Noncardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
Aliye O. Bricker, MD
Tan-Lucien H. Mohammed, MD, FCCP
Key Facts
Terminology
Acute lung injury is general term for hypoxemic respiratory failure due to alveolar epithelial and capillary endothelial injury
ARDS is subset of ALI
Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP) is idiopathic form of ARDS
ARDS commonly defined by ratio of PaO2:FiO2 < 200, whereas ALI PaO2:FiO2 < 300
ARDS divided into extrapulmonary and pulmonary causes
Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) is pathologic equivalent of ARDS
Imaging Findings
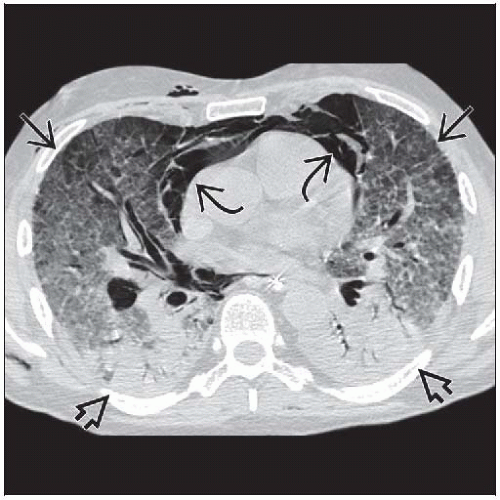
Typical pattern: Intense pulmonary opacification dependent lung (dorsal lung in supine position)
Ground-glass (GG) opacities layered on top of IPO
Normal lung (if any) occupies most nondependent lung
3 components: IPO, GG, and air layered like water, oil, and air in a glass
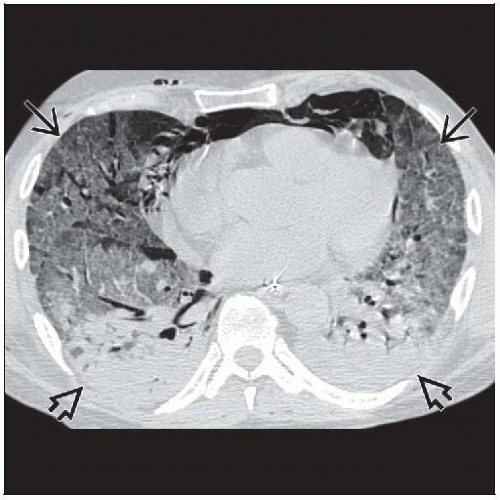
Survivors develop mild reticular pattern in anterior lung (85%), residual ground-glass opacities (60%), lobular hyperinflation (50%), emphysema (33%)
Pleural effusions (50%) (majority > 1 cm thick)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Cardiogenic Edema
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
Diffuse Pulmonary Infection
Clinical Issues
Mortality rate (50%)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, increased permeability edema, shock lung, adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), acute lung injury (ALI)
Definitions
Acute lung injury general term for hypoxemic respiratory failure due to alveolar epithelial and capillary endothelial injury
ARDS is subset of ALI
Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP) is idiopathic form of ARDS
Consensus definition of ALI/ARDS
Acute onset of hypoxemic respiratory failure
Stiff lung (decreased compliance)
Diffuse radiographic infiltration
Absence of left atrial hypertension
ARDS commonly defined by ratio of PaO2:FIO2 < 200, whereas ALI PaO2:FIO2 < 300
ARDS divided into extrapulmonary and pulmonary causes
Nearly any medical or surgical condition may result in ARDS
Common conditions: Sepsis, pneumonia, trauma, aspiration
Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) is pathologic equivalent of ARDS
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue: Intubated patient with diffuse bilateral lung disease
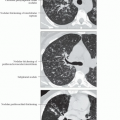
Patient position/location: Dependent intense pulmonary opacification (IPO) and more nondependent ground-glass opacities (like oil and water in a glass)
CT Findings
In contrast to radiographs, strikingly inhomogeneous distribution on CT
Following “typical” appearance idealized; in clinical situations wide range of radiographic abnormalities
Sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis of ARDS (70%)
Typical pattern more common with ARDS from extrapulmonary cause
Individual features
Ground-glass opacities
Intense parenchymal opacification may be due to consolidated lung or compressive atelectasis
Individual features nonspecific
Do not help differentiate ARDS from pulmonary or extrapulmonary cause or distinguish between other causes of diffuse infiltration
Morphology of typical pattern
IPO-dependent lung (dorsal lung in supine position)
Ground-glass (GG) opacities layered on top of IPO
Normal lung (if any) occupies most nondependent lung
3 components: IPO, GG, and air layered like water, oil, and air in a glass
Extent of abnormal lung averages 80% of lung volume
Distribution gravity dependent and will evolve into same pattern when placed prone (usually within 10-20 minutes)
Variation (atypical patterns)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree