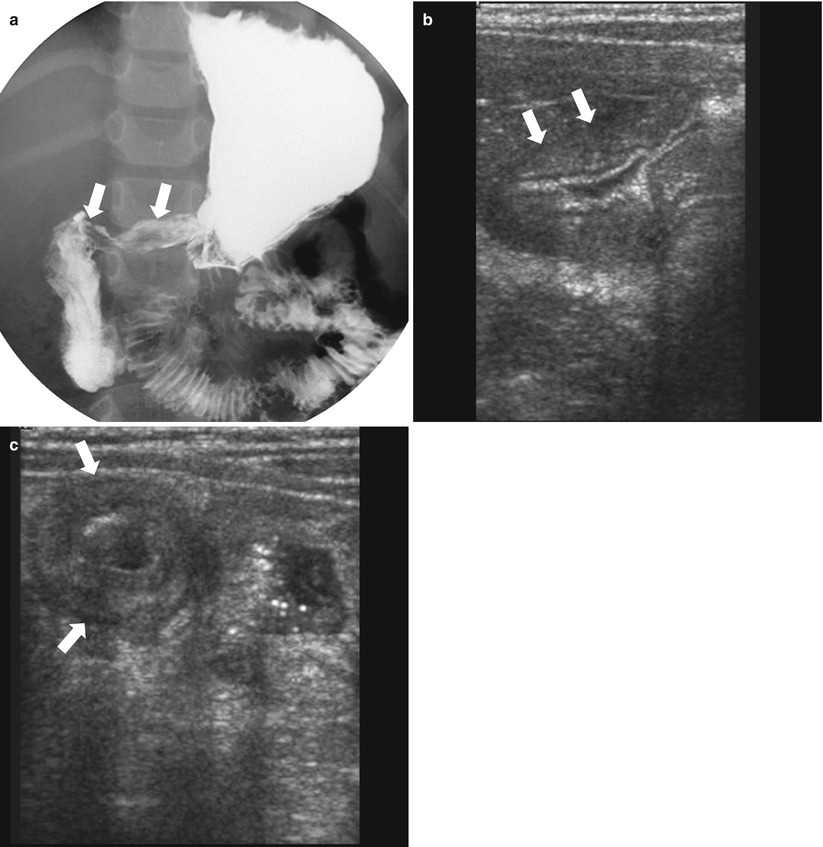
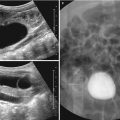
Fig. 21.4
Chronic granulomatous disease. (a) A 5-year-old boy with known chronic granulomatous disease presents with recurrent vomiting. Upper GI series demonstrates segmental narrowing of the antrum and collapsed duodenal bulb (arrows). (b, c) Ultrasound images show diffuse wall thickening in the distal antrum (arrows, b) and duodenal bulb (arrows, c) suggesting chronic granulomatous disease involvement
21.4.5 Graft-Versus-Host Disease
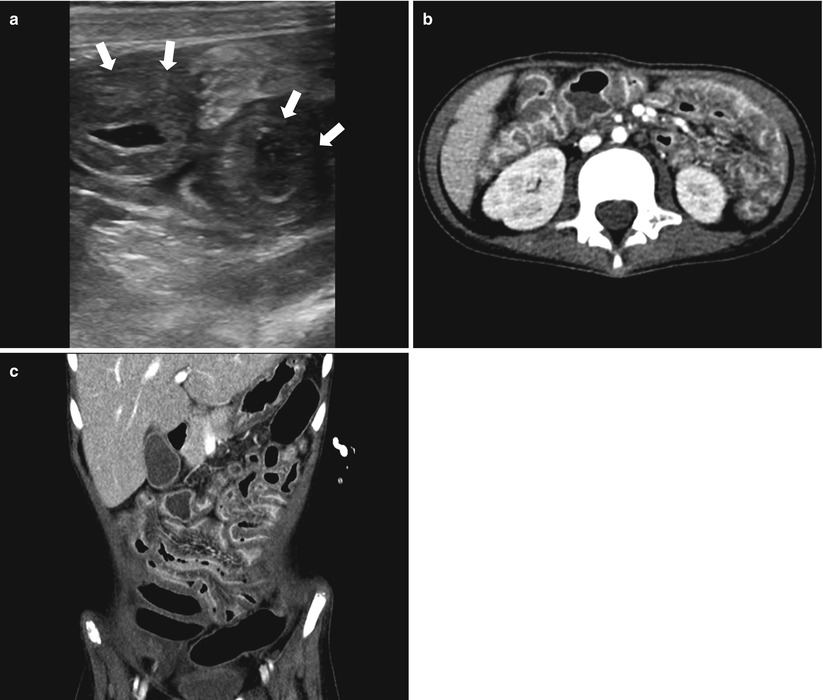
Fig. 21.5
Graft-versus-host disease. (a) Ultrasound of a 6-year-old boy with acute leukemia and recent stem cell transplantation shows diffuse bowel wall thickening in the small bowel loops with submucosal low echogenicity in the RLQ (arrows). (b, c) Axial and coronal contrast-enhanced CT show thickened bowel loops and a thin layer of mucosal enhancement
21.4.6 Pseudomembranous Colitis
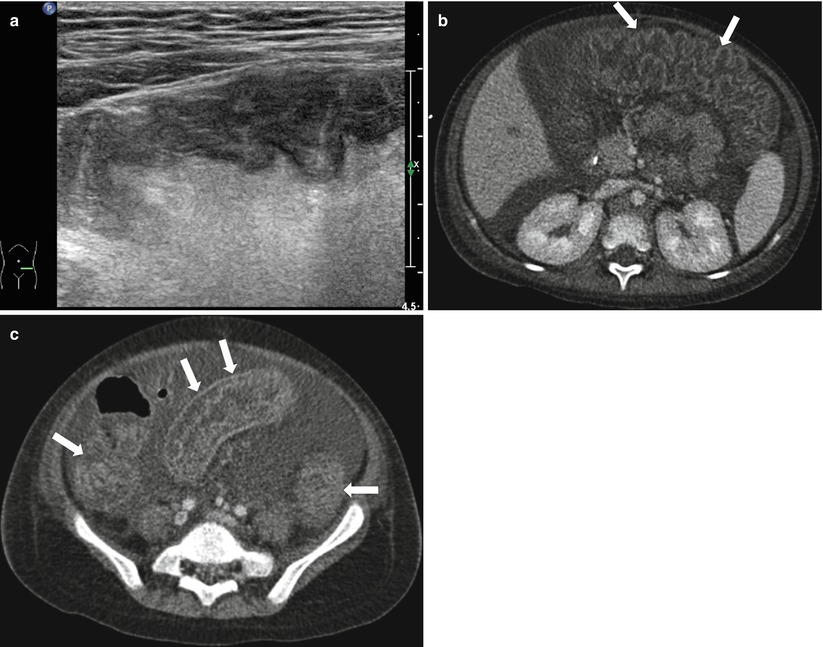
Fig. 21.6
Pseudomembranous colitis. (a) Ultrasound of a 4-year-old boy with acute leukemia shows diffuse bowel wall thickening in the LLQ. He has been treated with antibiotics since 7 days ago, and Clostridium difficile toxin assay was positive. (b, c) Axial images of contrast-enhanced CT show markedly thickened haustral folds in the entire colon suggesting “accordion sign” (arrows). Moderate amount ascites are also seen on CT images
21.4.7 Neutropenic Colitis
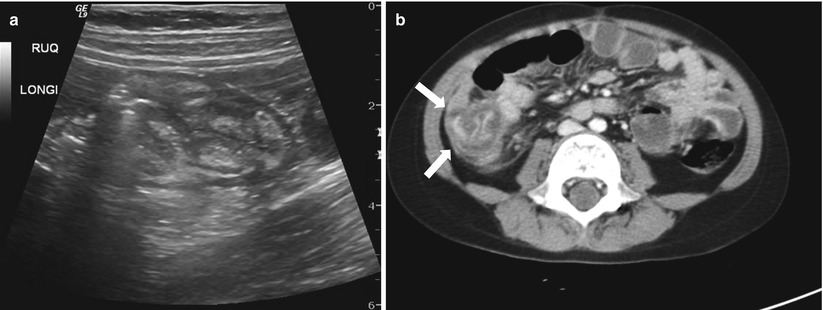
Fig. 21.7
Typhlitis in a 10-year-old with acute leukemia, status post bone marrow transplantation. (a) Ultrasound shows diffuse edematous thickening in the cecum and ascending colon. (b) Axial contrast-enhanced CT shows circumferential wall thickening of the cecum and ascending colon with pericolic fat strands (arrows)
21.4.8 Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
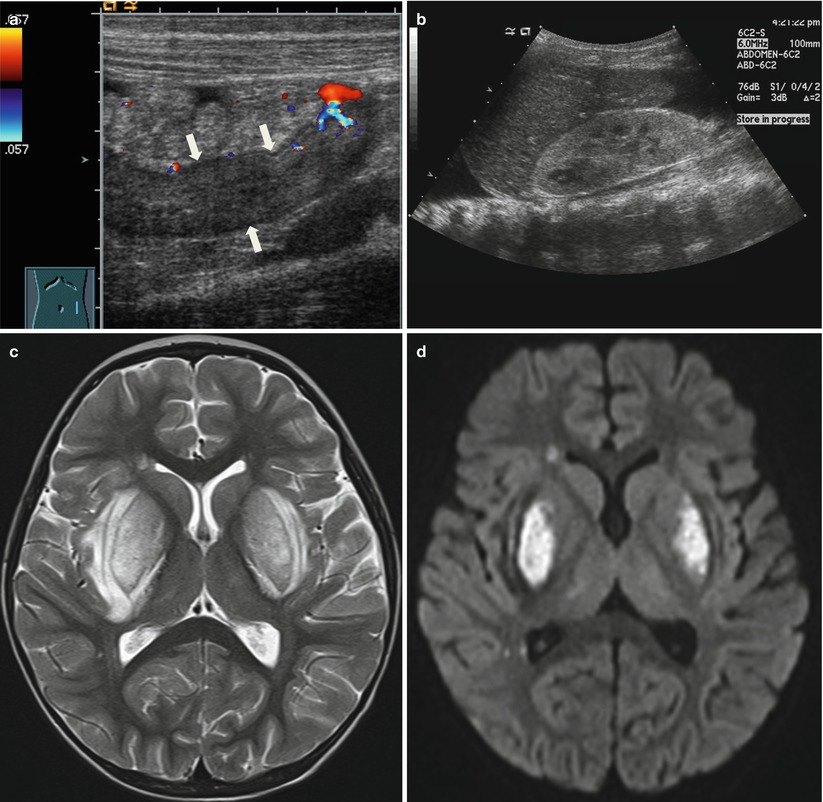
Fig. 21.8
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome. (a, b) Ultrasound of a 2-year-old girl with fever and anuria shows diffuse bowel wall thickening in the descending colon with decreased perfusion (a, arrows) and diffuse increased parenchymal echogenicity of the kidneys (b). There are moderate amount of pleural effusion and ascites. (c) Axial T2-weighted image shows bilateral edematous swelling in the basal ganglia. (d) Bilateral basal ganglia lesions shows restricted diffusion
21.4.9 Burkitt Lymphoma
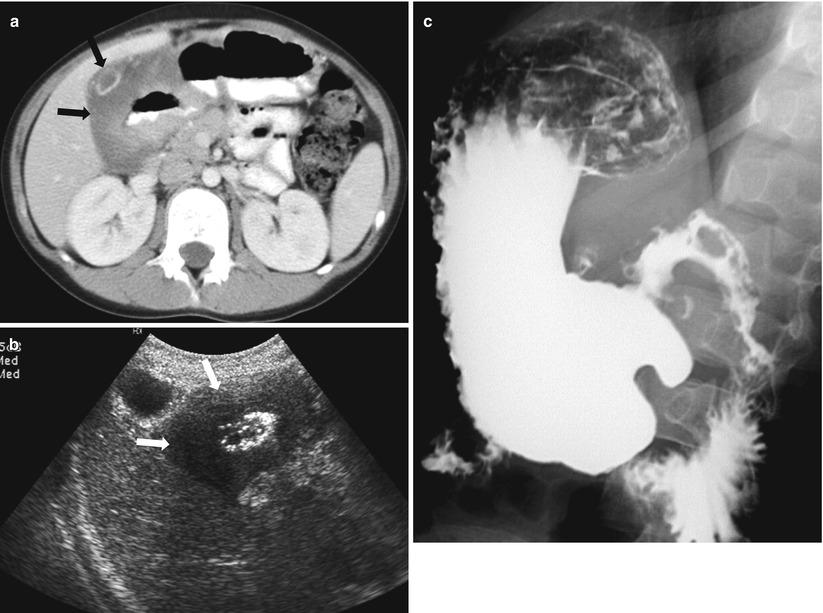
Fig. 21.9
Burkitt lymphoma with bowel involvement. (a) Contrast-enhanced CT of a 4-year-old boy presented with abdominal pain and vomiting shows hypoattenuating, diffuse wall thickening involving duodenal bulb and second portion of the duodenum (arrows). (b) Ultrasound shows diffuse hypoechoic lesion involving duodenum (arrows). (c) Upper GI series shows irregular fold thickening involving the duodenum first and second portions
21.4.10 Peutz–Jeghers Syndrome
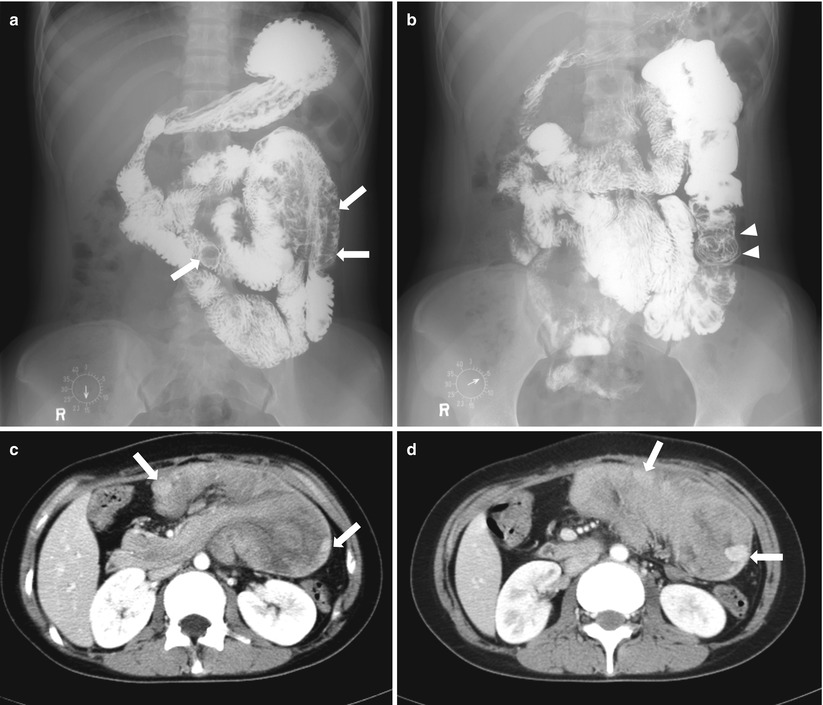
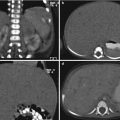
Fig. 21.10




Peutz–Jeghers syndrome. (a, b) Small bowel series show multiple polyps as filling defect in the proximal jejunum (a, arrows). Note the coil spring appearance at proximal jejunum suggesting intussusception (b, arrowheads). (c, d) Axial post-contrast CT of another patient with Peutz–Jeghers syndrome shows a huge small bowel intussusception due to polyps. Note the enhancing polyps within the intussusceptum (arrows)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree