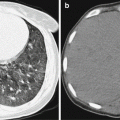
Fig. 22.1
Scarlet fever complicated by bronchopneumonia. The chest X-ray demonstrates thickened pulmonary markings in both lower lungs, with spot-shaped shadows that are more obvious in the right lower lung
(The case and the figure are provided by Tang, YH at Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai, China)
Case Study 2
A girl patient has chief complaint of fever and rash for 1 day with accompanying chill.
On physical examination, her temperature is 37.7 °C (rectal temperature), with pharyngeal congestion. The tonsils are swollen at the degree of 1, raspberry tongue. Many reddish maculopapules can be found on the skin all over the body that slightly protrude out of the skin surface. The color of these maculopapules fades away when pressed. The skin between maculopapules has obvious congestion. By auscultation, the respiratory sound is coarse in both lungs, with rare moist rales in the left lower lung. By laboratory tests, routine blood test found WBC 13.76 × 109/L, N 0.823, L 0.097, RBC 4.87 × 1,012/L, PLT 290 × 109/L, and CRP 14 mg/L; pharyngeal swab found viridans streptococci (++), streptococci positive, Neisseria (++), and no detected fungus.
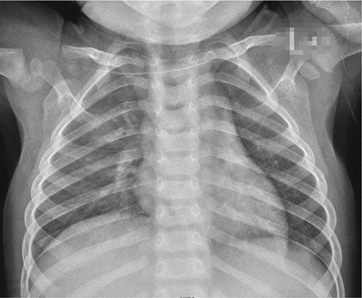

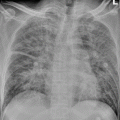
Fig. 22.2
Scarlet fever complicated by bronchopneumonia. The chest X-ray demonstrates increased blurry pulmonary markings of both lungs and scattered small patches of shadows in the inner zone of the middle and upper lung fields in the right lung
(The case and the figure are provided by Lao, Q at the City Children’s Hospital, Hangzhou, China)
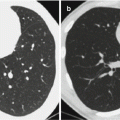
22.7.1.2 CT Scanning
CT scanning demonstrates thickened bronchovascular bundle. The lesions are diffused patches of shadows, with unclearly defined boundaries. Otherwise, they are scattered small flakes of parenchymal shadows or fused large flakes of shadows. Surrounding the small flakes of parenchymal shadows, obstructive emphysema or pulmonary atelectasis is commonly found. The adjacent lung field of obstructive atelectasis may have demonstrations of compensatory emphysema. In addition, CT scanning can detect small quantity of pleural effusion that tends to be missed by chest X-rays.
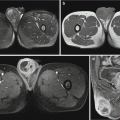
22.7.2 Reactive Arthritis After Streptococcal Infection
X-ray demonstrates cystic absorption and slight osteohyperplasia in the joints of the ankle, knee, hip, and sacroilium, with asymmetric narrowing of the articular space.
22.8 Basis for Diagnosis
22.8.1 Scarlet Fever
The clinical diagnosis of scarlet fever can be defined based on a history of contacting patients with scarlet fever or angina; clinical characteristic manifestations of typical skin rashes and desquamation, strawberry tongue, Pastia lines, and circumoral pallor; and laboratory findings of obviously increased level of peripheral blood routine test indicators. The definitive diagnosis can be made based on detected group A streptococci by pharyngeal swab or pus culture.
22.8.2 Scarlet Fever-Related Complications
22.8.2.1 Bronchopneumonia
Children with scarlet fever have signs and symptoms of respiratory infection.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree