Figure 1.5 illustrates the forces experienced by a proton being brought toward a nucleus; initially, an electrostatic (Coulomb) force of repulsion between the incoming proton and protons in the nucleus is present, which increases in magnitude (becoming more positive) as the incoming proton is brought closer, according to
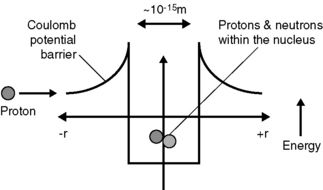
Figure 1.5 Illustration of the electrostatic (Coulomb) and strong force experienced by a charged particle approaching a nucleus. Once within range of the attractive strong force, the repulsive Coulomb force is overcome to hold nucleons together in the nucleus (the binding property of the strong force is represented as negative energy).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree