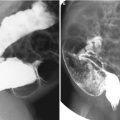
Fig. 25.1
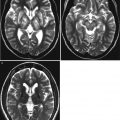
Acute pyelonephritis. Sagittal US of the right kidney (a) shows only mild pelvic dilatation. Sagittal US of the left kidney (b) shows diffuse swelling with increased cortical echoes and pelvic wall thickening. DMSA scan (c) demonstrates multiple photopenic areas in the left kidney. Contrast-enhanced CT (d) shows an enlarged left kidney with multiple, poorly enhanced regions. Voiding cystourethrography (e) demonstrates left-sided grade 5 VUR
25.4.2 Chronic Pyelonephritis
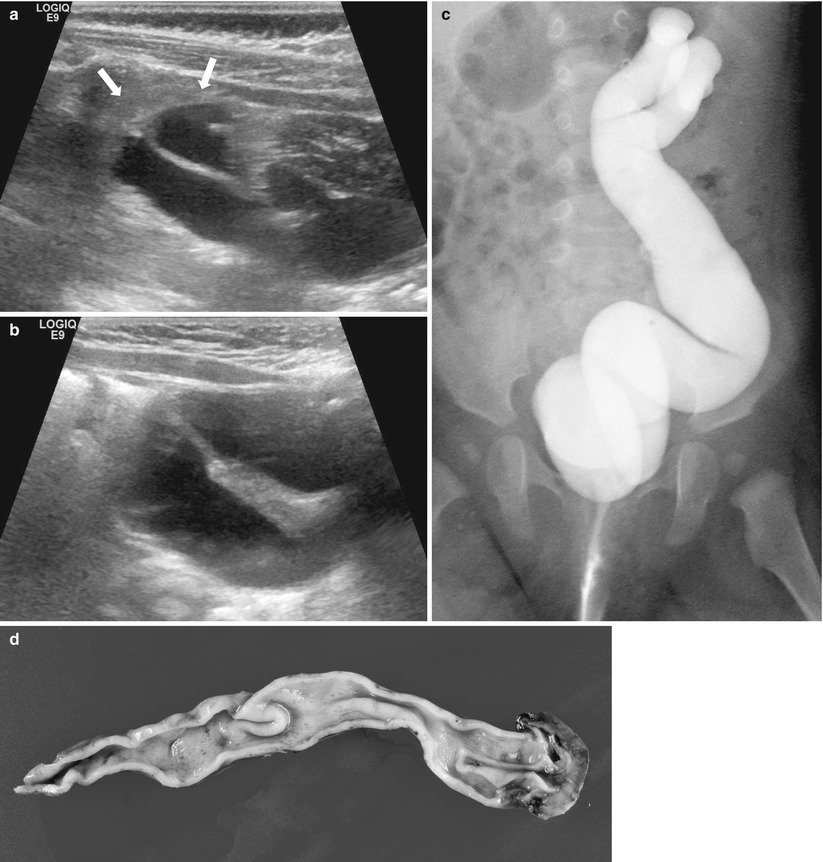
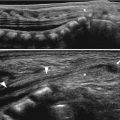
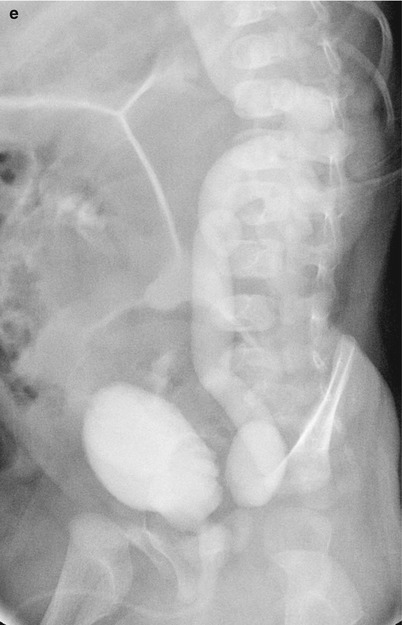
Fig. 25.2
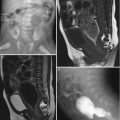
Chronic pyelonephritis (reflux nephropathy). Sagittal US of the left kidney shows small-sized kidney (arrows) with diffusely increased parenchymal echoes and poor corticomedullary differentiation and hydronephrosis (a) and ureter dilatation (b). Voiding cystourethrography (c) shows left-sided grade 5 VUR with megaureter. Gross specimen (d) shows a shrunken kidney without corticomedullary distinction, dilated ureter, and bifid renal pelvis
25.4.3 Renal Abscess
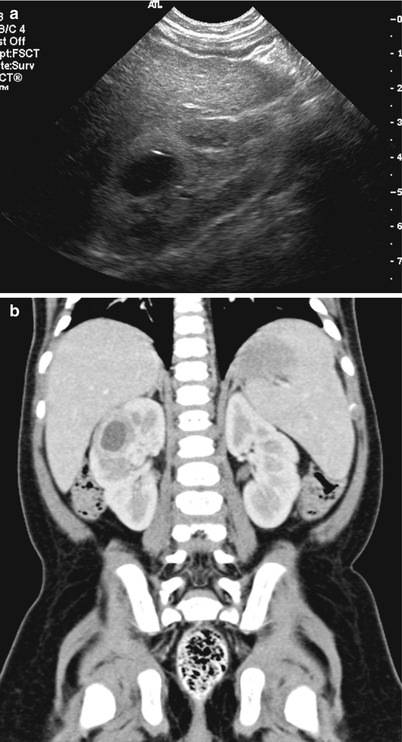
Fig. 25.3
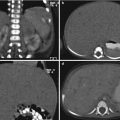
Renal abscess. Sagittal US of the right kidney (a) shows round hypoechoic abscess surrounded by hyperechoic, inflammatory parenchyma. Corresponding contrast-enhanced CT (b) demonstrates the abscess formation with wall enhancement
25.4.4 Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis
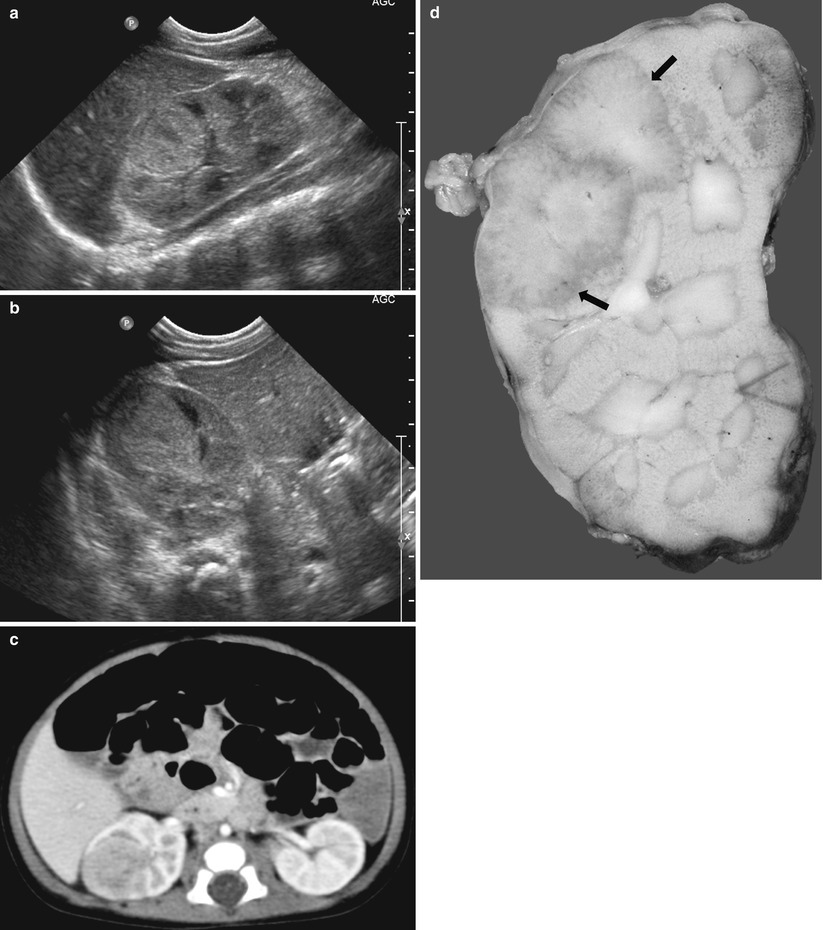
Fig. 25.4




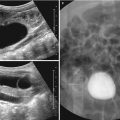
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. Sagittal (a) and transverse (b) US of the right kidney show round, hyperechoic mass-like lesion containing hypoechoic portions. Contrast-enhanced CT (c) shows poorly enhancing mass-like lesion in the right kidney. Gross specimen (d) shows a relatively well-demarcated, mass-like lesion (arrows) with scattered yellowish tint in the upper and mid portion of the kidney
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree