Chapter 102
Nasopharyngeal Infiltrative Ectopic Pituitary Adenoma
Epidemiology
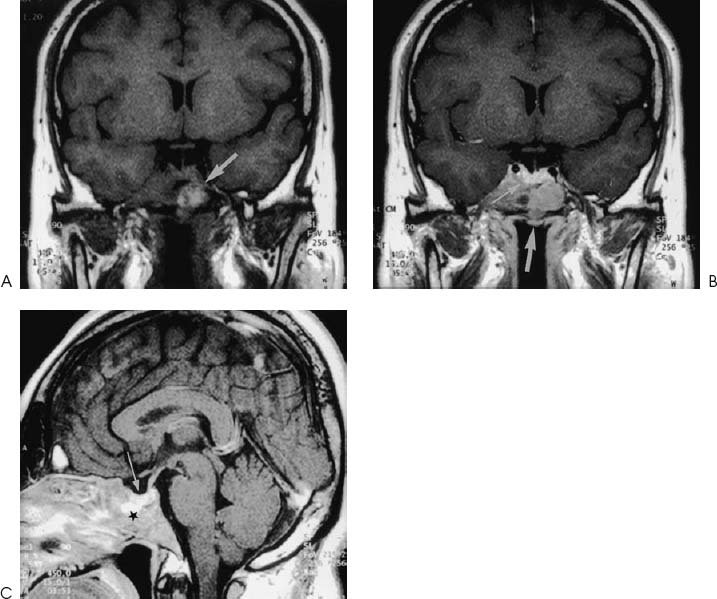
Ectopic pituitary adenomas are uncommon. In 73% of patients, the ectopic adenomas are located in an extracranial site, most frequent location being in the sphenoid sinus. Other extracranial sites include the nasal cavity, nasopharynx, petrous temporal bone, and clivus. The presence of ectopic pituitary tissue in the skull base is a common phenomenon, but a pituitary adenoma arising from these ectopic sites without sellar involvement is extremely rare. It is believed that the ectopic pituitary tissues represent remnants of the craniopharyngeal duct along the ingrowth of Rathke’s pouch.
Clinical Findings
Headache is a common symptom but the clinical manifestations of ectopic pituitary adenomas vary and they are mainly related to local mass effects. Fifty-eight percent of patients have functional activity at presentation. They include Cushing’s syndrome, acromegaly, hyperparathyroidism, amenorrhea, and multiple endocrine neoplasia.