(1)
Cleveland Clinic, Emeritus Staff, Cleveland, OH, USA
Keywords
Absorbed doseTumor uptake 82Sr–82Rb generatorEstimated Absorbed Dose from Intravenous Administration of 18F-FDG and 82Rb-RbCl in Humans
The dose estimate D in a human organ is made by using the following internal dosimetry equation (Saha 2013):
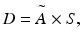
where à is the cumulated activity and S is the mean absorbed dose per cumulated activity. à is calculated from the initial administered activity and the biodistribution and residence time of the tracer in each organ and has the unit of μCi · h or MBq · h. S is calculated from the knowledge of physical characteristics of the radiation in question, the mass of the organ, and the absorption fraction of the radiation in the target organ and has the unit of rad/μCi · h or mGy/MBq · h. The values of S are available in literature for most common radiopharmaceuticals including 18F-FDG and 18Rb-RbCl. The experimental data for biodistribution and residence time are available in literature and used to calculate Ã. The following two tables give the absorbed doses per administered activity based on these calculations for 18F-FDG and 82Rb-RbCl, respectively (Tables 14.1 and 14.2).
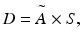
(14.1)
Table 14.1
Absorbed dose per unit administered activity of 18F-FDGa
Target organ | mGy/MBq | rad/mCi |
|---|---|---|
Brain | 0.046 ± 0.012 | 0.17 ± 0.044 |
Heart wall | 0.068 ± 0.036 | 0.25 ± 0.13 |
Kidneys | 0.021 ± 0.0059 | 0.078 ± 0.022 |
Liver | 0.024 ± 0.0085 | 0.088 ± 0.031 |
Lungs | 0.015 ± 0.0084 | 0.056 ± 0.031 |
Pancreas | 0.014 ± 0.0016 | 0.052 ± 0.0060 |
Red marrow | 0.011 ± 0.0017 | 0.040 ± 0.0062 |
Spleen | 0.015 ± 0.0021 | 0.056 ± 0.0078 |
Urinary bladder wallb | 0.073 ± 0.042 | 0.27 ± 0.16 |
Ovariesc | 0.011 ± 0.0015 | 0.041 ± 0.0055 |
Testesc | 0.011 ± 0.0016 | 0.041 ± 0.0057 |
Whole bodyd | 0.012 ± 0.00077 | 0.043 ± 0.0023 |
Effective dosed,e | 0.0190 | 0.070 |
Table 14.2
Absorbed dose per unit administered activity of 82Rb-RbCl
Adult absorbed radiation dosesa | ||
|---|---|---|
Organ | mGy/2220 MBq | rads/60 mCi |
Adrenals | 2.15 | 0.22 |
Stomach | 1.91 | 0.19 |
Small intestine | 3.11 | 0.32 |
Upper large intestine | 1.91 | 0.19 |
Lower large intestine | 1.91 | 0.19 |
Heart wall | 4.22 | 0.42 |
Kidneys | 19.1 | 1.92 |
Liver | 1.91 | 0.19 |
Lungs | 3.77 | 0.38 |
Ovaries | 0.84 | 0.084
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|