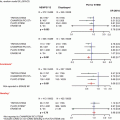
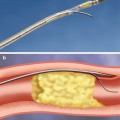
Fig. 25.1
Comparison images of coronary cross section. Histopathology (Lt) and IVUS (Rt) show quite similar findings; lumen, intimal plaque, and subintima space.* subintimal space
IVUS in CTO-PCI
The options of IVUS use in CTO-PCI are (1) identifying the optimal point for wiring at CTO entry, (2) IVUS-guided reentry from false lumen to true lumen, and (3) to determine appropriate strategy to cross wire to true lumen in retrograde approaches.
Identifying Optimal Position for CTO Entry
The entry point of the CTO segment is one of risk area where the wire can inadvertently migrate into the subintimal space or exit the vessel architecture altogether, especially in abrupt-/blunt-type CTO located at side branches. The IVUS catheter can be advanced into the side branch near the proximal cap and identify the intimal plaque position and center of intimal plaque (sweet spot) in angiogram (Fig. 25.2).
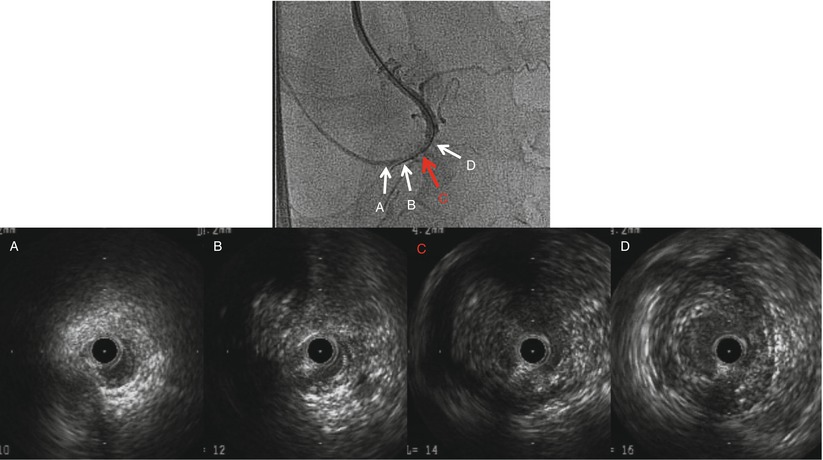

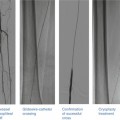
Fig. 25.2
IVUS demonstrates where is the best point (sweet spot) for wire advancement at entry of CTO lesion. In this RCA CTO case, second image from the right shows the sweet spot. arrows indicate IVUS images with corresponding area of the angiogram
In practice:
1.
Advance IVUS catheter to proximal side branch of CTO.
2.
Move transducer manually examining the IVUS image in real time.
3.
Stop transducer when IVUS shows entry of main branch occlusion.
4.
1 mm pull back transducer (mostly transducer advances 1 mm with dye injection) and take image to identify where is the correlated position in the angiogram.
Depending on the IVUS system and vessel-lesion characteristics, the IVUS catheter may remain inside the coronary for live imaging or withdrawn into the guide catheter during CTO wiring. Simultaneous IVUS observation during wire manipulation is useful, but sometimes the IVUS catheter disturbs CTO wire control. Once the proximal cap is penetrated, confirmatory IVUS can be performed easily by reinserting the IVUS into the coronary to reassure that the starting point is correct.
A case using IVUS to identify the sweet spot in CTO entry was shown in Fig. 25.3.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

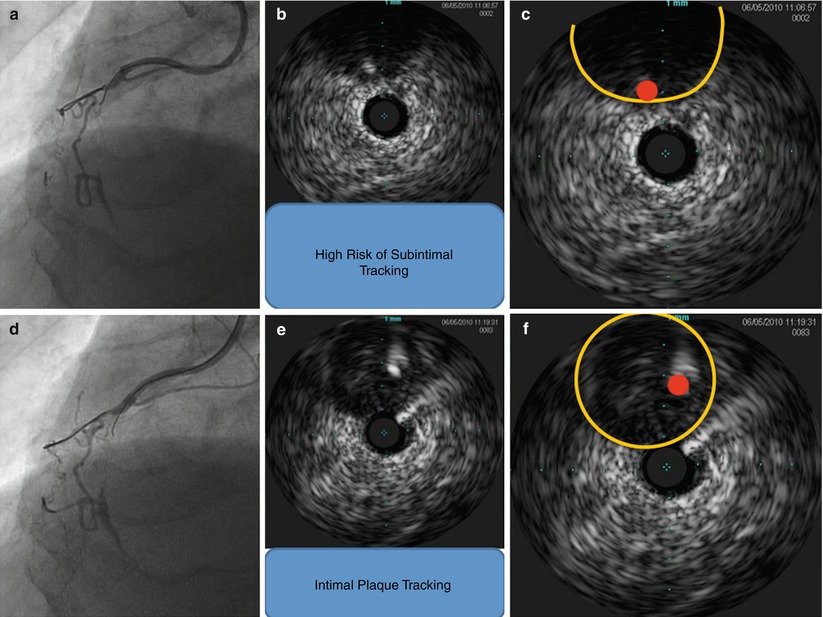
Fig. 25.3
RCA proximal – mid CTO case. First guide wire was advanced around EEM; on the other hand, second guide wire was clearly more inside and intra- intimal plaque. Using this IVUS information, we could avoid subintimal tracking. (a) the first guide wire was advanced into remaining channel, (b




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree