23 Internal Iliac Artery
K.I. Ringe, S. Meyer
The parietal and visceral arteries branch from the internal iliac artery in numerous ways.1–10 It is difficult to classify these types according to embryological development or by practical features. According to embryological development, the umbilical artery must be the main branch and the other arteries only side branches.7 After birth, the umbilical artery is no longer important, and in approximately 0.7% of all cases one umbilical artery is absent. These anomalies are not shown in the figures. Some recent studies have described and partly summarized such cases along with the relevant literature.11,12 The sequence of branches or trunk formations is extremely variable.6,13,14 This situation is also complicated by the various names of these arteries in the different anatomical nomenclatures. In some clinical studies, the internal iliac artery is still called the hypogastric artery.
23.1 All Arteries Branch from One Main Stem of the Internal Iliac Artery (10%)
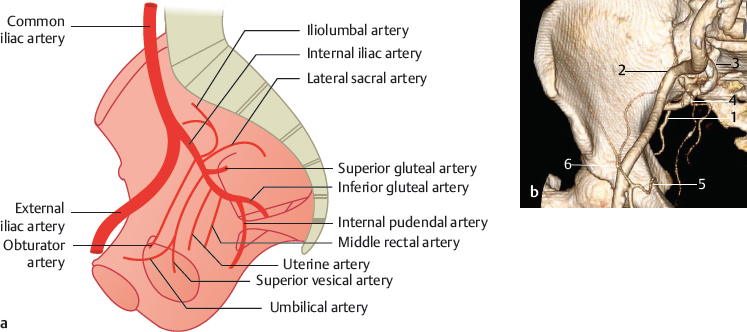
Fig. 23.1 One main stem of the internal iliac artery (10%). Schematic (a) and 3D VR CT (b). 1 Inferior gluteal artery; 2 external iliac artery; 3 internal iliac artery; 4 superior gluteal artery; 5 obturator artery; 6 epigastric artery.
23.2 The Iliac Artery Divides into Two Main Stems Which Give Off the Other Branches (60%)
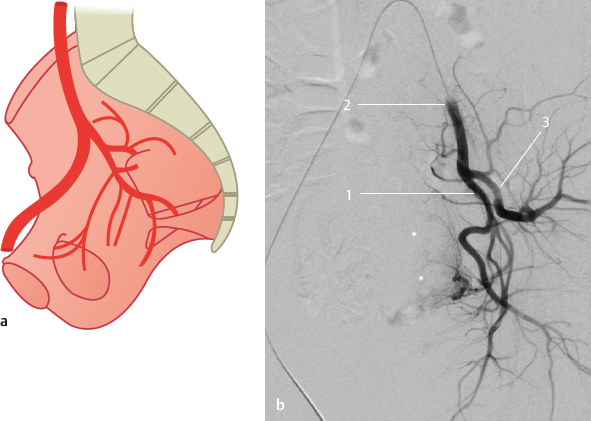
Fig. 23.2 The posterior main stem ends as the superior gluteal artery, the anterior trunk ends as the inferior gluteal and the internal pudendal arteries (35%). Schematic (a) and DSA (b). The DSA shows the left internal iliac artery dividing into two main stems which give off the other branches. The patient has uterine myoma (*) and was undergoing embolization therapy. 1 Anterior main stem; 2 internal iliac artery; 3 posterior main stem.
Fig. 23.3 The anterior stem ends as the internal pudendal artery, the posterior trunk divides into the superior and inferior gluteal arteries, which leave the pelvis through the suprapiriform and infrapiriform foramen (12%). Schematic (a) and oblique coronal 3D VR CT (b) of the right internal iliac artery. 1 External iliac artery; 2 internal iliac artery; 3 posterior stem; 4 anterior stem.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree