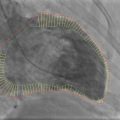
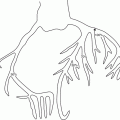
Fig. 3.1
Electrocardiogram
9.
An imaging pattern in which the left ventricle or left ventricular (LV) cavity appears larger on the stress images than at rest is called:
A.
Cardiomegaly
B.
Cardiomyopathy
C.
Transient ischemic dilation
D.
Transient ischemic attack
10.
At rest, the cardiac output and stroke volume:
A.
Are lower in a supine position than in an upright position
B.
Don’t change with the position shift
C.
Are higher in a supine position than in an upright position
D.
Change in opposite directions with the position shift
11.
Which of the following statements describing the concept of myocardial hibernation and/or stunning is FALSE?
A.
Myocardial hibernation and myocardial stunning may coexist in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy
B.
Repeated ischemic attacks may induce repetitive stunning
C.
There is a temporal progression from stunning to hibernation
D.
There is a temporal progression from hibernation to stunning
12.
Which view is recommended for performing a first-pass radionuclide angiography (FPRNA)?
A.
20–30° LAO
B.
30–50° LAO
C.
30–50° RAO
D.
20–30° RAO
13.
Which of the following statements correctly describes lung uptake of Tl-201 and the Tc-99m-based tracers?
A.
Lung uptake may be missed with Tc-99m tracers because of the more delayed onset of imaging compared with thallium
B.
Lung uptake may be missed with Tl-201 because of the more delayed onset of imaging compared with Tc-99m-based tracers
C.
Lung uptake of Tl-201- and Tc-99m-based tracers is independent from the timing of imaging
D.
Lung uptake of Tc-99m-based tracers has been more extensively validated than lung uptake of the Tl-201
14.
Which of the following PET algorithms uses the difference between arrivals of coincidence photons on both sides of the detector ring?
A.
Attenuation correction
B.
Random correction
C.
Scatter correction
D.
Time of flight
15.
The physiologic process of programmed cell death, by which organisms selectively target cells to be eliminated when they are no longer needed, is called:
A.
Angiogenesis
B.
Apoptosis
C.
Arteriosclerosis
D.
Necrosis
16.
In normal SPECT images, the lateral wall may often appear brighter than the contralateral septum because of:
A.
Structural variations of the myocardium—the apex is anatomically thinner than other myocardial regions
B.
Structural variations of the myocardium—the muscular septum is merging with the membranous septum
C.
Technical factors—the camera is physically farther away from the septal myocardial wall
D.
Technical factors—the patient motion
17.
All of the following are the major vasodilators used for pharmacologic MPI EXCEPT:
A.
Adenosine
B.
Dipyridamole
C.
Dobutamine
D.
Regadenoson
18.
Which of the following is identified as an index of the functional significance of a coronary stenosis?
A.
Coronary flow reserve (CFR)
B.
Myocardial blood flow (MBF)
C.
Summed rest score (SRS)
D.
Summed stress score (SSS)
19.
The diaphragmatic attenuation artifact results in a perfusion defect in the myocardial segments commonly supplied by the:
A.
Right coronary artery territory
B.
Left coronary artery
C.
Left anterior descending artery
D.
Circumflex artery
20.
During exercise, the value of arterial oxygen saturation normally does not decrease by more than:
A.
1 %
B.
5 %
C.
10 %
D.
20 %
21.
If a point source and a 360°orbit are used, an alignment error between the center of the electronic matrix of the camera and the mechanical center-of-rotation (COR) is called:
A.
A bull’s eye artifact
B.
A ring artifact
C.
A doughnut artifact
D.
A streak artifact
22.
The primary reason that Tc-99m pyrophosphate has NOT gained widespread clinical use is its limitation in the detection of:
A.
Unstable angina
B.
Early infarction
C.
Viable myocardium
D.
Hypokinetic ventricle
23.
Attenuation artifacts cause an increase in false-positive studies which results in MPI:
A.
Increased sensitivity
B.
Increased specificity
C.
Decreased sensitivity
D.
Decreased specificity
24.
Which of the following tracers exhibits kinetic properties that very closely approach those of the ideal tracer of myocardial blood flow?
A.
Fluorine-18 (F-18) fluorodeoxyglucose
B.
Nitrogen-13 (N-13) ammonia
C.
Oxygen-15–labeled (O-15) water
D.
Rubidium-82 (Rb-82)
25.
A state of persistent left ventricular dysfunction, resulting from a chronic and sustained reduction in myocardial blood flow is called:
A.
Myocardial infarction
B.
Myocardial ischemia
C.
Stunned myocardium
D.
Hibernating myocardium
26.
If the position of the patient is different during stress and rest imaging, soft tissue attenuation artifacts may produce:
A.
An irreversible perfusion defect mimicking ischemia
B.
A reversible perfusion defect mimicking ischemia
C.
An elevated transient ischemic dilation
D.
Wall motion abnormalities
27.
The application of three principles called justification, optimization, and limitation is aimed to:
A.
Restrict radiation dose
B.
Limit availability of diagnostic procedures
C.
Reduce availability of diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals
D.
Control employment
28.
In patients with coronary artery disease, coronary flow reserve (CFR):
A.
Decreases in proportion to the degree of stenosis severity
B.
Increases in proportion to the degree of stenosis severity
C.
Increases in proportion to the level of exercise
D.
Decreases in proportion to the patient weight
29.
The use of quantitative perfusion SPECT in myocardial perfusion imaging may assist in differentiating:
A.
Attenuation artifacts from true perfusion defects
B.
Horizontal from vertical motion artifacts
C.
Viable from necrotic myocardium
D.
Hibernating from stunning myocardium
30.
Which of the following findings from exercise ST is least likely to be associated with an adverse prognosis and multivessel CAD?
A.
Early onset of angina
B.
Ischemic ST-segment depression
C.
Premature atrial contractions
D.
Fall in blood pressure at low exercise workloads
31.
An increase in scintillator thickness will result in the camera’s:
A.
Increased sensitivity and increased resolution
B.
Increased sensitivity and decreased resolution
C.
Decreased sensitivity and increased resolution
D.
Decreased sensitivity and decreased resolution
32.
Which of the following medications will increase the sensitivity of Tc-99m-based tracers for detection of viable myocardium?
A.
Aminophylline
B.
Atropine
C.
Lasix
D.
Nitroglycerine
33.
Electrocardiogram-gated SPECT offers useful:
A.
Anatomical information
B.
Epidemiological data
C.
Functional information
D.
Retrospective data
34.
A PET study with which of the following tracers requires subtraction of blood pool activity?
A.
Fluorine-18 (F-18) fluorodeoxyglucose
B.
Nitrogen-13 (N-13) ammonia
C.
Oxygen-15–labeled (O-15) water
D.
Rubidium-82 (Rb-82)
35.
Which of the following diagnostic modalities/procedures is considered the gold standard by which other diagnostic tests for CAD are judged?
A.
Echocardiography
B.
Electrocardiography
C.
Cardiac catheterization
D.
Cardiac computed tomography
36.
Increased carbon dioxide production observed during exercise results in:
A.
Hyperthermia
B.
Hypertension
C.
Hyperventilation
D.
Hyperemia
37.
Dipyridamole causes vasodilation:
A.
Indirectly by inhibiting reuptake of adenosine
B.
Directly by binding to adenosine type A2A receptors
C.
Indirectly by promoting reuptake of adenosine
D.
Directly by blocking adenosine type A2A receptors
38.
Pattern of substrate uptake and utilization by the human myocardium in the fasting state is characterized by the:
A.
High rates of uptake and oxidation of glucose and lactate and the low rates of uptake of free fatty acid
B.
Low rates of uptake of glucose and lactate and the high rates of uptake and oxidation of free fatty acid
C.
Low rates of uptake of glucose and lactate and the low rates of uptake of free fatty acid
D.
High rates of uptake and oxidation of glucose and lactate and the high rates of uptake and oxidation of free fatty acid
39.
The view comprising long-axis tomograms generated by slicing in the vertical plane through the short-axis perspective is called:
A.
Vertical short-axis view
B.
Horizontal short-axis view
C.
Vertical long-axis view
D.
Horizontal long-axis view
40.
Automatic interpretations of ECG tracings are generally NOT accurate for:
A.
Cardiac axes
B.
Heart rates
C.
Intervals
D.
Repolarization abnormalities
41.
Improving the spatial resolution of a collimator by restricting the range of incident angles will result in the collimator’s:
A.
Decreased sensitivity
B.
Increased sensitivity
C.
Increased uniformity
D.
Decreased uniformity
42.
Relative number of beats collected at a specific R-R intervals is called a beat:
A.
Electrocardiogram
B.
Histogram
C.
Sinogram
D.
Pictogram
43.
The orientation that views the heart from the right ventricle to the left ventricle is called:
A.
Long-axis view
B.
Short-axis view
C.
Vertical long-axis view
D.
Horizontal long-axis view
44.
Which of the following statements CORRECTLY describes the kinetic properties of Rb-82?
A.
Rb-82 displays a nonlinear relationship between blood flow and myocardial activity concentrations
B.
The first-pass extraction fraction of Rb-82 is higher than that of N-13 ammonia
C.
Rb-82, after intravenous administration, reaches the “plateau phase” at flows 3.0–3.5 mL/min/g
D.
The first-pass extraction fraction of Rb-82 is higher than that of oxygen-15–labeled (O-15) water
45.
Flow through the coronary circulation depends on the pressure gradient between:
A.
The aorta and the left atrium
B.
The aorta and the right atrium
C.
The right and the left atrium
D.
The right and the left ventricle
46.
The frequency at which the filter value is equal to 0.5 is called:
A.
Roll-off
B.
Cut-off
C.
Nyquist
D.
Fourier
47.
All of the following pharmacological stress agents work directly on the coronary vessels to increase blood flow EXCEPT:
A.
Adenosine
B.
Dipyridamole
C.
Dobutamine
D.
Regadenoson
48.
In healthy persons, the PR, QRS, and QT intervals:
A.
Shorten as heart rate increases
B.
Shorten as heart rate decreases
C.
Lengthen as heart rate increases
D.
Are independent from heart rate
49.
The ability of the filters to both amplify and attenuate frequencies in selected ranges is a characteristic feature of:
A.
A low pass filter
B.
An active filter
C.
A high pass filter
D.
A ramp filter
50.
Which of the following is the most common reason for stopping an exercise test?
A.
Arrhythmia
B.
Chest pain
C.
Fatigue
D.
Headache
51.
Attenuation artifacts of the anterior and anterolateral myocardial walls may occur in men with:
A.
Anemia
B.
Cholelithiasis
C.
Gynecomastia
D.
Pneumonia
52.
Which of the following frame times is recommended for a first-pass radionuclide angiography (FPRNA)?
A.
5 ms
B.
25 ms
C.
55 ms
D.
85 ms
53.
The Butterworth filter is an example of:
A.
A high pass filter
B.
A ramp filter
C.
An active filter
D.
A low pass filter
54.
The images in a typical rest-stress myocardial perfusion study with Rb-82 chloride are acquired in the following order:
A.
Stress transmission scan, stress images, rest transmission scan, rest images
B.
Rest transmission scan, rest images, stress transmission scan, stress images
C.
Rest transmission scan, rest images, stress images, stress transmission scan
D.
Stress transmission scan, rest transmission scan, stress images, rest images
55.
A 73-year-old man with a history of CABG, and with a family history of a younger brother who had coronary artery bypass surgery, presents to ED with complaints of intermittent lightheadedness and dizziness. His ECG (Fig. 3.2) indicates:
A.
Atrial flutter
B.
Normal sinus rhythm
C.
Sinus bradycardia
D.
Ventricular pacemaker
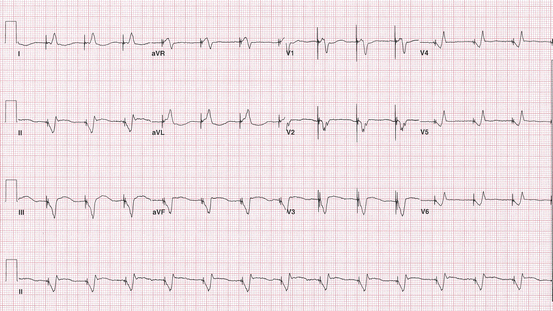

Fig. 3.2
Electrocardiogram
56.
An exercise workload of 3–5 METs (metabolic equivalent of task) is consistent with:
A.
Standing
B.
Walking at 1–2 mph
C.
Walking at 3–4 mph
D.
Playing single tennis
57.
An alkaloid that reduces vagal tone, consequently increasing the HR and enhancing conduction through the bundle of His is called:
A.
Aggrenox
B.
Aminophylline
C.
Aspirin
D.
Atropine
58.
Which of the following is usually chosen as the isoelectric point for ECG interpretation?
A.
The beginning of the P wave
B.
The PQ junction
C.
the QR junction
D.
The ending of the T wave
59.
Large, pendulous breasts are more likely to attenuate:
A.
The anterior myocardial wall
B.
The lateral myocardial wall
C.
The inferior myocardial wall
D.
The septal wall
60.
Exercise myocardial perfusion studies in patients with LBBB mimic stress-induced ischemia in the:
A.
Apex
B.
Anterior wall
C.
Inferior wall
D.
Septum
61.
Which of the following radiotracers has the shortest myocardial retention time?
A.
Tc-99m sestamibi
B.
Tc-99m teboroxime
C.
Tc-99m tetrofosmin
D.
Tl-201 thallous chloride
62.
The radiotracer administration through an adenosine infusion line may result in:
A.
Atrial fibrillation
B.
Transient atrioventricular block
C.
Transient ischemia
D.
Transient tachycardia
63.
Tc-99m tetrofosmin, when compared to Tc-99m sestamibi, has:
A.
A longer biological half-life
B.
More rapid liver clearance
C.
A longer physical half-life
D.
More rapid kidney clearance
64.
Which of the following describes the positrons emitted by N-13 NH3?
A.
Energy of 1.19 MeV and an average range of 2.8 mm
B.
Energy of 3.15 MeV and an average range of 2.8 mm
C.
Energy of 3.15 MeV and an average range of 0.4 mm
D.
Energy of 1.19 MeV and an average range of 0.4 mm
65.
An important cellular signaling molecule, as well as a powerful vasodilator with a short half-life of a few seconds in the blood, is called:
A.
Arginine
B.
Nitric oxide
C.
Nitrous oxide
D.
Nitroglycerine
66.
Figure 3.3 represents the LV volume curve derived from an 8-frame gated myocardial perfusion imaging study using 4D-MSPECT. The end systolic volume (ESV) of the LV is approximately:
A.
19 %
B.
23 %
C.
47 %
D.
60 %
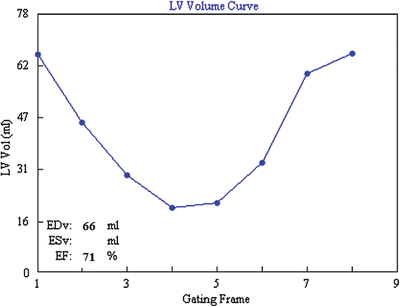

Fig. 3.3
Volume curve
67.
Regadenoson stimulated coronary vasodilation and an increase in coronary blood flow (CBF) results from:
A.
Blocking of the A2A adenosine receptor
B.
Inhibiting reuptake of adenosine
C.
Promoting reuptake of adenosine
D.
Triggering of the A2A adenosine receptor
68.
Myocardial oxygen consumption described as mixed venous oxygen saturation (MVO2) at a resting heart rate is about:
A.
2 ml O2/min per 100g
B.
4 ml O2/min per 100g
C.
8 ml O2/min per 100g
D.
16 ml O2/min per 100g
69.
Heterogeneity in myocardial blood flow (BF) in patients with CAD observed during a radionuclide stress test is caused by:
A.
Decreased BF in the normal territory and relatively unchanged BF in the territory supplied by the stenotic vessel
B.
Increased BF in the normal territory and relatively unchanged BF in the territory supplied by the stenotic vessel
C.
Increased BF in the normal territory and in the territory supplied by the stenotic vessel
D.
Decreased BF in the normal territory and in the territory supplied by the stenotic vessel
70.
When estimating functional capacity, the amount of work performed should be measured in:
A.
The number of stages achieved
B.
Heart rate (HR)
C.
Metabolic equivalent (MET)
D.
The number of minutes of exercise
71.
SPECT myocardial perfusion images usually use a standardized display in which data sets are normalized to:
A.
The maximum myocardial tracer content
B.
The mean myocardial tracer content
C.
The median myocardial tracer content
D.
The minimum myocardial tracer content
72.
When equilibrium radionuclide angiocardiography (ERNA) is performed, the best septal view is usually achieved at:
A.
150 RAO
B.
45° RAO
C.
15° LAO
D.
45° LAO
73.
Isolated reversible perfusion defect of the septum in patients with left bundle branch block (LBBB):
A.
Is commonly seen at low heart rates
B.
Is commonly seen in patients with low EF
C.
Is related to early relaxation of the septum
D.
Represents heterogeneity of flow between the LAD and left circumflex territories
74.
PET camera electronics are created such that counts are recorded only when signals from opposite side detectors are registered:
A.
Within a timing window and along a line crossing COR
B.
Within a timing window and along a line of response
C.
Within an annihilation event window and along a line of response
D.
Within an annihilation event window and along a line crossing COR
75.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) presents with a spectrum of diseases, from stable angina and unstable angina, to myocardial infarction. As per current guidelines, the particular syndrome is determined by all of the following EXCEPT:
A.
ECG findings
B.
Cardiac enzyme levels
C.
MPI findings
D.
Patient history
76.
All of the following statements correctly describe advantages of single-isotope MPI over dual isotope imaging EXCEPT:
A.
Single-isotope MPI allows the opportunity to perform imaging with attenuation correction
B.
Interpretation of images is easier since the same isotope is used for both rest and stress
C.
TID markers can be determined much more easily with single isotope protocols
D.
Single-isotope MPI routinely evaluates myocardial viability
77.
Figure 3.4 displays images acquired during a routine 32 frames multi-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan. The end systole image is labeled:
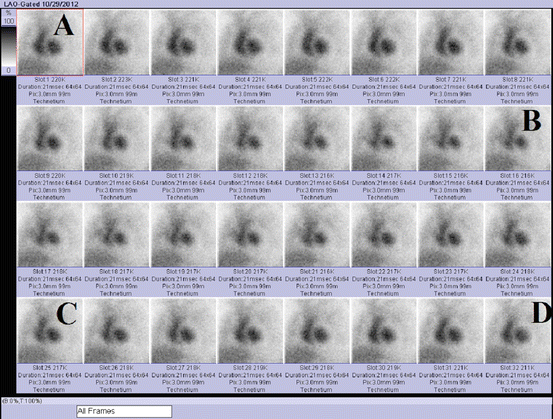

Fig. 3.4
MUGA scan
A.
D
B.
C
C.
B
D.
A
78.
If the patient’s resting heart rate is 60 beats/min, an 8-frame acquisition across the cardiac cycle comprises:
A.
100 ms per frame
B.
125 ms per frame
C.
150 ms per frame
D.
175 ms per frame
79.
The presence of interventricular septal flattening on MPI SPECT studies indicates:
A.
Left atrial overload
B.
Right atrial overload
C.
Left ventricle overload
D.
Right ventricle overload
80.
All of the following ECG changes observed during a stress test are classified as a positive ECG response to stress EXCEPT:
A.
≥1 mm flat or downsloping ST depression 60–80 ms from the J point
B.
≥1.5-mm upsloping ST depression 80 ms from the J point
C.
Premature atrial contraction
D.
≥1-mm ST elevation
81.
The appearance of the “Reverse redistribution” phenomenon can be created by all of the following EXCEPT:
A.
Tissue attenuation
B.
Motion artifact
C.
Dose extravasation
D.
Misalignment on SPECT slices
82.
The administration of Tc-99m albumin aggregate particles when performing a R-L shunt study involves the risk of causing:
A.
A heart attack
B.
A microemboli in the brain
C.
Cardiac arrhythmia
D.
A macroemboli in the lungs
83.
Sestamibi is principally cleared by:
A.
The hepatobiliary system
B.
Kidneys
C.
Skin
D.
The respiratory system
84.
Voluntary motion of the patient in response to discomfort experienced in the course of PET/CT imaging most commonly occur:
A.
At the beginning of the scan
B.
During the CT study
C.
During the PET study
D.
During the acquisition of the topogram
85.
Referral bias is a form of a systematic error that can result in:
A.
An overestimation of test specificity and an underestimation of test sensitivity
B.
An overestimation of test sensitivity and an underestimation of test specificity
C.
An overestimation of test sensitivity and test specificity
D.
An underestimation of test sensitivity and test specificity
86.
Which of the following stress test modalities has the highest sensitivity for the diagnosis of CHD?
A.
Exercise ECG testing
B.
Positron emission tomography
C.
SPECT perfusion imaging
D.
Stress echocardiography
87.
The maximal plasma concentration of regadenoson (Lexiscan) is achieved within:
A.
1 min after injection of Lexiscan
B.
1–4 min after injection of Lexiscan
C.
4–8 min after injection of Lexiscan
D.
8–12 min after injection of Lexiscan
88.
The ventricle has two alternating functions-systolic ejection and:
A.
Asystolic relaxation
B.
Diastolic ejection
C.
Diastolic filling
D.
Systolic filling
89.
Cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) crystals are:
A.
Solid-state detectors
B.
Liquid-state detectors
C.
Scintillation crystals
D.
Gas crystals
90.
Which of the following exercise stress test findings/symptoms indicate a low probability of coronary artery disease (select three)?
A.
Chest pain
B.
Achieved 85 % of the maximum predicted heart rate
C.
Dyspnea at low work rate
D.
No ST segment depression
E.
A physiological response in blood pressure
91.
Which of the following energy window settings is appropriate for the 70 keV and the 167-keV peak of Tl-201?
A.
15 % and 15 %
B.
15 % and 30 %
C.
30 % and 15 %
D.
30 % and 30 %
92.
A vasodilator should be used in stress testing for patients unable to perform the standard exercise stress test or in patients who have (select two):
A.
Acute asthma
B.
Electronically paced rhythms
C.
Left bundle branch block
D.
Third-degree AV block
E.
Systolic blood pressure less than 90mmHg
93.
False-negative (FN) test results of MPI relate to patients with:
A.
A positive test result who have CAD
B.
A negative test result who do not have CAD
C.
A positive test result who do not have CAD
D.
A negative test result who have CAD
94.
The major inotropic/chronotropic agent used for pharmacologic radionuclide myocardial perfusion (rMPI) is:
A.
Adenosine
B.
Atropine
C.
Dipyridamole
D.
Dobutamine
95.
A significant angiographic stenosis is present if a coronary artery is being narrowed by:
A.
25 % or greater diameter reduction
B.
45 % or greater diameter reduction
C.
70 % or greater diameter reduction
D.
90 % or greater diameter reduction
96.
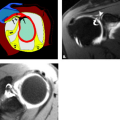
Figure 3.5 displays SA SPECT MPI images. Label D identifies the:
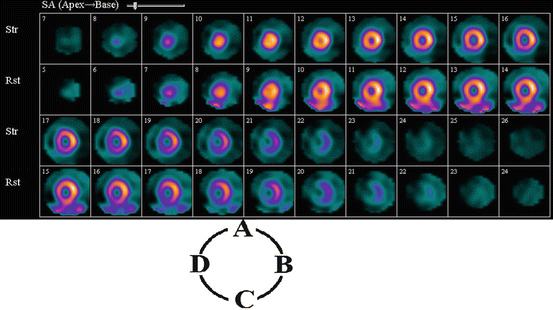

Fig. 3.5
SPECT MPI
A.
Anterior wall
B.
Inferior wall
C.
Lateral wall
D.
Septal wall
97.
Radiation exposure to patients from cardiac single isotope rest/stress technetium imaging is approximately:
A.
4–6 mSV
B.
8–10 mSV
C.
18–20 mSV
D.
25–30 mSV
98.
The typical end-diastolic volume (EDV) for the left ventricle is approximately:
A.
30 ml
B.
60 ml
C.
120 ml
D.
240 ml
99.
The American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) recommends the use of stress-only imaging in all of the following groups of patients EXCEPT:
A.
Patients without known coronary artery disease
B.
Patients without known history of prior myocardial infarction
C.
Patients in the selected low or low-intermediate risk population
D.
Patients in the selected high-intermediate or high-risk population
100.
All of the following are known confounders of exercise stress testing EXCEPT:
A.
Aggrenox
B.
Digoxin
C.
Left bundle branch block
D.
Left ventricular hypertrophy
101.
Tl-201 decays by electron capture to:
A.
Ag-47
B.
Hg-201
C.
Tl-204
D.
U-235
102.
Which of the following statements describing half-lives of the most widely available pharmacologic vasodilators is CORRECT?
A.
Regadenoson has a longer half-life than adenosine
B.
Adenosine has a longer half-life than dipyridamole
C.
Regadenoson has a longer half-life than dipyridamole
D.
Adenosine has a longer half-life than regadenoson
103.
Which of the following groups of patients with suspected CAD have the highest rate of false-negative MPI tests?
A.
Patients with no disease
B.
Patients with low pretest probability of disease
C.
Patients with intermediate pretest probability of disease
D.
Patients with high pretest probability of disease
104.
A PET acquisition, in which lead or tungsten septa divide detector rings such that only plane-by-plane LORs are detected, is known as:
A.
HD PET
B.
2D PET
C.
3D PET
D.
TOF PET
105.
The difference between the amount of oxygen that enters the heart and that which leaves the heart per minute is called:
A.
The oxygen reserve of the heart
B.
The oxygen consumption of the heart
C.
The coronary blood flow
D.
The coronary flow reserve
106.
The presence of a focal defect in rest images that was not seen on stress images, or a focal defect in stress images that appears more severe on rest images, is called:
A.
Reverse distribution
B.
Reverse redistribution
C.
Irreversible defect
D.
Reversible defect
107.
Which of the following hemodynamic effects are the most common after administration of Lexiscan?
A.
A decrease in heart rate and in blood pressure
B.
An increase in heart rate and a decrease in blood pressure
C.
A decrease in heart rate and an increase in blood pressure
D.
An increase in heart rate and in blood pressure
108.
Which of the following groups of patients have the highest risk of cardiac events when data from CT assessment of coronary-artery calcium (CAC) and information from MPI SPECT are combined?
A.
Patients with no CAC and normal SPECT MPI
B.
Patients with evidence of CAC and abnormal SPECT MPI
C.
Patients with evidence of CAC and normal SPECT MPI
D.
Patients with no CAC and abnormal SPECT MPI
109.
A sestamibi kit for clinical use requires the addition of Tc-99m and must then be used:
A.
Immediately
B.
Within 6 h of preparation
C.
Within 12 h of preparation
D.
Within 24 h of preparation
110.
Which of the following tests evaluating coronary artery disease is indicated in patients with an abnormal resting ECG?
A.
Exercise echocardiography
B.
Exercise stress test
C.
Treadmill MPI
D.
Planar imaging
111.
Sensitivity and specificity of exercise and vasodilator stress myocardial perfusion SPECT with Tc-99m-based tracers for the detection of angiographically significant CAD is:
A.
71 % and 91 %, respectively
B.
89 % and 75 %, respectively
C.
51 % and 79 %, respectively
D.
91 % and 51 %, respectively
112.
Which of the following radiopharmaceuticals is commonly used for detecting and quantifying R-L shunts?
A.
Tc-99m MAA
B.
Tc-99m MDP
C.
Tc-99m ECD
D.
Tc-99m DMSA
113.
The reduction in intensity of a beam of gamma rays, due to absorption and scatter, is called:
A.
Absorption
B.
Adsorption
C.
Attenuation
D.
Addition
114.
Adenosine is administered via an infusion pump at a dose of:
A.
280 μg/kg per min for 6 min
B.
140 μg/kg per min for 6 min
C.
140 μg/kg per min for 8 min
D.
2,800 μg/kg per min for 8 min
115.
Which of the following is considered a risk factor for coronary artery disease?
A.
Cholesterol greater than 200 mg/dL
B.
Diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmHg
C.
Systolic blood pressure greater than 120 mmHg
D.
Sudden cardiac death in a first-degree relative younger than 75 years
116.
Which of the following group of patients has the lowest ratio of non-diagnostic exercise stress test results?
A.
Patients with coronary artery disease
B.
Patients with orthopedic limitation
C.
Patients with peripheral vascular disease
D.
Patients with poor motivation
117.
A 79-year-old woman presents with diabetes, breast cancer, progressive fatigue, anorexia, and several near-syncopal episodes. An ECG is performed in the office. Choose from the following responses to interpret this ECG (Fig. 3.6):
A.
Atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response
B.
Normal sinus rhythm
C.
Sinus rhythm with frequent PVC in a pattern of bigeminy
D.
Ventricular pacemaker
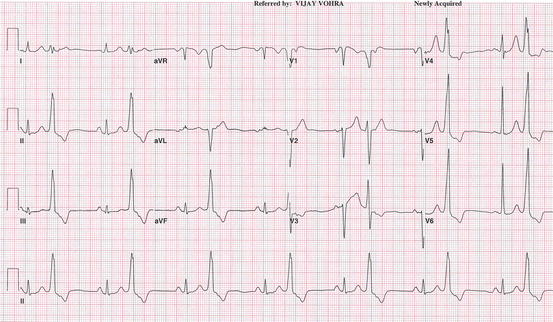

Fig. 3.6
Electrocardiogram
118.
Which of the following statements describing risk stratification with coronary artery calcium (CAC) is FALSE?
A.
A high coronary calcium score indicates the presence of extensive calcification
B.
A high coronary calcium score is indicative of atherosclerosis
C.
A high coronary calcium score implies severe stress-induced perfusion abnormalities
D.
Stress SPECT MPI is an appropriate test to perform after CT imaging demonstration of CAC
119.
What is the minimum amount of patient motion required to introduce a clinically significant artifact?
A.
Motion of 0.5 pixel
B.
Motion of 1 pixel
C.
Motion of 1.5 pixels
D.
Motion of 2 pixels
120.
Failure to achieve a target age-predicted HR in the absence of positive ECG changes is regarded as:
A.
A negative test
B.
A non-diagnostic test
C.
A positive test
D.
An equivocal test
121.
Methods that include either line source or computed tomographic (CT) techniques are employed to create:
A.
An emission scan
B.
An uniformity correction map
C.
An attenuation map
D.
A sinogram
122.
All of the following are absolute contraindications for adenosine stress testing EXCEPT:
A.
Active bronchospasm
B.
Dipyridamole treatment
C.
More than first-degree heart block
D.
Systolic blood pressure more than 90 mmHg
123.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

Which of the following patients may require a second low dose of Tl-201 injection at rest to improve sensitivity for the detection of myocardial viability?
A.
Patients with arrhythmia
B.
Patients with hyperkinetic left ventricle
C.
Patients with severe hypertension
D.




Patients with severe ischemia
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree