Chapter 19 Interventional Techniques
TRANSTHORACIC NEEDLE BIOPSY
Indications
Transthoracic needle biopsies (Box 19-1) are performed most commonly for the diagnosis of an indeterminate solitary pulmonary nodule. Not all solitary pulmonary nodules that are suspect for bronchogenic carcinoma require biopsy. If the pretest probability is very high for lung cancer or a biopsy is unlikely to have any impact on management, TNB should not be performed. For example, if a patient presents with a long history of smoking and a new, irregular, spiculated nodule in the lung, the likelihood is extremely high that this represents a lung cancer, and it is reasonable to proceed directly to staging and resection. Other indications for TNB include undiagnosed mediastinal masses, a hilar mass when the bronchoscopy result is negative, single or multiple pulmonary nodules in a patient with a known extrathoracic malignancy or a suspicion of metastatic disease, and suspected infectious lesions manifesting as solitary nodules, masses, or very focal areas of consolidation, particularly in the immunocompromised host.
Box 19-1 Indications for Transthoracic Needle Biopsy
Indeterminate solitary pulmonary nodule
Hilar mass when bronchoscopy is negative
Single or multiple nodules when metastases are suspect
Contraindications
Most contraindications to TNB are relative rather than absolute (Box 19-2). The most important are bleeding diatheses. A prebiopsy prothrombin time (PT), partial thromboplastin time (PTT), and platelet count are recommended. A careful history of coagulation abnormalities or the ingestion of drugs such as aspirin, which may lead to abnormal platelet function, should be obtained. Patients with low platelet counts who require an emergent biopsy, such as an immunocompromised patient with pulmonary infection, can receive platelet transfusions. Biopsy of lesions that have a marked vascular supply should be avoided.
Box 19-2 Relative Contraindications to Transthoracic Needle Biopsy
COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
Technique
Prebiopsy Imaging
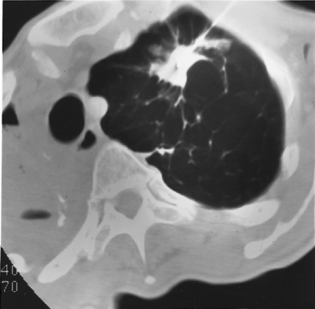
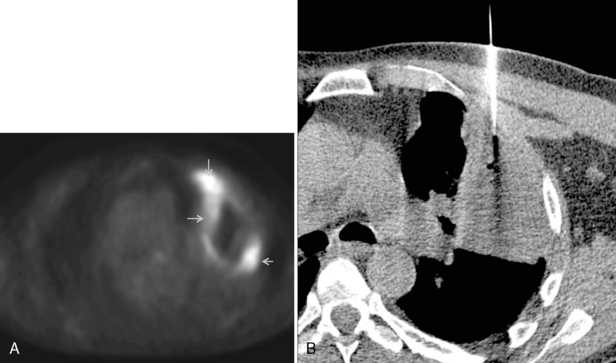
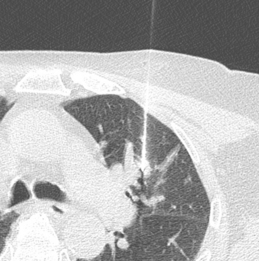
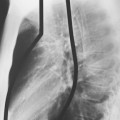
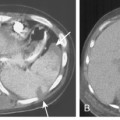
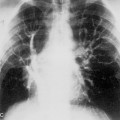
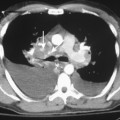
Computed tomography (CT) is highly recommended before TNB. CT is useful in providing a specific benign diagnosis in certain instances, such as a calcified granuloma or hamartoma, and it can provide information concerning the optimal approach to the lesion (Figs. 19-1 and 19.2). Areas of necrosis within large masses can be identified. Such areas should be avoided because they often produce nondiagnostic samples. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) is also useful for identifying the viable portion of the tumor (Fig 19-3). Vascular lesions such as aneurysms or arterial venous malformations can be easily recognized on contrast-enhanced CT.
Imaging Guidance
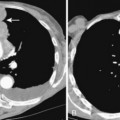
Fluoroscopy or CT can be used for imaging guidance. Ultrasound is occasionally used for chest wall or peripheral lesions abutting the pleura. Fluoroscopically guided biopsies are usually reserved for large masses (Fig. 19-4). Fluoroscopy allows real-time, moment-to-moment visualization and often enables the biopsy to be performed in less time than that required for a CT-guided biopsy. However, we prefer to use CT for imaging guidance in all transthoracic needle biopsies. It allows a more complex approach, and safe and accurate sampling of hilar or mediastinal masses is possible. CT also provides better visualization of severe emphysematous areas or bullae, which may lie within the path of a needle. Real-time, continuous CT fluoroscopy combines the advantages of standard fluoroscopy with CT guidance.
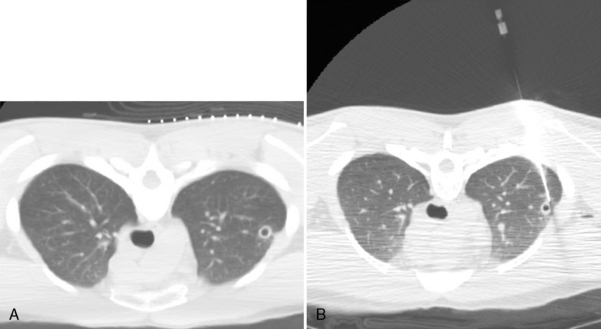
Technical Factors
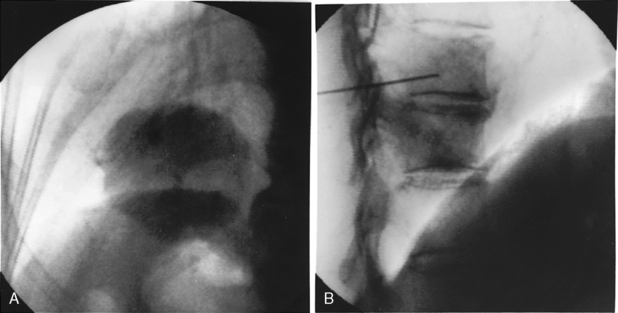
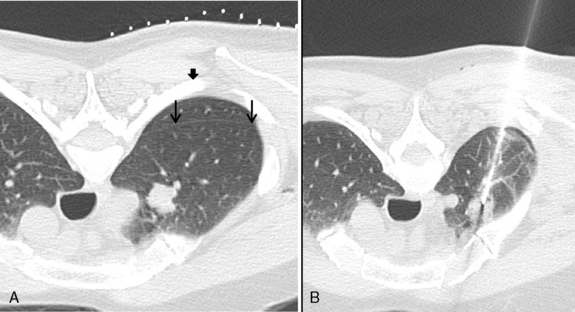
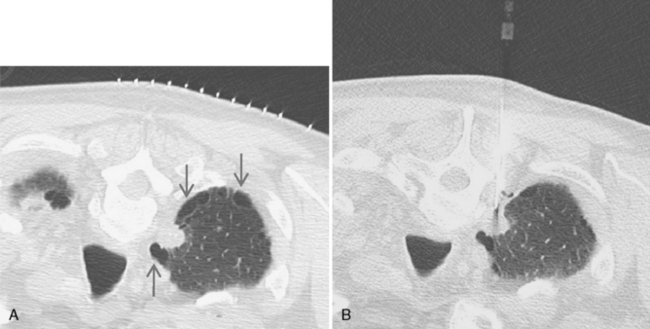
The shortest, most vertical biopsy path should be chosen based on the prebiopsy CT scan (Fig. 19-5). Interlobar fissures, pulmonary vessels, bullae, and areas of severe emphysema should be avoided (see Fig. 19-1). Sometimes, this can be achieved by tilting the CT gantry (Fig. 19-6). Paraspinal and extrapleural saline injection creates safer access to paramediastinal lesions (Fig. 19-7). The patient is placed in a position that provides a safe approach—prone, supine, or occasionally, decubitus—as indicated. After a scanogram is performed, thin-section, 2- to 5-mm CT slices are obtained through the lesion with a localizing grid in place on the skin overlying the lesion. A desired skin puncture site is identified using the grid, and the patient is prepared and draped in a sterile manner. After the injection of local anesthesia, a small puncture is made in the skin and subcutaneous tissues with a scalpel.