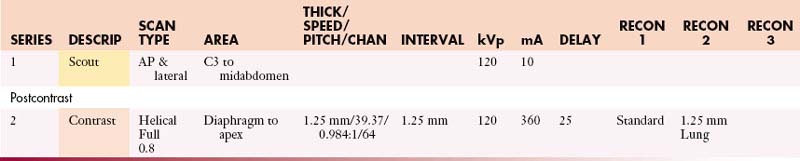
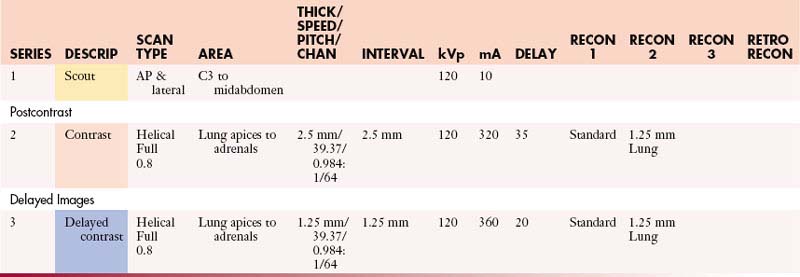
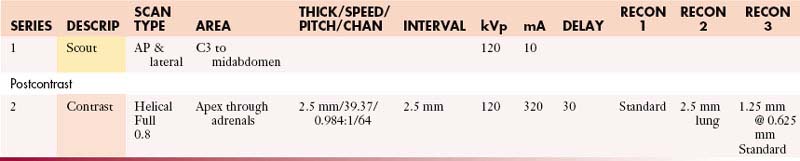
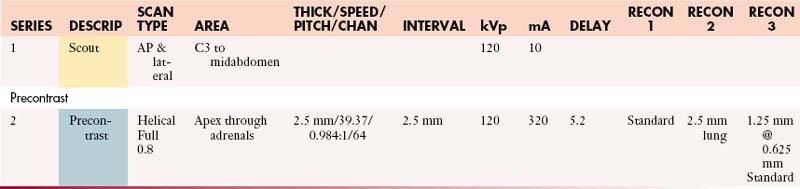
Chapter 42 Protocols for Imaging Studies in the Oncologic Patient
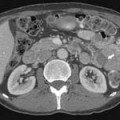
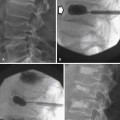
Well-thought-out protocols imaging sophisticated imaging studies are critical to ensure that the resultant images have the best possible chance to answer the clinical question. In the case of oncologic patients, this usually hinges on whether disease is stable, has regressed, or has progressed and whether there are new sites of disease. Beyond this fundamental question, our patients may have unexpected findings as well as complications from therapy. The ability to answer such questions relies on high-quality images and, in the case of computed tomography (CT), the best quality titrated with the least radiation exposure because patients generally go into a lifetime of surveillance. This is a significant challenge. In patients undergoing imaging for surgical intervention, especially for cure, these studies need to be directly targeted to the most likely sites of metastases (e.g., high-quality liver imaging for metastases in patients with orbital, choroidal melanoma) and have optimal image quality to detect metastatic disease.1–5 Imaging with multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) can be performed in multiple phases, and developing protocols to detect hyper- as well as hypovascular metastases is critical in evaluating patients with tumors such as carcinoid, islet cell tumors of the pancreas, and a number of other primaries. Timing of the contrast bolus and subsequent imaging is critical in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as well as current MDCT scanning.6–8
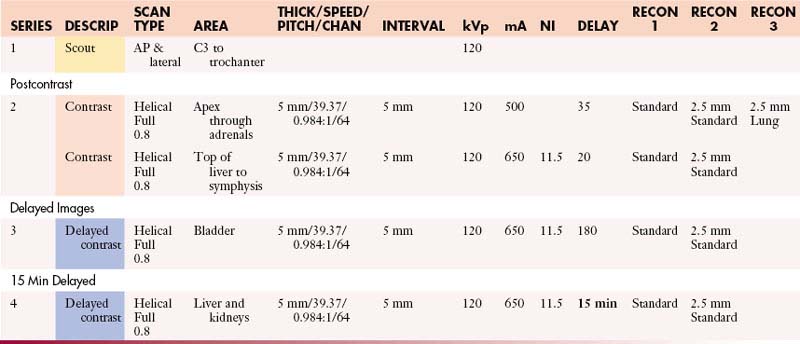
MDCT: CT Imaging
Chest Protocols (MDCT 64 Slice)
Abdomen/Pelvis Protocols (MDCT 64 Slice)
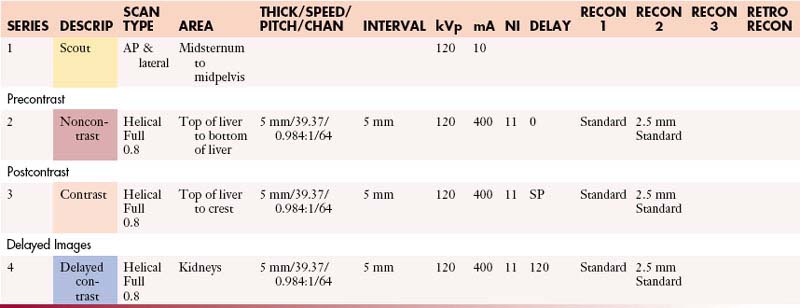
Abdomen without and with Contrast
Abdomen and Pelvis with Contrast
Abdomen and Pelvis without Contrast
Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
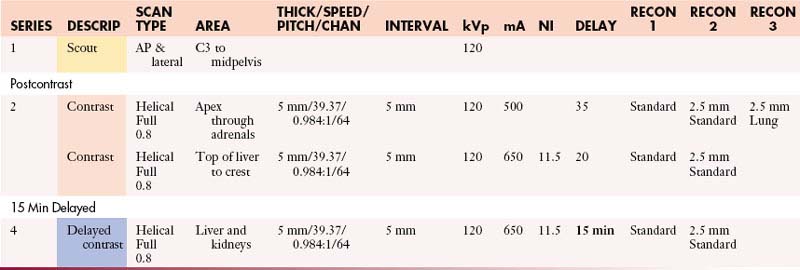
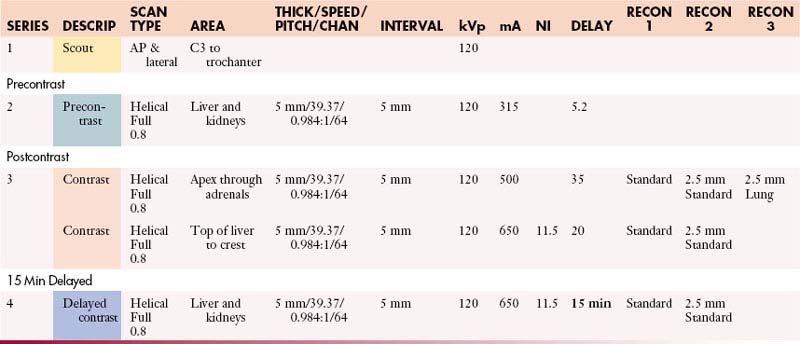
Adrenals: Abdomen with Contrast
Adrenals: Abdomen without and with Contrast
Adrenals: Abdomen and Pelvis with Contrast
Adrenals: Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Adrenals: Chest and Abdomen with Contrast
Adrenals: Chest and Abdomen without and with Contrast
Adrenals: Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis with Contrast
Adrenals: Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Angiogram/Venogram: Abdomen and Pelvis
Appendiceal/Peritoneal: Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Appendiceal/Peritoneal: Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Bowel Carcinoid: Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Chest and Abdomen with Contrast
Chest and Abdomen without Contrast
Chest and Abdomen without and with Contrast
Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis with Contrast
Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without Contrast
Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Gastric: Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
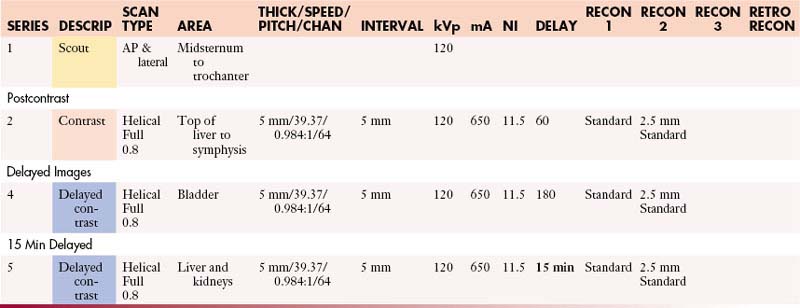
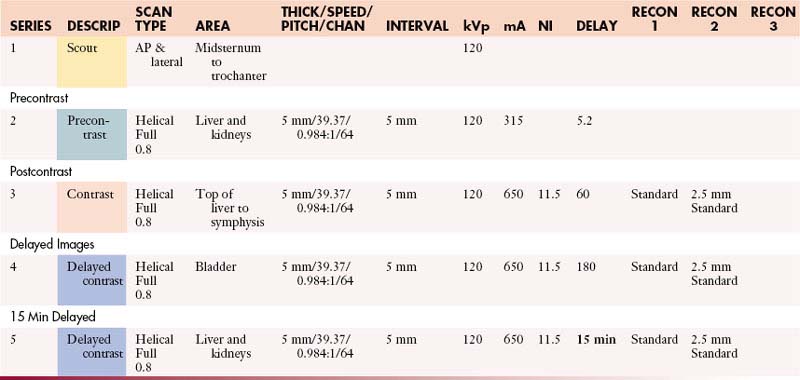
Liver: Abdomen without and with Contrast
Liver: Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Liver: Chest and Abdomen without and with Contrast
Liver: Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Lymphoma without and with Contrast
Pancreas: Abdomen without and with Contrast
Pancreas: Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Pancreas: Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Pancreatic Islet Cell: Abdomen without and with Contrast
Post Cystectomy: Abdomen and Pelvis with Contrast
Post Cystectomy: Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis with Contrast
Post Cystectomy: Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Renal: Chest and Abdomen without and with Contrast
Renal: Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Renal + 3D: Abdomen without and with Contrast
Renal + 3D: Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Renal + 3D: Chest and Abdomen without and with Contrast
Renal + 3D: Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Enterography (Small Bowel): Abdomen and Pelvis with Contrast
Enterography (Small Bowel): Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Enterography (Small Bowel): Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis with Contrast
Enterography (Small Bowel): Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Urogram: Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Urogram: Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis without and with Contrast
Musculoskeletal (MSK) Protocols (MDCT 64 Slice)
MSK (Bridging Protocol) with Contrast
MSK (Bridging Protocol) without Contrast
MSK (Metal Protocol) with Contrast
MSK (Metal Protocol) without Contrast
MSK Operating Room Hi-Res Protocol (64 Slice)
Operating Room High-Res Protocol with Contrast
Operating Room High-Res Protocol without Contrast
Operating Room Standard Protocol (64 Slice)
Operating Room Standard Protocol with Contrast
Operating Room Standard Protocol without Contrast
MSK (Soft Tissue Protocol) with Contrast
MSK (Soft Tissue Protocol) without Contrast
MSK (Standard Protocol) with Contrast
MRI Protocols
Body Protocols (1.5 T)
MDCT: CT Imaging
Chest Protocols (MDCT 64 Slice)
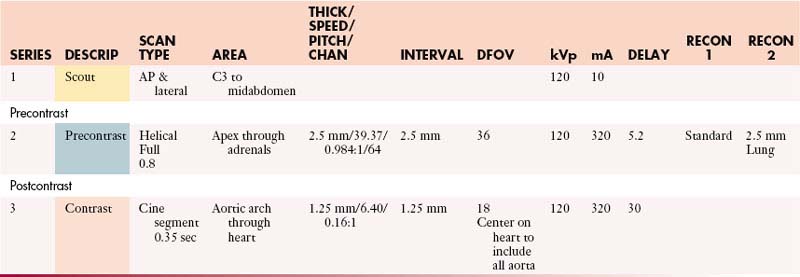
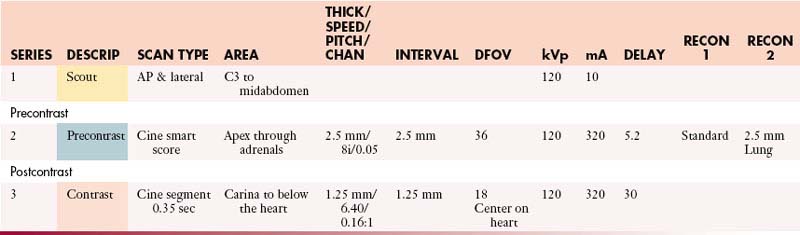
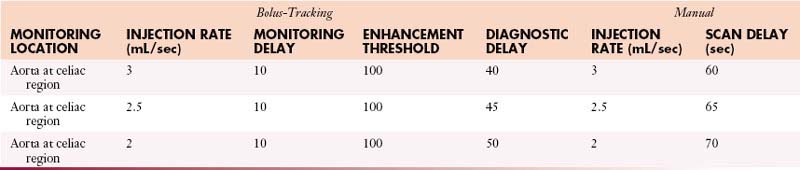
Aorta (Gated Study)
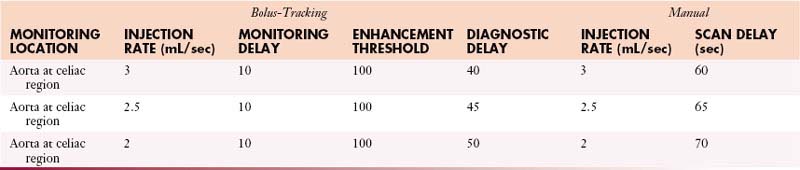
IV Contrast: Iso-osmolar and saline
Volume: 125 mL iso-osmolar and 50 mL saline
| ISO-OSMOLAR (mL/sec) | SALINE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 | 30 |
Coronal: 2.5 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—standard algorithm
Sagittal: 2.5 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—lung algorithm
Oblique-sagittal: 0.8 mm @ 2.5 mm default—standard algorithm (candy cane view)
Scanning direction from superior to inferior.
Check heart rate on arrival. Call radiologist for heart rate > 70 bpm.
Select postcontrast pitch and FOV based on heart rate and patient size.
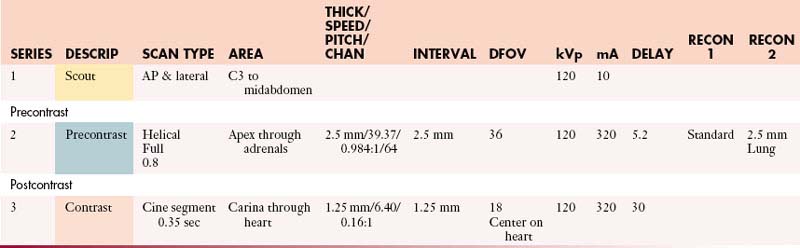
Cardiac Tumor (Gated Study)
IV Contrast: Iso-osmolar & saline
Volume: 125 mL iso-osmolar and 50 mL saline
| VISIPAQUE (mL/sec) | SALINE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 | 30 |
Coronal: 0.8 mm @ 2.5 mm or default—standard algorithm
Sagittal: 0.8 mm @ 2.5 mm or default—lung algorithm
Scanning direction from superior to inferior.
Check heart rate on arrival. Call radiologist for heart rate > 70 bpm.
Select postcontrast pitch and FOV based on heart rate and patient size.
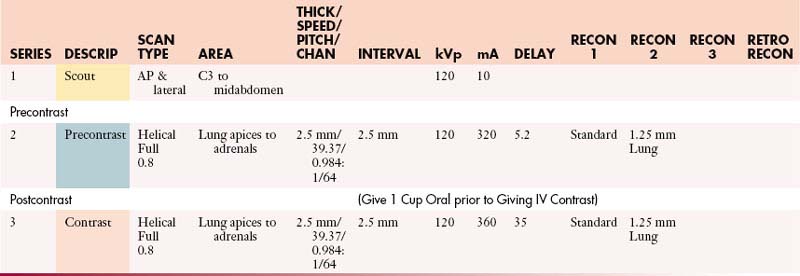
Chest with Contrast
IV Contrast: Contrast 320 mgI/mL
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 3 | 30 |
| 2.5 | 35 |
| 2 | 40 |
Coronal: 2.5 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—standard algorithm
Sagittal: 2.5 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—lung algorithm
Chest without Contrast
Coronal: 2.5 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—standard algorithm
Sagittal: 2.5 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—lung algorithm
Coronary Artery Screening (Gated Study)
IV Contrast: Iso-osmolar & saline
Volume: 125 mL iso-osmolar and 50 mL saline
| ISO-OSMOLAR (mL/sec) | SALINE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 | 30 |
Coronal 0.8 mm @ 2.5 mm or default—standard algorithm
Sagittal 0.8 mm @ 2.5 mm or default—lung algorithm
Scanning direction from superior to inferior.
Check heart rate on arrival. Call radiologist for heart rate > 70 bpm.
Select postcontrast pitch and FOV based on heart rate and patient size.
Esophageal Leak Protocol
16 oz 2% barium sulfate or Gastroview for postcontrast chest
IV Contrast: Contrast 320 mgI/mL
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 3 | 35 |
Coronal: 1.25 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—standard algorithm
Sagittal: 1.25 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—lung algorithm
Scanning direction from superior to inferior.
Low-Dose Surveillance Chest with Contrast (Nodule or Lung Cancer)
IV Contrast: Contrast 320 mgI/mL
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 3 | 30 |
| 2.5 | 35 |
| 2 | 40 |
Perfusion Chest without and with Contrast
Scanning direction from superior to inferior.
Schedule patient in rose & green zones ONLY and before 5:00 PM.
PE Protocol
IV Contrast: Contrast 350 mgI/mL
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 4.2 | 20 |
Coronal: 1.25 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—standard algorithm
Sagittal: 1.25 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—lung algorithm
Scanning direction from inferior to superior.
Superior Vena Cava Venogram
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 3 | 35 |
Coronal: 0.8 mm @ 2.5 mm or default—standard algorithm
Sagittal: 0.8 mm @ 2.5 mm or default—lung algorithm
Coronal: 0.8 mm @ 2.5 mm or default—standard algorithm
Sagittal: 0.8 mm @ 2.5 mm or default—lung algorithm
Scanning direction from superior to inferior.
Bilateral arm injection will be determined by the radiologist.
Chest with Contrast (Virtual Bronchoscopy)
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 3 | 30 |
| 2.5 | 35 |
| 2 | 40 |
Coronal: 2.5 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—standard algorithm
Sagittal: 2.5 mm @ 0.8 mm or default—lung algorithm
Abdomen/Pelvis Protocols (MDCT 64 Slice)
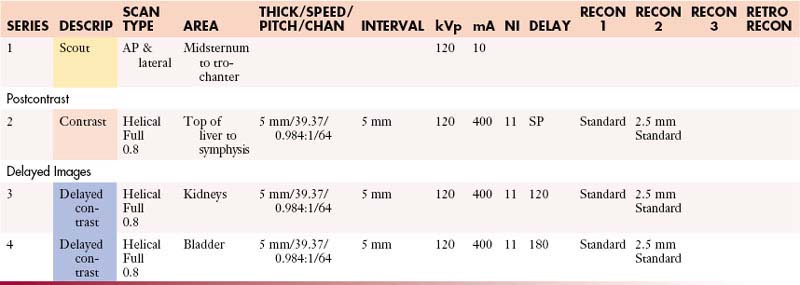
Abdomen and Pelvis with Contrast
GI Contrast: 2% barium sulfate or Gastrografin or water (oral & rectal)
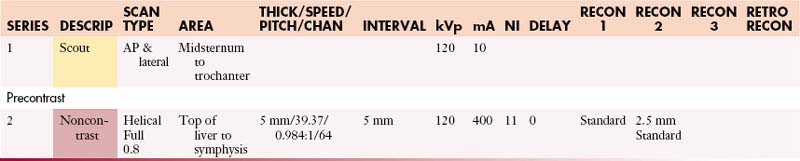
Abdomen and Pelvis without Contrast
GI Contrast: 2% barium sulfate or Gastrografin or water (oral & rectal)
Abdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
GI Contrast: 2% barium sulfate or Gastrografin or water (oral & rectal)
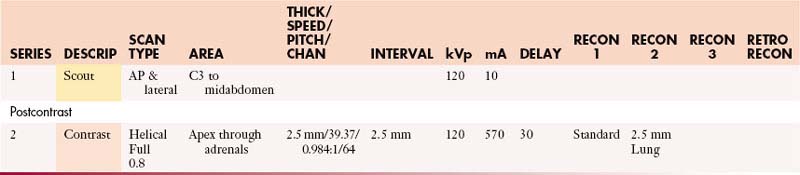
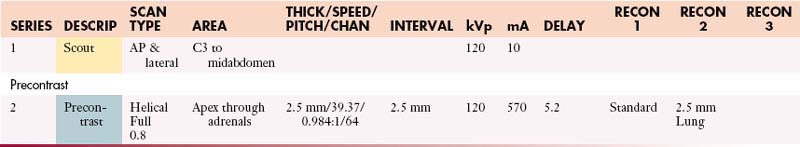
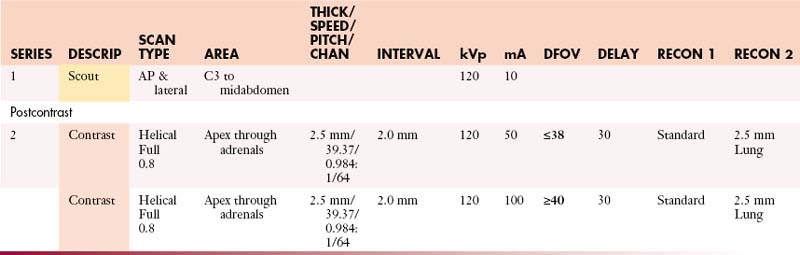
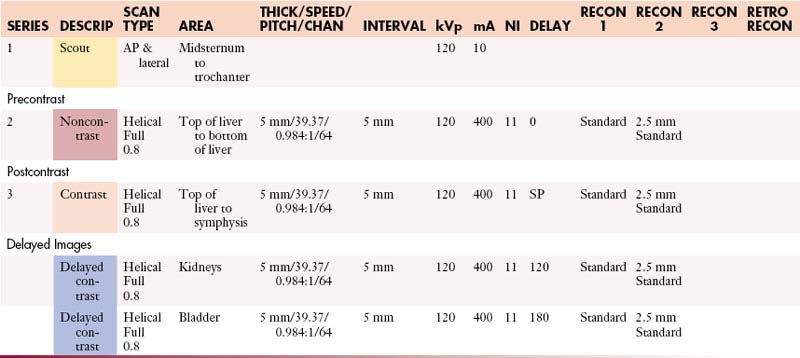
AdrenalsAbdomen with Contrast
GI Contrast: 2% barium sulfate or Gastrografin or water (oral)
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 5 | 60 |
AdrenalsAbdomen without and with Contrast
GI Contrast: 2% barium sulfate or Gastrografin or water (oral)
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 5 | 60 |
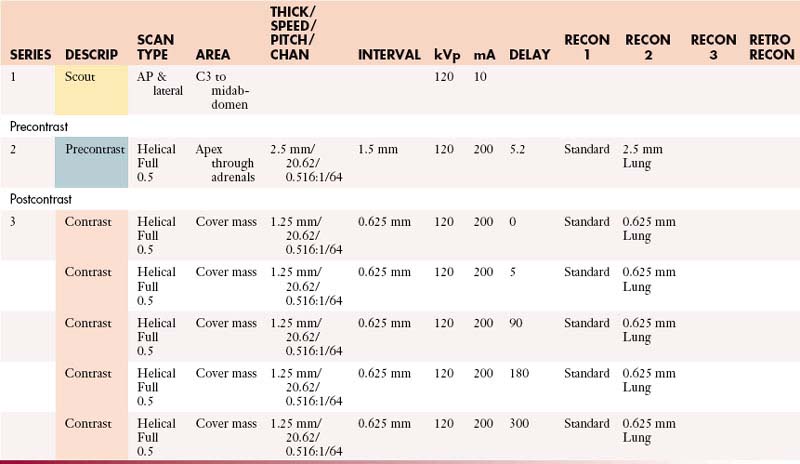
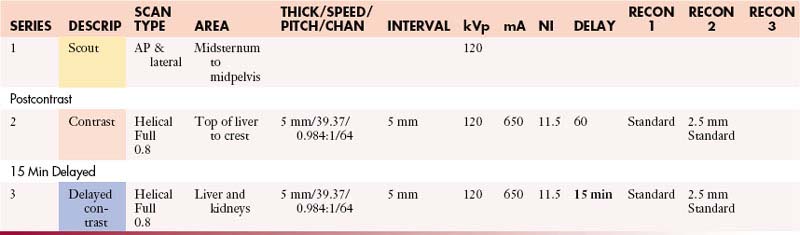
AdrenalsAbdomen and Pelvis with Contrast
GI Contrast: 2% barium sulfate or Gastrografin or water (oral & rectal)
IV Contrast: Contrast 350 mgI/mL
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 5 | 60 |
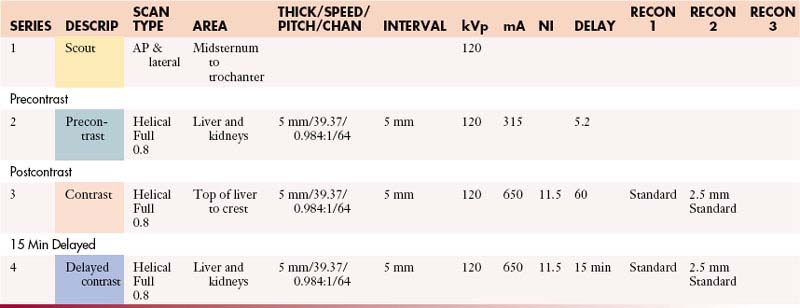
AdrenalsAbdomen and Pelvis without and with Contrast
GI Contrast: 2% barium sulfate or Gastrografin or water (oral & rectal)
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 5 | 60 |
AdrenalsChest and Abdomen with Contrast
GI Contrast: 2% barium sulfate or Gastrografin or water (oral)
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 5 | 60 |
AdrenalsChest and Abdomen without and with Contrast
GI Contrast: 2% barium sulfate or Gastrografin or water (oral)
| Manual | |
|---|---|
| INJECTION RATE (mL/sec) | SCAN DELAY (sec) |
| 5 | 60 |