Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
Melissa L. Rosado-de-Christenson, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Proliferation of atypical smooth muscle cells in lungs & lymphatics associated with pulmonary cysts
Imaging Findings
Radiography
Normal or increased lung volumes
Diffuse bilateral reticular opacities
HRCT
Thin-walled air-filled pulmonary cysts diffusely distributed throughout lung
Top Differential Diagnoses
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Centrilobular Emphysema
Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia (LIP)
Laryngeal Papillomatosis
Pathology
Widespread interstitial infiltrate of immature short spindle cells resembling smooth muscle cells
Similar findings in TSC in which micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia may also be present
Clinical Issues
Affects women of childbearing age who present with progressive dyspnea, pneumothorax, or chylothorax
Variable prognosis with median survival of 8-10 years after diagnosis
Diagnostic Checklist
Radiographs may appear normal or near normal
Patients presenting with pneumothorax may be misdiagnosed with primary spontaneous pneumothorax
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM)
Synonym: Lymphangiomyomatosis
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC)
Definitions
Proliferation of atypical smooth muscle cells in lungs and thoracic & retroperitoneal lymphatics
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Woman of childbearing age; progressive dyspnea
Radiography: Large volumes, reticular opacities, chylothorax, or spontaneous pneumothorax
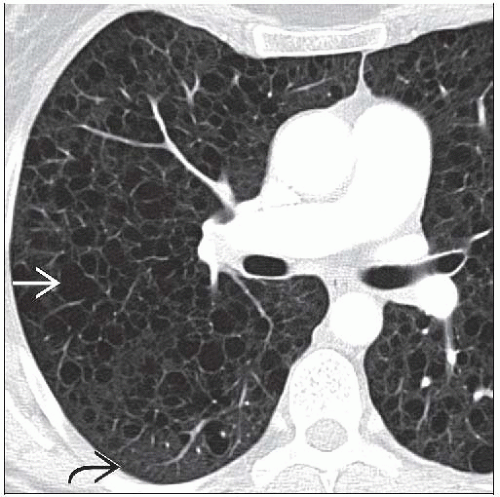
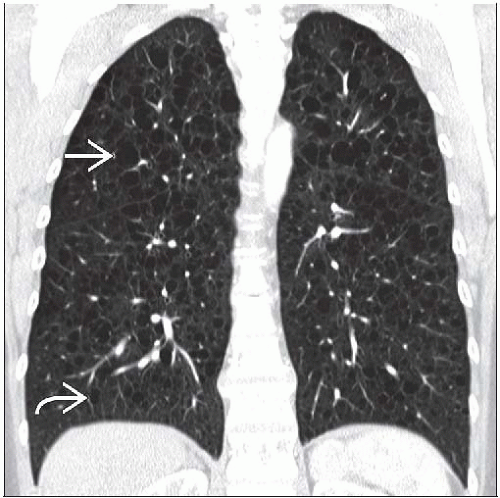
CT: Diffuse bilateral thin-walled air-filled cysts with intervening normal lung
Patient position/location: Diffuse bilateral pulmonary involvement
Size: Variable cyst sizes ranging from 2-5 mm, but larger cysts ranging from 6-12 mm may also occur
Morphology: Spherical cysts with smooth thin walls
CT Findings
Lung
Diffuse bilateral thin-walled cysts with normal intervening lung
Relative sparing of lung apices & lung bases
Visualization of lung cysts in patients with normal or near-normal radiographs
Pulmonary involvement may be initially mild but becomes profuse & severe as disease progresses
Variable cyst sizes, typically 2-5 mm, but larger cysts 6-10 mm & dominant cysts also observed
Typically smaller cysts in early disease and larger cysts in late disease
Typically round cysts; ovoid & polygonal cysts; polygonal cysts more common in severe disease
Cyst walls range from barely perceptible to 2-4 mm in thickness
Pleura
Other
Lymphadenopathy; thoracic, abdominal, pelvic
Renal angiomyolipomas in 20-54%
Radiographic Findings
Lung
Normal or increased lung volumes
Diffuse bilateral symmetric reticular opacities
Radiographs may appear normal in spite of involvement with cystic disease
Pleura
Pneumothorax in 39-53%
Pleural effusion in 10-20%; unilateral or bilateral
Imaging Recommendations
Best imaging tool
HRCT is more sensitive than radiography
Extent of disease correlates with expiratory volumes and diffusion capacity
Protocol advice: Coronal reformations help confirm diffuse cephalocaudal pulmonary involvement
Screening recommendations
Women with TSC: Once after age of 18
Women with unexplained recurrent pneumothorax
Women with little or no tobacco use who have diagnosis of primary spontaneous pneumothorax (or emphysema)
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
M = F; smokers
Upper lung predominant involvement
Small cysts of variable sizes, some with bizarre shapes
Thin & nodular irregular cyst walls
Associated small irregular pulmonary nodules
Centrilobular Emphysema
Smokers, occurs in both males and females
Upper lobe predominant involvement
Centrilobular lucencies with imperceptible walls; visualization of central lobular artery
Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia (LIP)
Adult women; 50-60 years of age
Immunosuppression, Sjögren syndrome
Thin-walled air-filled lung cysts of various sizes
Ground-glass opacity & poorly defined nodules
Tracheobronchial Papillomatosis
Males; history of laryngeal papillomatosis
Thick- or thin-walled cysts of variable shapes
Association with pulmonary & tracheal nodules
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Adult men; over 65 years of age
Low lung volumes; peripheral lower lung involvement
Honeycomb subpleural cysts of variable size
Architectural distortion & traction bronchiectasis
PATHOLOGY
General Features
General path comments
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree