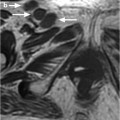
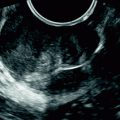
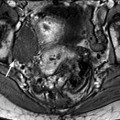
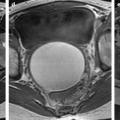
Jean Noel Buy1 and Michel Ghossain2
(1)
Service Radiologie, Hopital Hotel-Dieu, Paris, France
(2)
Department of Radiology, Hotel Dieu de France, Beirut, Lebanon
Abstract
During the fifth and sixth weeks, the genital system is in an indifferent state. Two pairs of genital ducts are present, the mesonephric ducts (or Wolffian ducts) and paramesonephric ducts (or mullerian ducts).
18.1 Embryology [1, 2]
18.1.1 Development of the Female Genital Ducts and Glands
1.
During the fifth and sixth weeks, the genital system is in an indifferent state. Two pairs of genital ducts are present, the mesonephric ducts (or Wolffian ducts) and paramesonephric ducts (or mullerian ducts).
2.
The paramesonephric ducts develop lateral to the gonads and to mesonephric ducts on each side from longitudinal invaginations of the mesothelium on the lateral aspects of the mesonephroi. The edges of these paramesonephric grooves approach each other and fuse to form the paramesonephric ducts. The funnel-shaped cranial ends of these ducts open into the peritoneal cavity. Caudally, the paramesonephric ducts run parallel to the mesonephric ducts until they reach the future pelvic region of the embryo. Here they cross ventral the mesonephric ducts, approach each other in the median plane, and fuse to form a Y-shaped uterovaginal primordium.
3.
This tubular structure projects in the dorsal wall of the urogenital sinus 1 and produces an elevation the sinus tubercle which defines the site of the future hymenal membrane.
4.
Contact of the uterovaginal primordium with the urogenital sinus induces the formation of paired endodermal outgrowths – the sinovaginal bulbs. They extend from the urogenital sinus to the caudal end of the uterovaginal primordium. The sinovaginal bulbs fuse to form a vaginal plate. Later the central cells of this plate break down, forming the lumen of the vagina. The epithelium of the vagina is derived from the peripheral cells of the vaginal plate.
Until fetal life, the lumen of the vagina is separated from the cavity of the urogenital sinus by a membrane – the hymen. The membrane is formed by invagination of the posterior wall of the urogenital sinus, resulting from expansion of the caudal end of the vagina. The hymen usually ruptures during the perinatal period.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree