6
Pancreas
Acute Pancreatitis
Overview
 The two most common causes are gallstones and alcohol
The two most common causes are gallstones and alcohol
 Other etiologies include iatrogenic (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography [ERCP]), drugs, trauma, neoplasm, hypercalcemia, hypertriglyceridemia, infections, idiopathic
Other etiologies include iatrogenic (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography [ERCP]), drugs, trauma, neoplasm, hypercalcemia, hypertriglyceridemia, infections, idiopathic
Signs and Symptoms
 Epigastric pain radiating to the back accompanied with nausea and vomiting
Epigastric pain radiating to the back accompanied with nausea and vomiting
 May develop classic signs of Grey Turner’s sign (flank ecchymosis) or Cullen’s sign (periumbilical ecchymosis); suggests hemorrhagic pancreatitis
May develop classic signs of Grey Turner’s sign (flank ecchymosis) or Cullen’s sign (periumbilical ecchymosis); suggests hemorrhagic pancreatitis
 Pancreatitis may lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or systemic inflammatory response (SIRS) with resultant hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea, etc.
Pancreatitis may lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or systemic inflammatory response (SIRS) with resultant hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea, etc.
Diagnosis
 Elevated amylase and lipase—no correlation between the serum level and the prognosis or the severity of the disease process
Elevated amylase and lipase—no correlation between the serum level and the prognosis or the severity of the disease process
 Ranson’s criteria:
Ranson’s criteria:
• Upon admission:
 Age >55 years
Age >55 years
 White blood cell count >16,000 cells/mm3
White blood cell count >16,000 cells/mm3
 Glucose >200 mg/dL
Glucose >200 mg/dL
 Serum lactate dehydrogenase >350 IU/L
Serum lactate dehydrogenase >350 IU/L
 Aspartate aminotransferase >250 IU/L
Aspartate aminotransferase >250 IU/L
• At 48 hours:
 Hematocrit decrease >10%
Hematocrit decrease >10%
 Blood urea nitrogen elevation >5 mg/dL
Blood urea nitrogen elevation >5 mg/dL
 Calcium <8 mg/dL
Calcium <8 mg/dL
 Arterial PO2 <60 mmHg
Arterial PO2 <60 mmHg
 Base deficit >4 mEq/L
Base deficit >4 mEq/L
 Estimated fluid sequestration >6 L
Estimated fluid sequestration >6 L
• Number of Ranson’s signs: Risk of mortality
0–2: 0%
3–4: 15%
5–6: 50%
>6: 70%–90%
Complications
 Pancreatic pseudocyst
Pancreatic pseudocyst
 Necrotizing pancreatitis
Necrotizing pancreatitis
 Infected pancreatic necrosis
Infected pancreatic necrosis
 Visceral pseudoaneurysm
Visceral pseudoaneurysm
Treatment
 Supportive measures: IV fluid resuscitation, bowel rest to limit pancreatic enzyme secretions, TPN or postpyloric nasojejunal feeding, pain control, alcohol withdrawal prophylaxis, antibiotics for infected or necrotizing pancreatitis
Supportive measures: IV fluid resuscitation, bowel rest to limit pancreatic enzyme secretions, TPN or postpyloric nasojejunal feeding, pain control, alcohol withdrawal prophylaxis, antibiotics for infected or necrotizing pancreatitis
 If pancreatitis is caused by gallstones, then patient should undergo a semielective cholecystectomy with intraoperative cholangiogram during the same hospitalization
If pancreatitis is caused by gallstones, then patient should undergo a semielective cholecystectomy with intraoperative cholangiogram during the same hospitalization
 Surgical treatment is usually reserved for patients with infected or necrotizing pancreatitis who are not improving despite maximal medical management
Surgical treatment is usually reserved for patients with infected or necrotizing pancreatitis who are not improving despite maximal medical management
• Involves necrosectomy, drain placement, and possible serial abdominal washouts
RADIOLOGY
Pancreatitis with Surrounding Fluid
 Plain film findings
Plain film findings
• Duodenal ileus may be seen
• Sentinel dilated loop of transverse colon can be seen with acute pancreatitis
• Effacement of the psoas fat plane
• Chronic pancreatitis may show pancreatic calcifications
 US findings
US findings
• Chronic pancreatitis shows main pancreatic duct dilatation beyond the normal 3 mm
• Acute pancreatitis will manifest as a diffuse or focal hypoechogenicity of the pancreas with or without surrounding peripancreatic fluid
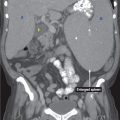
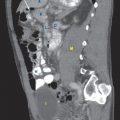
 CT findings (Fig. 6.1)
CT findings (Fig. 6.1)
• Diffuse or focal pancreatic edema with peripancreatic fat stranding
• May be associated with surrounding fluid collections
• Areas of non-enhancement of the pancreas would be concerning for necrotizing pancreatitis
• Areas of high attenuation fluid within the pancreas would be concerning for hemorrhagic pancreatitis
• May see associated complications including pseudocyst, splenic vein thrombosis, or splenic artery pseudoaneurysm
 MRCP findings
MRCP findings
• Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by dilatation or multifocal stenosis of main pancreatic duct sometimes with narrowing of the intrapancreatic segment of the common bile duct
• Acute pancreatitis may manifest as a diffuse or focal T2 hyperintense signal within and/or surrounding the pancreas
FIGURE 6.1
A. Liver
B. Kidney
C. Vertebra
D. Descending aorta
E. Spleen

Pancreatitis with Necrosis
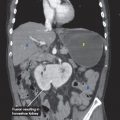
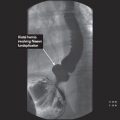
 CT findings (Fig. 6.2)
CT findings (Fig. 6.2)
• Areas of nonenhancement seen within pancreatic parenchyma in the setting of acute pancreatitis
• Presence of air bubbles within loculated areas of necrotic tissue and fluid is highly suggestive of infection
FIGURE 6.2 A,B
A. Liver
B. Kidney
C. Vertebra
D. Small bowel loops
E. Stomach
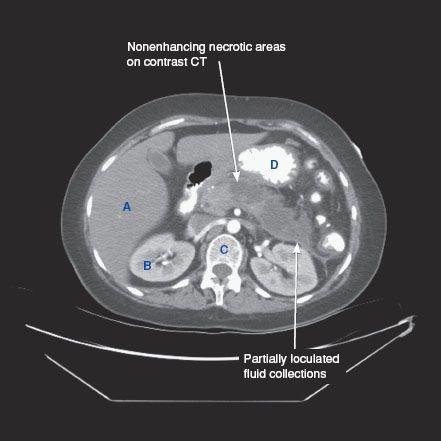
FIGURE 6.2 A
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree