Figure 15.1
Water bath positioning. To facilitate visualization of small parts, have the patient place the affected area in a container of water, and hover the probe over the area of interest
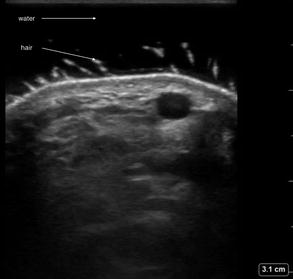
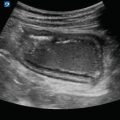
Figure 15.2
Water bath ultrasound. Dorsal hand ultrasound using a water bath showing separation of transducer from the tissue of interest
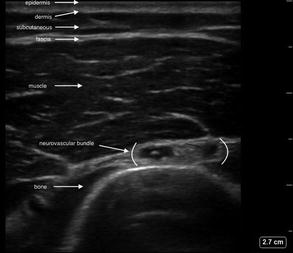
Figure 15.3
Soft tissue layers. Soft tissue layers identified from superficial to deep including epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis), fascia, muscle, bone
Skin and Soft Tissue Pathology
Cellulitis
Disruption of the skin with invasion of bacteria causing an infection of the dermis and subcutaneous fat.
Cellulitis can be identified by increased echogenicity and thickening of the subcutaneous tissue with hyperechoic areas of inflamed soft tissue outlined by hypoechoic fluid between these areas [1, 2]:
This is referred to as cobblestoning [1].
These findings are due to the accumulation of subcutaneous edema.
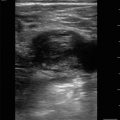
Figure 15.4—Cellulitis.
Video 15.2—Cellulitis.
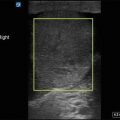
Figure 15.5—Cellulitis with increased soft tissue edema.
Video 15.3—Cellulitis with increased soft tissue edema.
Abscess
Walled off bacterial infection resulting in a collection of purulent fluid.
Will be identified as a hypoechoic fluid collection containing debris [1] with irregular borders and the absence of posterior enhancement:
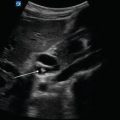
Figure 15.6—Abscess
Video 15.4—Abscess
Internal swirling of the fluid will typically occur with compression and can help distinguish fluid-filled collection from solid mass:
Video 15.5—Abscess with internal swirling from compression
There will be an absence of internal Doppler flow.
Air in the abscess cavity is significant for gas-forming organisms and will need emergent treatment:
This can be identified as echogenic areas within the abscess cavity [2] with dirty posterior shadowing and posterior reverberations.
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Severe infection that causes death of tissue and spreads rapidly along the fascial planes.
Early necrotizing fasciitis will often resemble cellulitis with a cobblestone appearance.
In advanced cases, the skin will be thickened and the fascia will appear thickened and brightly echogenic with adjacent accumulation of fluid [2–4]:
A fluid layer measuring greater than 4 mm deep to the fascia greatly increases the likelihood for the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis [2, 3].
Figure 15.7—Necrotizing fasciitis with perifascial fluid.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree