 located adjacent to the odontoid tip. The ossicle is in orthotopic position, and CVJ alignment is normal.
located adjacent to the odontoid tip. The ossicle is in orthotopic position, and CVJ alignment is normal.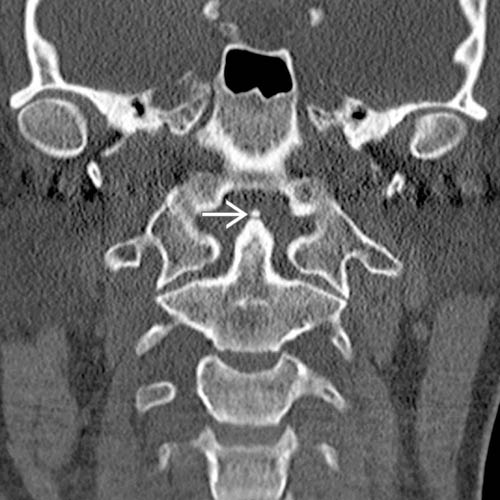
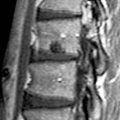
 . Note that there is minimal flattening of the odontoid tip adjacent to the ossicle, supporting classification as a persistent terminal odontoid ossicle.
. Note that there is minimal flattening of the odontoid tip adjacent to the ossicle, supporting classification as a persistent terminal odontoid ossicle.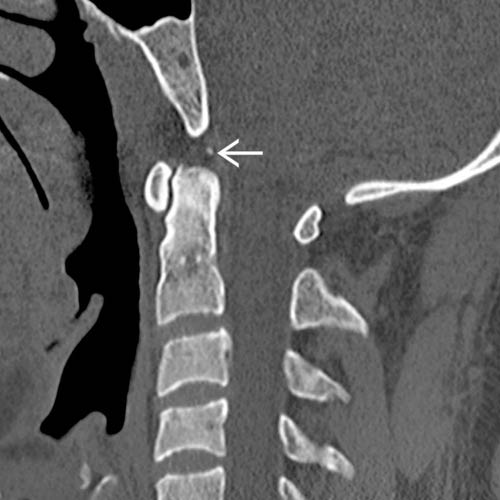
 positioned between the odontoid tip and clivus. The odontoid tip has remodeled.
positioned between the odontoid tip and clivus. The odontoid tip has remodeled.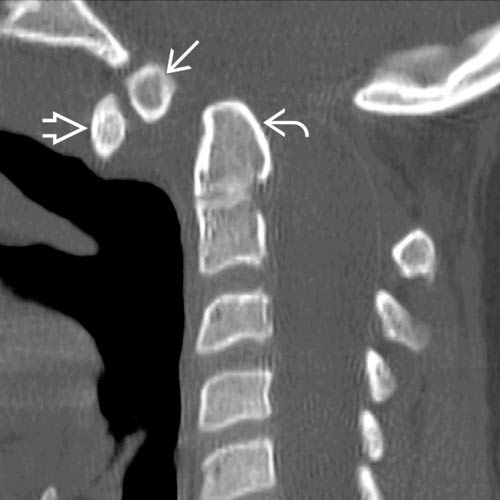
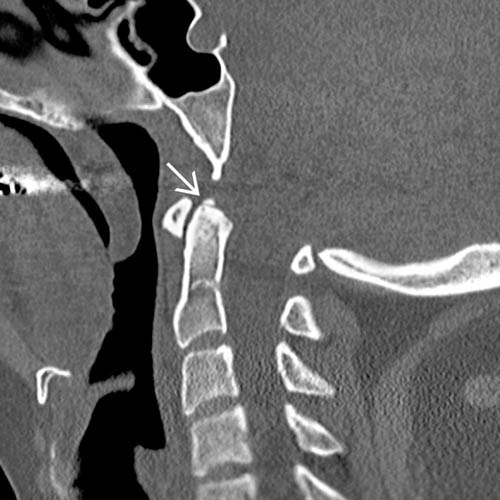
 relative to the nearly normal-sized odontoid process
relative to the nearly normal-sized odontoid process  . There is a large dystopic ossiculum terminale
. There is a large dystopic ossiculum terminale  . Although debatable, the nearly normal size of the odontoid process favors classification as an ossiculum terminale rather than os odontoideum.
. Although debatable, the nearly normal size of the odontoid process favors classification as an ossiculum terminale rather than os odontoideum.IMAGING
General Features
• Best diagnostic clue
 Separate ossicle with intact cortical margin positioned above normal-sized odontoid process in adolescent or adult
Separate ossicle with intact cortical margin positioned above normal-sized odontoid process in adolescent or adult




 Separate ossicle with intact cortical margin positioned above normal-sized odontoid process in adolescent or adult
Separate ossicle with intact cortical margin positioned above normal-sized odontoid process in adolescent or adultStay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree