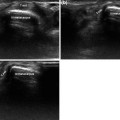
Fig. 6.1
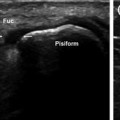
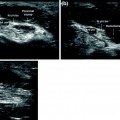
Radial nerve. The radial nerve (empty arrow) runs deep in the forearm in close proximity to the radius a schematic diagram, b sonographic scan along the short axis of the nerve: distally, the course of the nerve becomes more superficial and crosses over the myotendinous junctions of the long abductor and short extensor of the thumb before dividing into terminal cutaneous branches (c–e)
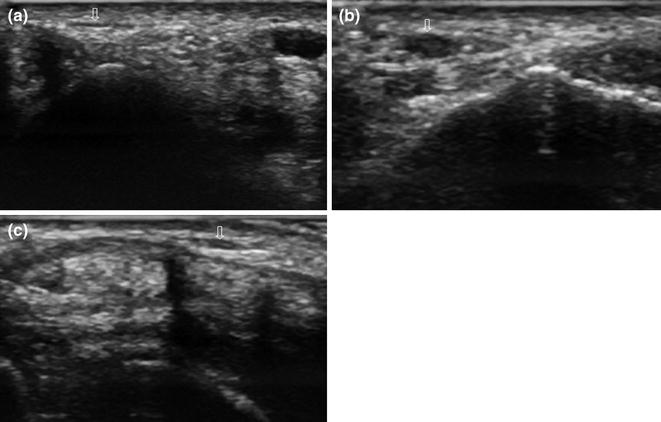
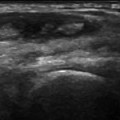
Fig. 6.2
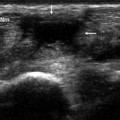
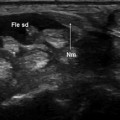
Wartenberg’s syndrome. In the proximal portion of the wrist, the radial nerve (empty arrow) presents a normal fascicular appearance. Moving distally, this fascicular aspect is lost, and the nerve appears enlarged and hypoechoic (Wartenberg’s syndrome). The normal appearance is then restored in the more distal portion
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree