101 Spatial Saturation
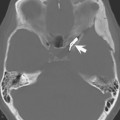
Spatial saturation is an important technique for the reduction of motion artifacts, specifically ghosting (displaced false images of a body region). In this approach, an additional radiofrequency (RF) pulse is applied at the beginning of a pulse sequence to eliminate the signal from unwanted tissue. Magnetization in the area of the designated slab does not have sufficient time to recover (prior to the actual imaging part of the pulse sequence) and thus does not contribute to the observed signal.
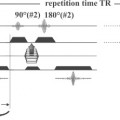
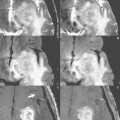
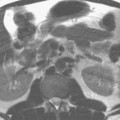
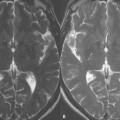
A presaturation pulse can be applied either within (Fig. 101.1) or parallel to (Fig. 101.2) the imaging plane. The only difference between the two images in Fig. 101.1 is that a presaturation pulse (graphically shown by the label) has been applied during the acquisition of Fig. 101.1B
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree