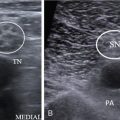
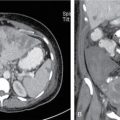
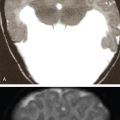
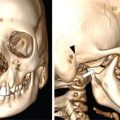
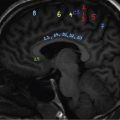
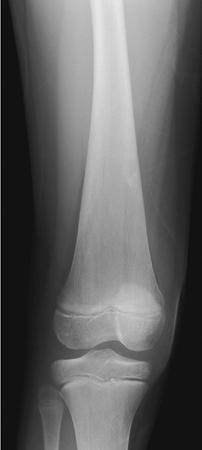
Sudha Kiran Das, Rudresh Hiremath Storage disorders are a heterogeneous group of inherited defects in metabolism characterized by accumulation of substrate within the cells, resulting in a wide spectrum of diseases that are classified based on the substrate accumulated and its clinical sequel. The commonly known diseases under this comprise Gaucher disease, lysosomal storage disorder, amyloidosis, glycogen storage disorders, mastocytosis. Gaucher disease is one of the most common lysosomal storage disorders caused by deficiency of enzyme beta-glucocerebrosidase resulting in accumulation of undegraded lipids like glucocerebroside within the macrophages of reticuloendothelial system. It is rare disorder with autosomal recessive inheritance having more than 300 mutations in glucocerebrosidase gene. Epidemiology: Disease is more commonly seen in Ashkenazi Jews with incidence of 1 in 500–1000, whereas in general population disease is quite rare with incidence of 1 in 50,000–100,000. No sex predilection. Depending on the severity, there is 70%–90% reduction in the enzyme activity of glucocerebrosidase resulting in accumulation of toxic glucocerebroside within the lysosomes. These lysosomes are in turn scavenged by the macrophages, resulting in increase in their size and morphological changes. Macrophages filled with unprocessed glucocerebroside are called as Gaucher cells which get accumulated in the reticuloendothelial system and affects organs like the bone marrow, spleen and liver resulting in downgrading of their function. Clinical Features: Clinically, Gaucher disease is classified into three types: Type 1: Known as nonneuropathic type with no central nervous system involvement. It is most common type of Gaucher disease seen predominantly in the second decade but can occur at any age. Patients present with symptoms of bone pain, pathological fractures, bone infarcts, osteonecrosis, hepatosplenomegaly and haematological disturbances. Patients with Gaucher disease will have haematological abnormalities like anaemia and thrombocytopenia with resultant clinical features of fatigue, easy bruising and nosebleeds. Type 2: It is referred as acute neuropathic type and disease becomes evident by 6 months of life with progressive neurological deterioration. Death ensues by 1–2 years of life. Patients will have significant hepatosplenomegaly, seizures, mental retardation, strabismus and spasticity. Type 3: This type is called as subacute neuropathic type with mild symptoms. Age of onset is 2–6 years and presents with variable hepatosplenomegaly and seizures. Lysosomal storage diseases are a group storage disorders comprising of nearly 51 genetically identified disorders and a small subset of acquired disorders, the latter because of inhibition of a-mannosidase II either drug induced or due to ingestion of certain plant materials. Owing to different mutations of the same gene, there is marked clinical heterogeneity, and they are further classified as infantile and adult type. Deficient activity of the lysosomal enzymes either due to altered property or absence is caused by genetic mutations, leading to substrate accumulation in different cell types and tissues that is one of the major causative pathways. Nonenzymatic mutations can also result in storage of substrates. Normally, most lysosomal hydrolases are present in sufficiently high amount that their respective substrate does not accumulate. Accumulation of undegraded substrate occurs only when the residual enzyme activity is less than the critical threshold of 10%–15% of the normal enzyme activity. Usually, the residual enzyme activity results in juvenile or adult onset of the disease, and absence of enzyme activity is manifested as severe infantile onset. The prevalence of these individual disorders ranges from 1 in 57,000 for Gaucher disease to 1 in 4.2 million for sialidosis. As a group of disorders, the prevalence is 1 per 7700 live births. Most lysosomal storage diseases affect different cell types, tissues and organs. The brain lesions are particularly prevalent, which comprises two-thirds of all lysosomal diseases. Constellation of disorders grouped under LSD can be classified as detailed in Table 2.6.1. MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS MPS-I Hurler, Scheie syndrome α-l-iduronidase Dermatan sulphate, Heparan sulphate CNS, Connective tissue, heart, skeleton, cornea MPS-II hunter syndrome Iduronate sulfatase Dermatan sulphate, heparan sulphate MPS-III sanfilippo syndrome Subtype A Subtype B Subtype C Subtype D Sulfaminidase α-N-Acetylglucosaminidase Acetyl Co A aglucosaminide acetyltransferase N-acetylglucosamine 6-sulfatase Heparan sulphate CNS MPS-IV Morquio syndrome Type A Type B Galactose 6-sulfatase β-Galactosidase Chondroitin-4 sulphate, keratan sulphate Keratan sulphate Cartilage, skeleton, cornea, heart Cartilage, bone, cornea MPS-VI Maroteaux–Lamy syndrome Arylsulfatase β-Nacetylgalactosamine 4-sulfatase Dermatan sulphate Skeleton, cornea, heart MPS-VII sly syndrome β-Glucuronidase Dermatan sulphate, heparan sulfate, chondroitin 4-8-sulphate CNS, connective tissue, skeleton, heart MPS-IX hyaluronidase deficiency Hyaluronidase Hyaluronan Periarticular soft tissue Sphingolipidoses (LIPID STORAGE DISEASES) Glucocerebrosidosis (Gaucher disease) Infantile type 2 Juvenile type 3 Adult type 1 β-Glucocerebrosidase Glucosylceramide CNS, spleen, liver, bone marrow Spleen, liver, bone marrow Fabry disease α-Galactosidase Trihexosylceramide Blood vessels of skin, kidney and brain Schindler disease (type I) α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase Sialylated and asialopeptides and oligosaccharides CNS, PNS Metachromatic leukodystrophy Late infantile form Late onset form Multiple sulfatase deficiency Arylsulfatase A Arylsulfatase A At least 7 lysosomal sulfatases and a microsomal sulfatase Galactosylsulfatide CNS, liver, kidney, gallbladder CNS, visceral organs and skeleton Niemann–Pick disease Type A Type B Type C (NPC-1 and NPC-2) Sphingomyelinase Proteins required for lipid transport through late endosome Sphingomyelin Unesterified cholesterol and spingolipids CNS, liver, spleen, bone marrow CNS, liver, spleen GM1-gangliosidosis β-galactosidase GM1-ganglioside, oligosaccharides, keratan sulphate CNS, skeleton, viscera GM2-gangliosidosis Tay–Sachs disease, A variant Sandhoff disease AB variant Galactosialidosis Globoid cell leukodystrophy (Krabbe disease) β-hexosaminidase A β-hexosaminidases A and B Deficiency of GM2 – activator protein Protective protein/cathepsin A, resulting in deficiency of bgalactosidase and aneuraminidase Galactosylcerebroside, β galactosidase GM2-ganglioside GM2-ganglioside, oligosaccharides GM2-ganglioside Glycolipids and oligosaccharides Galactosylsphingosine CNS CNS CNS CNS, spleen, liver, skeleton CNS Farber granulomatosis Ceramidase Ceramide Subcutaneous nodules, joints, larynx, liver, lung, heart Wolman disease Acid lipase/cholesterol esterase Triglycerides, cholesteryl esters Liver, spleen, adrenal DISORDERS OF GLYCOPROTEIN DEGRADATION Aspartylglucosaminuria Aspartylglucosaminidase Fragments of glycoprotein, aspartyl-2-deoxyl-2- acetamide glycosylamine, N-linked oligosaccharides CNS, connective tissue, bone marrow a-Mannosidosis α-Mannosidase N-linked oligosaccharides CNS, skeleton, liver, spleen b-Mannosidosis β-mannosidase N-linked oligosaccharides CNS, skeleton, liver, spleen Fucosidosis α-fucosidase Oligosaccharides and glycolipids CNS, spleen, liver Sialidosis (mucolipidosis I) Neuraminidase Fragments of glycoprotein CNS, spleen, liver, skeleton NEURONAL CEROID LIPOFUSCINOSIS (NCL) Infantile NCL (CLN-1) Palmitoyl protein thioesterase Protein, saposins A and D CNS, heart, endothelial cells, retina Congenital NCL (CLN-10) Cathepsin D (CTSD) Protein CNS, liver Classic late infantile NCL (CLN-2) Pepstatin-sensitive protease, tripeptydylpeptidase Mitochondrial subunit C of ATPase synthase CNS, retina Late infantile (Indian variant) NCL (CLN-6) Endoplasmic reticulum transmembrane protein CNS, heart, endothelial cells Late infantile (Turkish variant) NCL (CLN-7) Protein CNS Late infantile (Finnish variant) NCL (CLN-5) Transmembrane protein CNS, heart, endothelial cells Juvenile NCL (CLN-3) (Battenin) lysosomal transmembrane protein CNS, heart, endothelial cells, retina Adult NCL (CLN-4) Unknown CNS, heart, endothelial cells Progressive epilepsy with mental retardation, Northern epilepsy (CLN-8) Transmembrane protein CNS Juvenile variant (CLN-9) Unknown CNS GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE Pompe disease, type IIEarly and late onset a-Glucosidase (acid maltase) Glycogen CNS, muscle, heart DISORDERS OF PROTEIN DEGRADATION Pycnodysostosin Cathepsin K Collagen Osteochondrodysplasia Experimental dilated cardiomyopathy Cathepsin L Sarcomeric protein Heart Papillon–Lefeʹvre syndrome Cathepsin C Proteins Periodontal disease and palmoplantar keratosis Neuronal loss and brain atrophy Cathepsins B and L Proteins CNS ABNORMAL LYSOSOMAL MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Mucolipidosis-II (I-cell disease) N-acetylglucosaminylphosphotransferase resulting in multiple enzyme deficiencies Mucopolysaccharides, lipids, glycoproteins CNS, connective tissue, skeleton, heart, kidney Mucolipidosis-III (pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy) Joint and connective tissue predominantly Mucolipidosis-IV TRPML-1 Lipids CNS, connective tissue Danon disease Deficiency of LAMP-2 Glycogen CNS, muscle, heart Infantile osteopetrosis and neurona OSTM1 Chloride Channel 7 Glycoproteins and glycolipids CNS, skeleton DISORDERS OF LYSOSOMAL EFFLUX Cystinosis Cysteine efflux mediator Cysteine Kidney Salla disease Sialic acid efflux mediator Free sialic acid CNS Infantile dialiuria CNS, kidney, liver OTHERS Acid phosphatases Acid phosphatases CNS, skeleton
2.6: Storage and infiltrative disorders
Gaucher disease
Pathology
Radiological features
Lysosomal storage disorders
Pathology
Epidemiology and classification
Disease
Deficient Enzyme
Storage Products
Organs Involved
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine