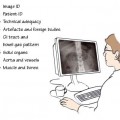
29.1 US referral checklist

US referral checklist (see Chapter 7)
The referrer carries the responsibility to ensure the correct and complete information is conveyed to the Imaging Department so that the patient is appropriately diagnosed and managed.
- Patient identification: The referrer must ensure that the Imaging Department receives the correct identification details of the patient to be investigated: full name, date of birth and hospital identification number are the essentials.
- Clinical status: The referrer must convey the patient’s clinical condition and urgency of the referral to the Imaging Department.
- Patient mobility: Optimal images are obtained in slim patients using a sophisticated multifunctional departmental US machine. However, in some cases patients are too unwell to travel to the US department and thus US can be performed with a portable machine. US investigations using older portable machines are more limited in their imaging capacity and therefore may provide less detailed information compared with newer portable or departmental machines. The referrer must always consider the patient’s clinical condition and refer for a departmental US study investigation if possible.
- Patient location and travel details: The need for a clinical escort should be conveyed. The points of departure and return, and contact details must also be notified to the Imaging Department to ensure the patient is transferred safely and efficiently.
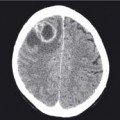
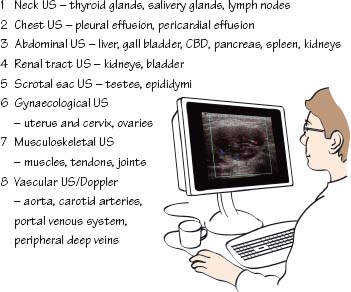
- Indications: US often reveals a wide range of chest and abdominal pathology as well as subcutaneous, musculoskeletal and vascular pathology. US is also commonly used for interventional radiology procedures, e.g. biopsy and drainage of fluid collections. The referral indication should always include a salient history and a specific question to be answered by US.
- Contraindications:

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree