Figure 16.1
Patient position. Lean the patient’s head back and apply a copious amount of gel on top of a closed eyelid
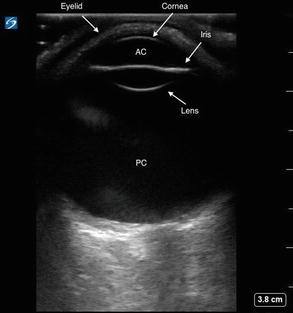
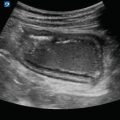
Figure 16.2
Normal ocular ultrasound. A normal eye will maintain its shape with a round cornea, anterior chamber, iris, lens, and posterior chamber. Adjust the depth to visualize the entire globe and optic nerve
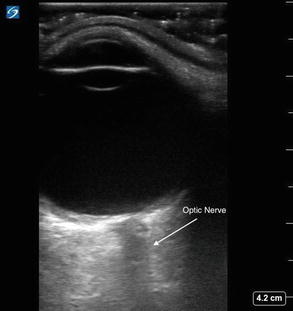
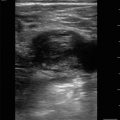
Figure 16.3
Optic nerve. The nerve is hypoechoic and will be flanked on both sides by its more hyperechoic sheath

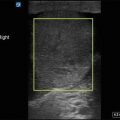
Figure 16.4
ONSD measurement. Measure the diameter 3 mm posterior to the optic disc
Ocular Pathology
Vitreous Hemorrhage
Extravasation of blood into the posterior chamber is most commonly due to posterior vitreous detachment (PVD), however, can be also be due to trauma or even be idiopathic
Appears as echogenic debris within the posterior chamber:
Can appear as layering of echogenic material posteriorly [2]
May only be visualized during dynamic eye imaging as swirling of echogenic debris while the eye is moving
Figure 16.5—Vitreous hemorrhage
Video 16.2—Vitreous hemorrhage
Retinal Detachment (RD)
Separation of the retina from the underlying epithelium.
Thick echogenic band posteriorly.
With dynamic eye movements, there will be little movement of the echogenic band, which will remain attached to an area near the optic nerve and the ora serrata [1]:
The attachment points help differentiate a retinal detachment from a posterior vitreous detachment.
Often associated with vitreous hemorrhage.
Figure 16.6—Retinal detachment.
Video 16.3—Retinal detachment.
Posterior Vitreous Detachment
Degenerative process in which the vitreous gel loses its attachment to the membrane.
Increase the gain to identify PVD, which will appear as a smooth, thin membrane and echogenic material within the posterior chamber.
With dynamic movements of the eye, echogenic material will swirl within the posterior chamber [2].
Can be confused with retinal detachment.
The retina will remain attached at the optic nerve or ora serrata.
Figure 16.7—Posterior vitreous detachment.
Video 16.4—Posterior vitreous detachment.
Retrobulbar Hematoma
Lens Dislocation
With a complete dislocation, the lens will not be seen in its usual central location just posterior to the anterior chamber.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree