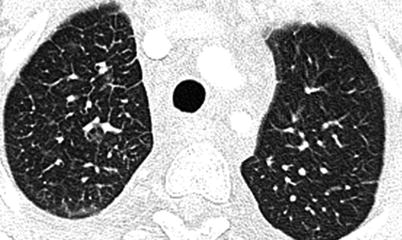
Fig. 15.1
Surfactant protein B mutation in a full-term newborn boy. (a) Frontal chest radiograph shows diffuse hazy granular opacity resembling respiratory distress syndrome of prematurity. (b)Axial lung window CT image demonstrates diffuse ground-glass pulmonary opacification
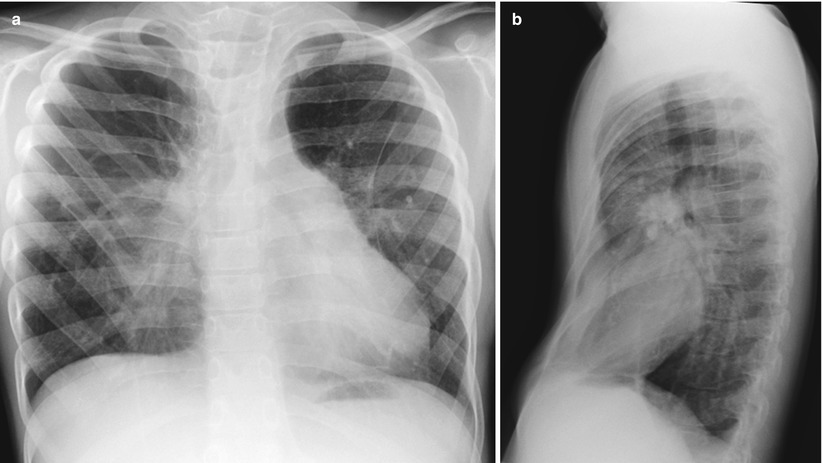
Fig. 15.2
ABCA3 mutation in a 5-year-old boy. (a) Frontal chest radiograph shows increased coarse interstitial opacities in both lungs. (b) Lateral chest radiograph demonstrates a pectus excavatum
15.5.2 Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia
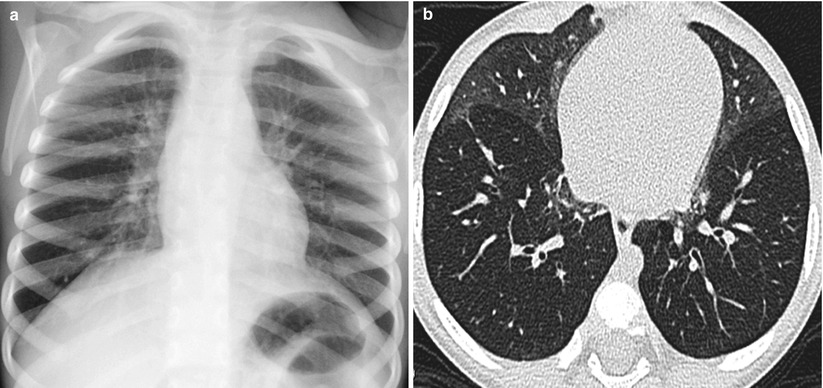
Fig. 15.3
Neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy in a 5-month-old boy who presented with persistent tachypnea, retractions, hypoxemia and crackles. (a) Frontal chest radiograph shows pulmonary hyperinflation with opacities in the perihilar and paramediastinal regions. (b) Axial lung window CT image demonstrates geographic ground-glass opacities in the right middle lobe and lingula
15.5.3 Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
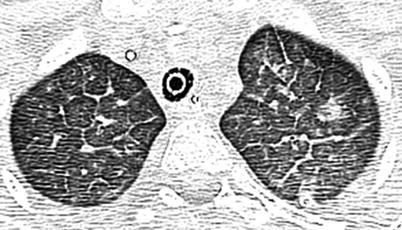
Fig. 15.4
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in an 8-year-old girl. Axial lung window CT image shows bilateral ground-glass opacities with smooth intra- and interlobular septal thickening in polygonal shapes, an appearance known as crazy paving
15.5.4 Pulmonary Lymphangiomatosis
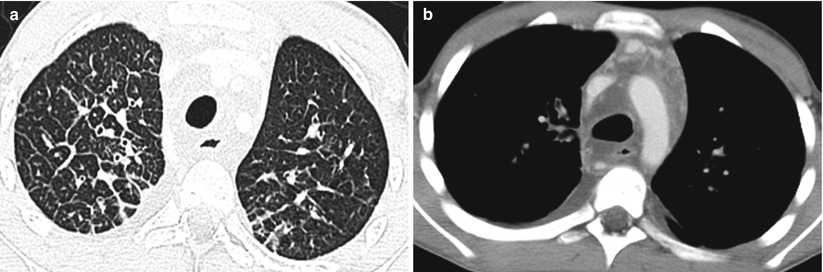
Fig. 15.5
Pulmonary lymphangiomatosis in a 5-year-old boy. (a) Axial lung window CT image shows interlobular septal thickening in both lungs. (b) Axial soft tissue window CT image demonstrates mediastinal edema and bilateral pleural effusions
15.5.5 Bronchiolitis Obliterans (Swyer–James–Macleod Syndrome)
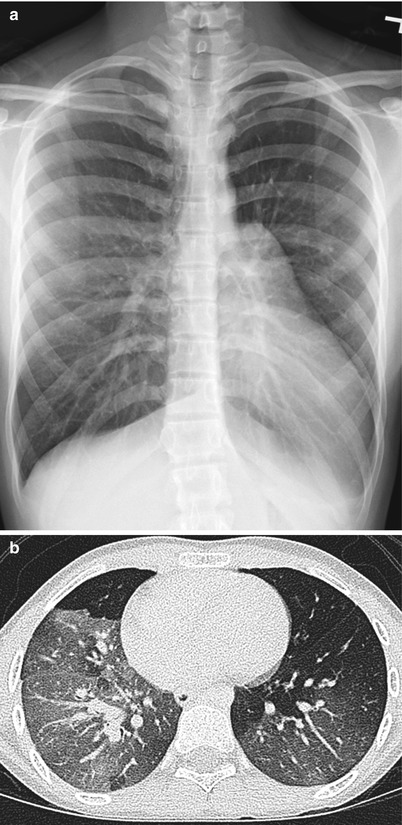
Fig. 15.6
Bronchiolitis obliterans (Swyer–James–Macleod syndrome) in a 6-year-old girl with multiple vial pneumonias. (a) Frontal chest radiograph shows hyperlucent left lung with decreased lung volume and underlying pulmonary vessels in comparison to the right lung. (b) Axial lung window CT image demonstrates accentuated hyperlucent oligemic segments of lung, worse on the left side than the right side
15.5.6 Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
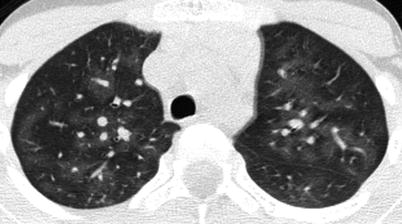
Fig. 15.7
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis in an 8-year-old boy who presented with worsening cough, fatigue, and repetitive bird exposure in his parents’ farm. Axial lung window CT image shows scattered lobular areas of ground-glass attenuation in both lungs
15.5.7 Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia
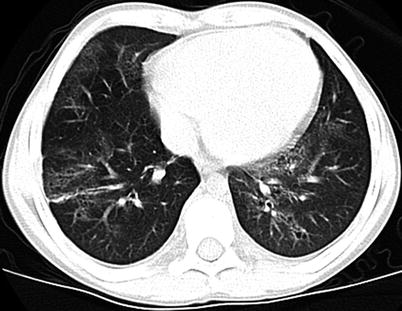
Fig. 15.8
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia in an 11-year-old boy who presented with dry cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Axial lung window CT image shows a combination of ground-glass opacification and traction bronchiectasis
15.5.8 Systemic Sclerosis
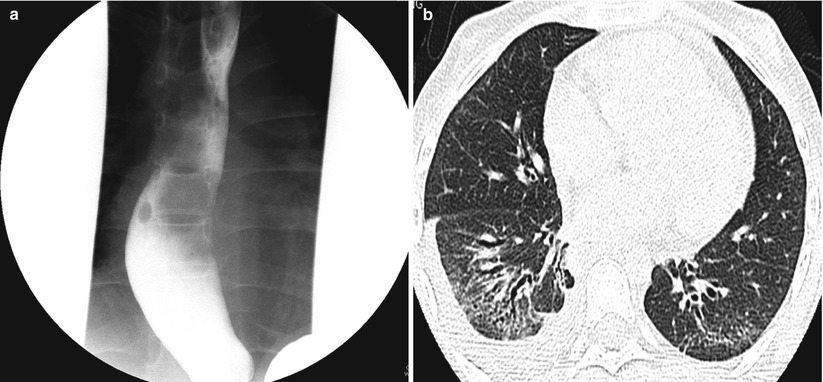
Fig. 15.9
Systemic sclerosis in a 13-year-old girl. (a) Frontal fluoroscopic spot image obtained during barium swallow study shows a dilated esophagus. (b) Axial lung window CT image demonstrates clusters of small cysts at the lung periphery, resembling honeycombing, ground-glass opacification, and bronchiectasis