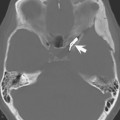
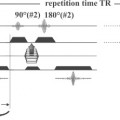
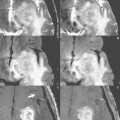
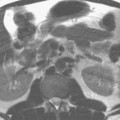
68 Proton Spectroscopy (Chemical-Shift Imaging)
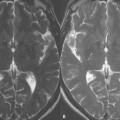
The major healthy brain metabolite peaks that are seen on long TE spectra include N-acetylaspartate (NAA) at 2.02 ppm, choline (Cho) at 3.20 ppm, and creatine (Cr) at 3.02 ppm and 3.9 ppm (see Case 67). Variable TE values in the sequence provide the ability to control the T2 “contrast” of the spectral peaks in the same way tissue T2 contrast is controlled in 2D FSE MR imaging. Short TE measurements are important for the detection of metabolite signals that have a short T2 decay and are not visible on long TE spectra. These include myo-inositol (mI) at 3.56 ppm, glutamine and glutamate (Glx) between 2.05-2.5 ppm and 3.65-3.8 ppm, and glucose at 3.43 ppm. These, short TE metabolites are also critical in the assessment of the developing brain in pediatric imaging.
A major limitation of SVS (see Case 67
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree