PET Radiopharmaceuticals: Perfusion Compounds [13N]Ammonia, [15O]Water, [82RB]Rubidium, and Other Generator Products of Clinical Relevance
Simon M. Ametamey
Peter Bläuenstein
P. August Schubiger
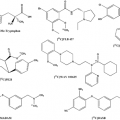
Cerebral and cardiac perfusion studies by PET provide quantitative measurements and permit assessment of perfusion abnormalities in patients with cerebrovascular and cardiovascular disease. Regional cerebral blood flow measurements with PET also are useful in the evaluation of new drugs. Oxygen 15–labeled water ([15O]water), nitrogen 13–labeled ammonia ([13N]ammonia), and rubidium 82 ([82Rb]) are the most common PET tracers used in clinical routine for perfusion measurements. These PET imaging agents are taken up in the cells of normal myocardium or brain in relation to blood supply. In practice, studies using these radiopharmaceuticals require repeated measurements in the same individual and during the same experimental session. Whereas 15O and 13N are produced by cyclotron irradiation of appropriate target materials, 82Rb is generator produced and thus does not require an on-site cyclotron. Other generator products are copper 62 (62Cu) and gallium 68 (68Ga). They may be of interest as labels of various compounds. Clinically most relevant is probably 68Ga-OTATOC and similar compounds, which serve as markers of endocrine active tumors such as carcinoids and may eventually replace 111In-octreotide.
[13N]Ammonia: Radionuclide Production and Synthesis
Nitrogen 13 (13N; T1/2, 10 minutes) is produced by bombarding a natural water target with 16.5-MeV protons via the nuclear reaction 16O(p,α)13N. The target material is usually aluminum, but targets made of nickel or titanium also are in use. Of all the [13N]-labeled radiopharmaceuticals, [13N]ammonia is the most commonly used agent for PET studies. There are two methods for its production. In the first method, the 13N-labeled nitrates/nitrites formed by proton irradiation of water are reduced by either titanium (III) chloride, titanium (III) hydroxide, or DeVarda’s alloy in alkaline medium (1). After distillation, trapping, and sterile filtration, the [13N]ammonia is ready for clinical application. In the second method, oxidation of 13N to [13N]nitrates/nitrites is prevented in situ by the addition of ethanol as free radical scavenger to the target content (2). The target content is transferred to a small cation-exchange column to trap [13N]ammonium ions. A final injectable solution of [13N]ammonia is obtained upon eluting with saline and after passage through a sterile filter.
[15O]Water: Radionuclide Production and adiosynthesis
A number of nuclear reactions are used for the production of 15O (T1/2, 2 minutes), but the 14N(d,n)15O is most widely used (3). The energy of the deuterons lies in the range of 8 to 10 MeV, and the target material is aluminum. The target content is a mixture of nitrogen and 0.2% to 1% of oxygen. The 15O atoms formed react with the carrier oxygen to give [15O]O2. 15O-labeled water then is produced by reacting hydrogen with [15O]O2 over a palladium–alumina catalyst at 200°C. The [15O]water vapor formed is trapped in sterile isotonic saline by bubbling the solution with nitrogen as carrier gas.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree