Chapter 6 Procedures in radiography
 All patients follow a standardised pathway through the imaging department, coming in to contact with the same key areas regardless of their examination.
All patients follow a standardised pathway through the imaging department, coming in to contact with the same key areas regardless of their examination. Mobile radiography provides a diagnostic service for patients who are unable to attend the X-ray department.
Mobile radiography provides a diagnostic service for patients who are unable to attend the X-ray department. Mobile radiography introduces radiation safety issues which should be addressed during all examinations.
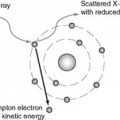
Mobile radiography introduces radiation safety issues which should be addressed during all examinations. The use of contrast media enhances areas that may not be visualised during conventional examinations.
The use of contrast media enhances areas that may not be visualised during conventional examinations. Some contrast media can cause undesirable side- effects in patients and all patients should be observed after the introduction of the contrast medium to ensure swift action in the event of a reaction.
Some contrast media can cause undesirable side- effects in patients and all patients should be observed after the introduction of the contrast medium to ensure swift action in the event of a reaction.INTRODUCTION
Radiology is an integral department within the hospital in that many inpatients are required to have at least one radiological examination in some form or another during their hospital stay. There are many other sources of referral forimaging examinations, ranging from outpatient clinics to accident and emergency departments (Table 6.1).
Table 6.1 Referral sources and input in a diagnostic imaging department
| Referring source | Diagnostic imaging input |
|---|---|
| Medical/surgical | Departmental appendicular and axial skeletal radiography |
| Departmental chest and abdominal radiography | |
| Mammography | |
| Dental | |
| Mobile ward radiography | |
| Departmental and theatre based fluoroscopic examinations | |
| Non ionic iodinated contrast studies | |
| Theatre based appendicular and axial skeletal radiography | |
| CT, MRI, US, RNI | |
| Outpatients/GPs | Departmental appendicular and axial skeletal radiography |
| • Orthopaedic | Departmental chest and abdominal radiography |
| • ENT | Mammography |
| • Gynaecology | Dental |
| • Obstetrics | Departmental fluoroscopic examinations |
| • Oncology | Non ionic iodinated contrast studies |
| • Paediatric | CT, MRI, US, RNI |
| • Care of the elderly | |
| Accident and emergency | Departmental appendicular and axial skeletal radiography |
| Departmental chest and abdominal radiography | |
| Mobile resuscitation unit radiography | |
| CT, MRI, US |
CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; RNI, radionuclide imaging; US, ultrasound
PATIENT PATHWAYS THROUGH THE IMAGING DEPARTMENT
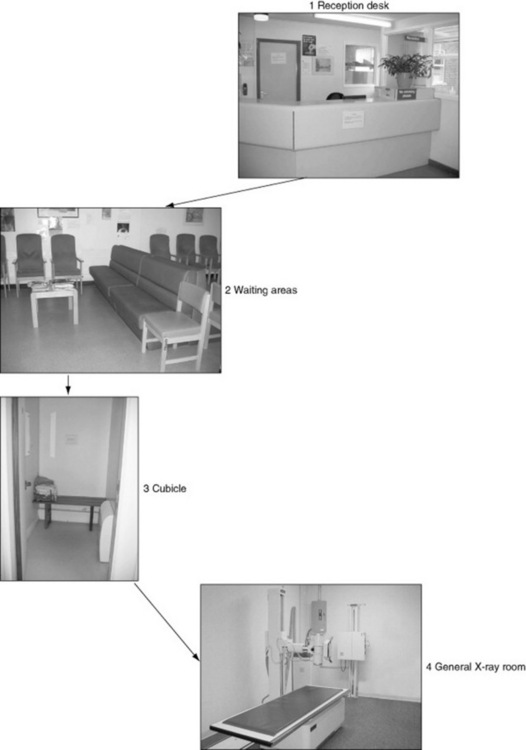
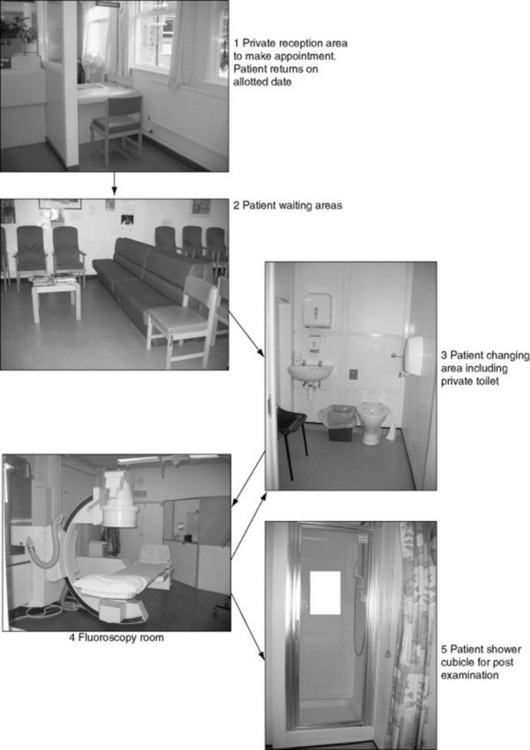
Figure 6.1 A patient’s pathway through a diagnostic imaging department for routine appendicular, axial, chest and abdominal radiography.
RECEPTION DESK
This is most likely to be the first contact point that a patient or carer has with a diagnostic imaging department. It has been documented that patients should be given good quality information with regards to their care and be sufficiently informed before any medical examination takes place. It is therefore essential that the information process begins well. The reception team must be able to converse with the patients to ascertain their personal details; however, they must also be aware that there is the potential to be overheard by others. In some departments there is a line indicated by a stripe on the floor, indicating that only one patient should be at the desk at one time, whereas in other departments there may be a separate cubicle in which to ask personal details (Fig. 6.3). There are various notices informing patients of the no-smoking policy and zero tolerance of aggressive behaviour.
WAITING AREA
The patient will usually be directed to a sub-waiting area close to the X-ray room where their examination is to be carried out. In Figure 6.4 it can be seen that chairs have wipeable upholstery to reduce the risk of cross-infection. The chairs are also ranging in height and style to suit patients with mobility problems. A waiting area should be light and airy and have a selection of reading materials. The inclusion of wipeable toys may also be preferable in areas dealing with small children. It is important that if there is a delay due to unforeseen circumstances, the patients are aware of the time delay; this can often defuse difficult situations.
CHANGING CUBICLE
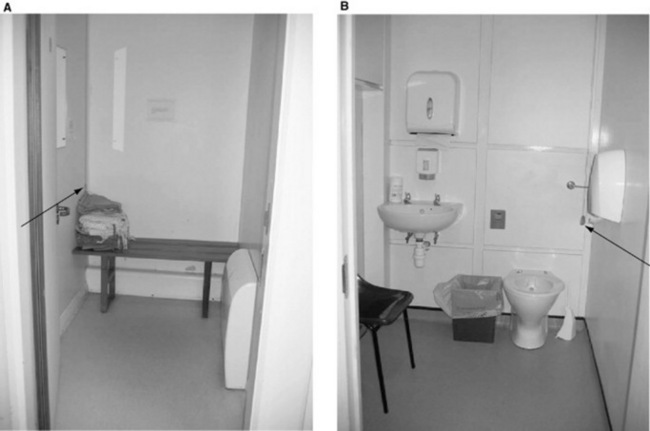
A changing cubicle should contain a bench or chair to sit on. There should be a supply of gowns to accommodate both male and female statures. The door should be lockable but with safety locks in case of emergencies and patients should not be placed in a cubicle for long periods of time.Some hospitals provide baskets/lockers for the patient’s clothes in order to reduce the risk of theft and also free up cubicles for a more rapid throughput of patients.
For certain examinations (e.g. barium enemas) where patients may need to access a toilet promptly after the examination, a cubicle with toilet and shower facilities should be used. An emergency cord is also essential in case a patient feels unwell (Fig. 6.5).
GENERAL X-RAY ROOM
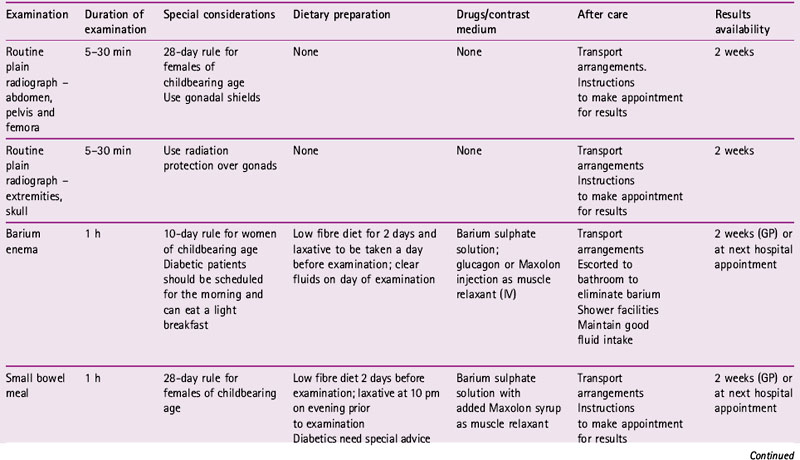
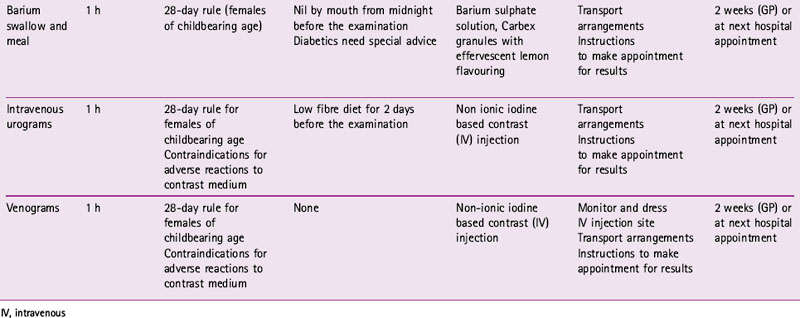
In the X-ray room it is important to remember that to a member of the public, old or young, this room containing lots of big pieces of machinery may look rather frightening. Therefore, it is important to make the patient comfortable and at ease by giving instructions in simple non-jargon terms. For example, to most people a bed or couch is what you lie on, not a table, so be aware of potential confusion. Following the examination the patient should be asked to wait until the image is checked and then given information on when and how to get the results. Table 6.2 shows patient preparation and aftercare for some typical departmental examinations.
MOBILE RADIOGRAPHY
The imaging of a patient using equipment other than the static department-based equipment is commonly known as mobile or portable radiography. However, the term portable only relates to equipment that can be carried. Mobile radiography can be divided into two distinct types:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree