and Vincent L. Sorrell2
(1)
Division of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Department of Radiology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, Kentucky, USA
(2)
Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Gill Heart Institute, University of Kentucky, Lexington, Kentucky, USA
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this chapter (doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-25436-4_27) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
27.1 Case Challenge #1
27.1.1 Problem
Clinical Highlights
A 58-year-old male undergoes evaluation for chest pain after coronary artery stenting.
Images for Review


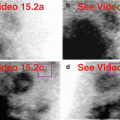
Fig. 27.1
(a)Stress “black-on-white” raw projection images at usual contrast setting for heart (Video 27.1a, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(b)Stress “white-on-black” raw projection images at usual contrast setting for heart (Video 27.1b, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(c)Stress “black-on-white” raw projection images with enhanced contrast setting (Video 27.1c, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(d)Stress/rest processed SPECT images (HLA)
(e)Stress and rest gated SPECT images (Video 27.1d, frame 1) (HLA)
Characterize the Pertinent Finding(s)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ hot □ cold
Pleura: □ hot □ cold
Lungs: □ hot □ cold
Myocardium and pericardium: □ hot □ cold
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ hot □ cold
Peritoneum: □ hot □ cold
Liver: □ hot □ cold
Spleen: □ hot □ cold
Stomach: □ hot □ cold
Kidneys and female reproductive system: □ hot □ cold
State Your Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ normal □ multinodular goiter
Pleura: □ normal □ effusion
Lungs: □ normal □ tuberculosis
Myocardium and pericardium: □ normal □ pericardial effusion
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ normal (right auricular appendage) □ abnormal (right auricular appendage)
Vascular system: □ normal □ extravasation at injection site
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ normal □ cracked crystal
Peritoneum: □ normal □ peritoneal dialysate
Liver: □ normal □ post-thermal ablation cyst
Spleen: □ normal □ cyst
Stomach: □ normal □ chronic distension
Kidneys and female reproductive system: □ normal □ end-stage kidneys
27.1.2 Solution
Additional Annotated Images
(f)Stress “black-on-white” raw projection image with enhanced contrast (Video 27.1e, frame 7),99mTc sestamibi, “hot” right atrial focus (blue oval)
(g)Stress/rest processed SPECT images (HLA), “hot” right atrial focus (yellow ovals)
(h)Stress and rest gated SPECT image (Video 27.1f, frame 7) (HLA), “hot” right atrial focus (yellow ovals on representative images)
The Pertinent Findings
Chest:
Right atrium and right ventricle: ■ hot □ cold
Abdomen
Not applicable
The Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest:
Right atrium and right ventricle: ■ normal (right auricular appendage)
Abdomen
Not applicable
Discussion
Chest
There is a discrete focus of radiopharmaceutical localization in the region of the right atrium. It has an appearance characteristic of right auricular appendage, a common and normal finding seen on the raw projection data (a, b, c, f). Note its superior and deep location. It is enhanced by altering the color presentation (compare b to c and to f). The processed SPECT images (d, g) and the gated SPECT images (e, h) confirm its location and provide the key clue to its etiology and, thus, its clinical significance as a normal finding. It should not be misconstrued as a pathologic mediastinal mass. The small, mild, fixed apical defect is normal apical thinning. Incidental note of “septal rocking” (e) of unclear etiology (no history or left bundle branch block (LBBB) nor cardiac surgery).
The thyroid gland and injection sites (arms up) are not included in the field-of-view.
Abdomen
There is no abnormality.
Relevant Chapter(s)
Chapter 13
27.2 Case Challenge #2
27.2.1 Problem
Clinical Highlights
A 56-year-old female was found to have elevated calcium and parathormone (PTH) levels. Parathyroid SPECT scintigraphy is performed to identify and localize the culprit hyperfunctioning parathyroid gland as the cause of primary hyperparathyroidism.
Images for Review



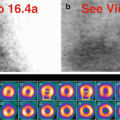
Fig. 27.2
(a)Raw projection images (360° Video 27.2a, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(b)Axial, coronal, sagittal SPECT images
(c)Axial, coronal, sagittal fused SPECT/CT images
Characterize the Pertinent Finding(s)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ hot □ cold
Parathyroid glands: □ hot □ cold
Breasts: □ hot □ cold
Chest wall: □ hot □ cold
Pleura: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ hot □ cold
Liver: □ hot □ cold
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ hot □ cold
Spleen: □ hot □ cold
Stomach: □ hot □ cold
Small intestine and large intestine: □ hot □ cold
State Your Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ normal □ diffuse toxic goiter
Parathyroid glands: □ normal □ parathyroid adenoma, ectopic
Breasts: □ normal □ malignant mass
Chest wall: □ normal □ contamination artifact
Pleura: □ normal □ effusion
Vascular system: □ normal □ extravasation at injection site
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ normal □ malfunctioning photomultiplier tube
Liver: □ normal □ hepatocellular malignancy
Biliary system and gallbladder □ normal □ biliary stricture with obstruction
Spleen: □ normal □ malignant mass
Stomach: □ normal □ free99mTc pertechnetate
Small intestine and large intestine: □ normal □ barium
27.2.2 Solution
Additional Annotated Images
(d)Raw projection image (Video 27.2b, frame 6),99mTc sestamibi, deep mediastinal focus (green circle), right parotid gland (orange arrow), right submandibular gland (pink arrow), thyroid gland (blue box)
(e)Axial, coronal, sagittal SPECT images, deep mediastinal focus (yellow ovals)
(f)Axial, coronal, sagittal fused SPECT/CT images, deep mediastinal focus (yellow ovals)
The Pertinent Findings
Chest
Thyroid gland: ■ hot □ cold
Parathyroid glands: ■ hot □ cold
Breasts: □ hot ■ cold
Abdomen
Liver: ■ hot □ cold
The Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Thyroid gland: ■ normal
Parathyroid glands: ■ parathyroid adenoma, ectopic
Breasts: ■ normal
Abdomen
Liver: ■ normal
Discussion
Chest
On the images of the chest, the visualized salivary glands and thyroid gland are normal (a, d). There is subtle but definite focal radiopharmaceutical localization deep in the midline chest superior to the heart (a, d). The SPECT and SPECT/CT images (the latter created with fusion software) localize the focus to the middle mediastinum situated between the anterolateral aspect of the trachea and the great vessels (b, c, e, f). The final diagnosis is ectopic parathyroid adenoma deep in the mediastinum as cause of primary hyperparathyroidism.
Why is this case presented in a book on SPECT MPI? Because this condition can be discovered on SPECT MPI, and one should be aware of its presentation. As in this case, fusion can be performed with software if there is a previous chest CT or MRI. Also, in contradistinction to 27.1, this lesion is not related to the right atrium and should not be misinterpreted as a normal finding.
Note that the relatively photopenic (“cold”) normal breast tissue does not compromise the examination.
Abdomen
The liver is seen because imaging commenced shortly after radiopharmaceutical administration according to the parathyroid imaging protocol, and the99mTc sestamibi has not yet cleared through the normal physiologic mechanism (a, d).
Relevant Chapter(s)
Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 19
27.3 Case Challenge #3
27.3.1 Problem
Clinical Highlights
A 65-year-old female presents with acute worsening of chronic dyspnea.
Images for Review



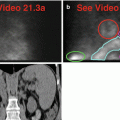
Fig. 27.3
(a)Rest raw projection images (Video 27.3a, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(b)Stress raw projection images (Video 27.3b, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(c)Stress/rest processed SPECT images (SA) (with and without AC)
(d)Stress/rest processed SPECT images (HLA) (with and without AC)
(e)Stress and rest gated SPECT images (Video 27.3c, frame 1) (SA, VLA, HLA)
Characterize the Pertinent Finding(s)
Chest
Chest wall: □ hot □ cold
Skeleton: □ hot □ cold
Pleura: □ hot □ cold
Lungs: □ hot □ cold
Mediastinum: □ hot □ cold
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ hot □ cold
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ hot □ cold
Peritoneum: □ hot □ cold
Liver: □ hot □ cold
Spleen: □ hot □ cold
Stomach: □ hot □ cold
Adrenal glands: □ hot □ cold
State Your Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Chest wall: □ normal □ malignant soft-tissue mass
Skeleton: □ normal □ metastases
Pleura: □ normal □ effusion
Lungs: □ normal □ hyperexpansion/diffuse process
Mediastinum: □ normal □ malignant mass
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ normal □ enlargement/hypertrophy
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ normal □ metallic artifact
Peritoneum: □ normal □ ascites
Liver: □ normal □ cystic mass
Spleen: □ normal □ enlargement
Stomach: □ normal □ duodenogastric reflux
Adrenal glands: □ normal □ malignant mass
27.3.2 Solution
Additional Annotated Images
(f)Rest raw projection image (Video 27.3d, frame 33),99mTc sestamibi, right ventricle (red box), left ventricle (pink box), stomach (green oval)
(g)Stress raw projection image (Video 27.3e, frame 35), ),99mTc sestamibi, right ventricle (red box), left ventricle (pink box), stomach (green oval)
(h)Stress/rest processed SPECT images (SA) (with and without AC), right ventricle (yellow ovals), septal wall (orange lines)
(i)Stress/rest processed SPECT images (HLA) (with and without AC), right ventricle (yellow ovals)
The Pertinent Findings
Chest
Lungs: ■ hot □ cold
Right atrium and right ventricle: ■ hot ■ cold
Abdomen
Stomach: ■ hot ■ cold
The Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Lungs: ■ hyperexpansion/diffuse process
Right atrium and right ventricle: ■ enlargement/hypertrophy
Abdomen
Stomach: ■ duodenogastric reflux
Discussion
Chest
The upper lungs are diffusely “hot,” while the lower lungs are more normal in their uptake pattern; the diaphragms are flattened indicating hyperexpanded lungs (a, b).
There is an extremely enlarged right ventricular cavity on the raw data (a, b, f, g) distorting the shape of the heart on the processed images (c, d, h, i). The right ventricular myocardium appears thickened and “hotter” than normal (a, b). Note the flattened septum evident on the raw data (a, b) as well as on the processed data (c, d, h, i). The left ventricle appears normal in size and has a normal perfusion pattern (c, d). The left ventricular function is normal with a normal ejection fraction of 53 %; note the enlarged right ventricle on gated SPECT images (e). The final diagnosis is a huge right ventricle related to pulmonary hypertension due to underlying chronic lung disease.
Abdomen
On rest raw images (a, f), the stomach is “hot” but clears with fluid, appearing “cold” on stress raw images (b, g). This is due to duodenogastric reflux, a common finding. The gastric activity does not impact on the interpretation of the reconstructed images (c, d).
Relevant Chapter(s)
Chapters 10, 13, and 22
27.4 Case Challenge #4
27.4.1 Problem
Clinical Highlights
A 55-year-old male, a longtime smoker, has a history of tuberculosis.
Images for Review



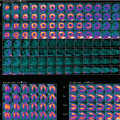
Fig. 27.4
(a)Rest raw projection images (Video 27.4a, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(b)Stress raw projection images (Video 27.4b, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(c)Stress/rest processed SPECT images (SA, VLA, HLA)
(d)Stress and rest gated SPECT images (Video 27.4c, frame 1) (SA, VLA, HLA)
Characterize the Pertinent Finding(s)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ hot □ cold
Breasts: □ hot □ cold
Pleura: □ hot □ cold
Lungs: □ hot □ cold
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ hot □ cold
Diaphragm: □ hot □ cold
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ hot □ cold
Peritoneum: □ hot □ cold
Liver: □ hot □ cold
Stomach: □ hot □ cold
Adrenal glands: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
State Your Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ normal □ benign tumor
Breasts: □ normal □ malignant primary tumor
Pleura: □ normal □ effusion
Lungs: □ normal □ hyperinflation and volume loss with mediastinal shift
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ normal □ enlargement
Diaphragm: □ normal □ flattening
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ normal □ belt buckle
Peritoneum: □ normal □ ascites
Liver: □ normal □ hepatomegaly with retention in left lobe
Stomach: □ normal □ duodenogastric reflux into fundus
Adrenal glands: □ normal □ benign tumor
Vascular system: □ normal □ contamination related to injection
27.4.2 Solution
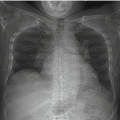
Additional Images
(e)AP chest radiograph
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree