Reformat in sagittal plane to see aorta and SMA
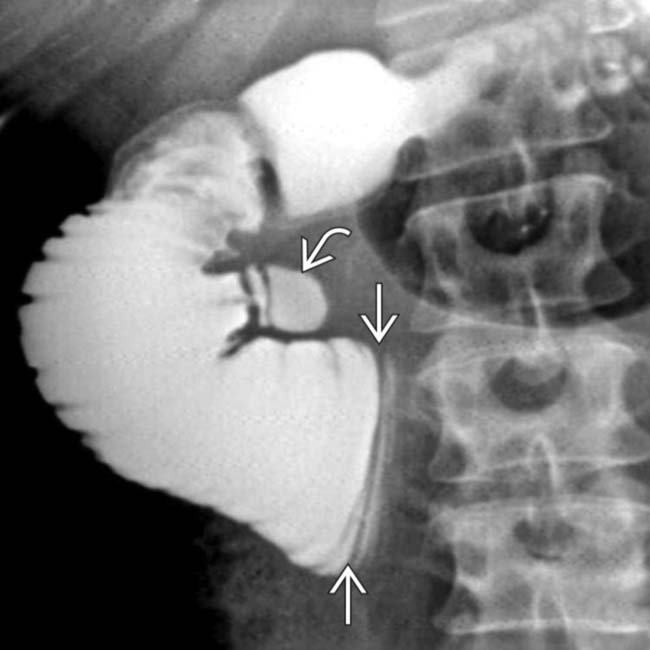
 of the 3rd portion of duodenum as it crosses over the midline, with dilation and slow emptying of the proximal duodenum. There is also a duodenal diverticulum
of the 3rd portion of duodenum as it crosses over the midline, with dilation and slow emptying of the proximal duodenum. There is also a duodenal diverticulum  .
.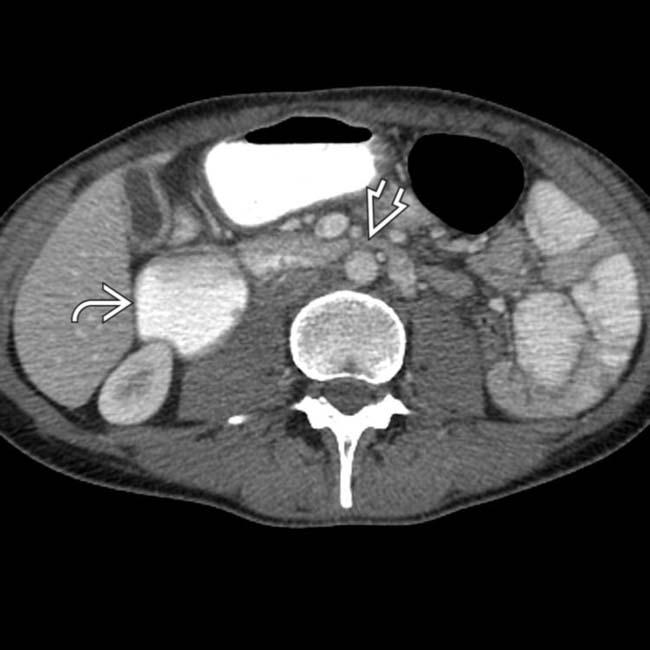
 and stomach. The 3rd portion of the duodenum
and stomach. The 3rd portion of the duodenum  is compressed as it passes between the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery (SMA).
is compressed as it passes between the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery (SMA).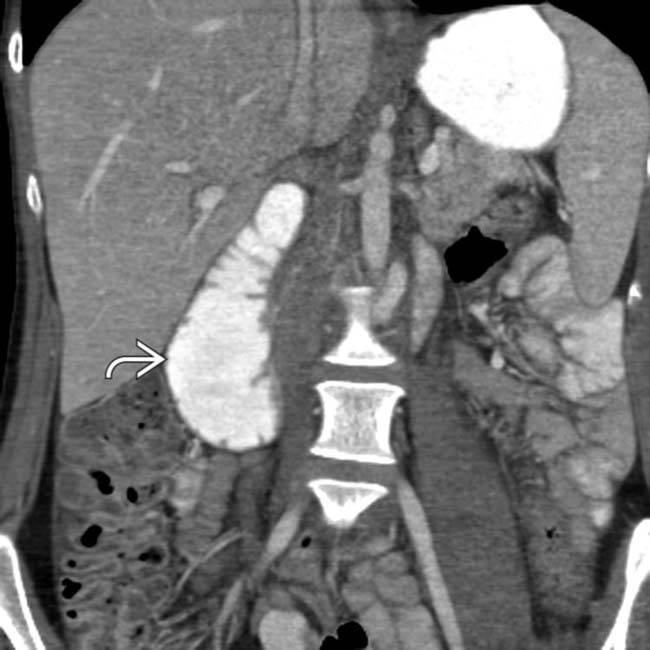
 , while the remaining bowel is collapsed. Note this patient’s thin body habitus.
, while the remaining bowel is collapsed. Note this patient’s thin body habitus.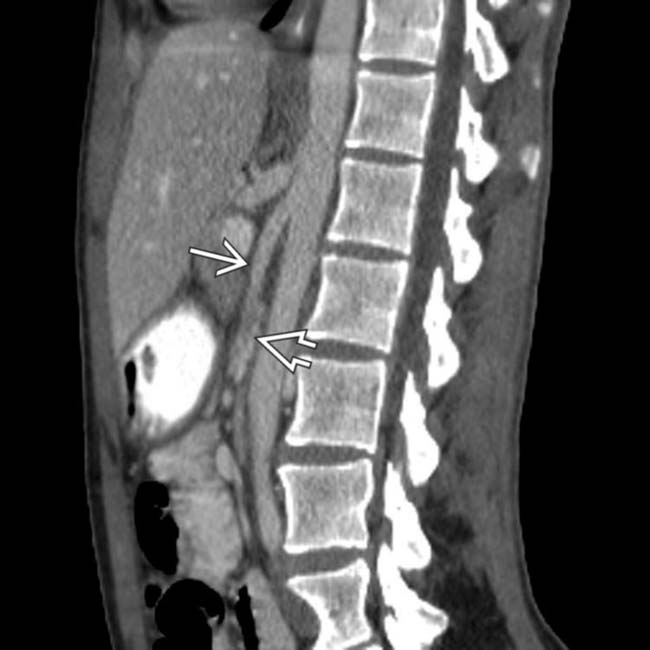
 and the aorta, with compression of the 3rd portion of duodenum
and the aorta, with compression of the 3rd portion of duodenum  as it passes between these vessels.
as it passes between these vessels.IMAGING
General Features
• Best diagnostic clue
 Dilated 1st and 2nd portions of duodenum with abrupt, straight-line transition to collapsed duodenum as it crosses spine
Dilated 1st and 2nd portions of duodenum with abrupt, straight-line transition to collapsed duodenum as it crosses spine




 Dilated 1st and 2nd portions of duodenum with abrupt, straight-line transition to collapsed duodenum as it crosses spine
Dilated 1st and 2nd portions of duodenum with abrupt, straight-line transition to collapsed duodenum as it crosses spineStay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






