Balaji Ayyamperumal It is important to recognize the variations of normal anatomy in the head and neck become perhaps more important medically and surgically. The variations discussed here in the following headings are complimented by a few other details discussed in other related chapters. All sinus variants are discussed under the Chapter 3.24 Paranasal sinuses – Anatomy and pathology. Critical Variants are discussed here with clinical applications: Mostly seen in the tympanic segment near the oval window. Severe anomalies of the course of the facial nerve occur in the tympanic and vertical portions. The horizontal segment at times is displaced inferiorly to cover the oval window or lies exposed over the promontory. The facial canal is usually rotated laterally. Tegmen of the mastoid and attic usually passes in a horizontal plane slightly lower than the arcuate eminence produced by the top of the superior semicircular canal. A depression of the tegmental plate is caused by the deepening of the floor of the middle cranial fossa forming a groove lateral to the attic and to the labyrinth. The low hanging dura may cover the roof of the external auditory canal. The risk of penetration of the cranial cavity during surgery should be anticipated.
3.3: Normal variants in ear and nose imaging
Introduction
Sinuses
Attachment of the main sphenoid septum
Hyperpneumatization in sphenoid sinus
Normal variants of temporal imaging (Table 3.3.1)
Facial nerve dehiscence
Diagnosis
Findings
Comments
Cochlear cleft
Especially in children. Lucency lateral to apical turn.
Non retrofenestral otosclerosis.
Lucent periotic zone in infants
Incudal “hole”
Lucency in incus body.
Partial volume effect.
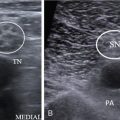
High jugular bulb
The jugular bulb is above the caudal level of the posterior semicircular canal or above IAC.
Frequently a diverticulum of the jugular bulb.
Fatty marrow in petrous apex
High signal intensity on T1 and T2 turbo spin echo.
Misinterpreted as lesion when unilateral. Compare signal intensity with subcutaneous fat.
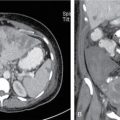
Bulging sigmoid sinus
Anterior impression on the posterior surface of the mastoid.
To be avoided during mastoidectomy.
Pseudofractures
Cochlear aqueduct, petromastoid canal.
Be aware of sutures.
Dural exposure
Variations of jugular bulb (high, asymmetric jugular bulb)
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine