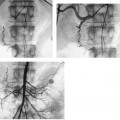
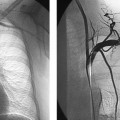
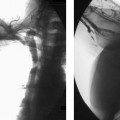
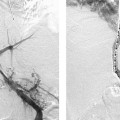
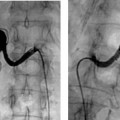
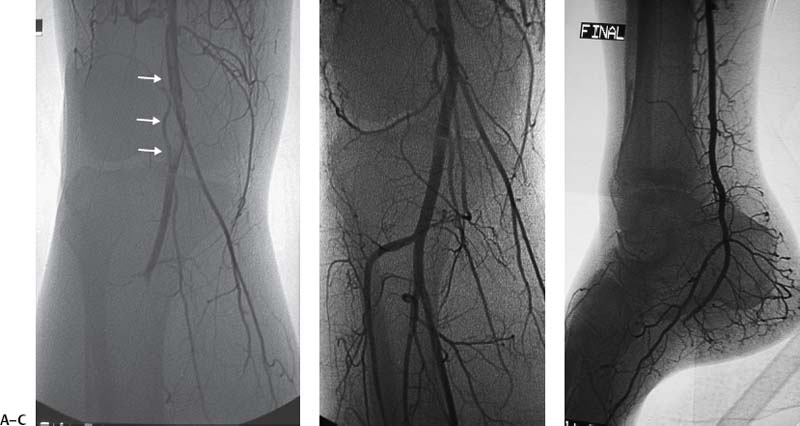
CASE 10 A 58-year-old male with a hypercoagulable disorder discontinued his Coumadin (Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, New Jersey) therapy 7 days prior to developing acute right lower leg and foot pain. He presented to the emergency room with a cold, painful, pulseless right foot. Both motor and sensory function were intact. Doppler exam did not reveal audible pulse signals. Figure 10-1 Arterial thrombolysis. (A) Initial angiogram shows abrupt occlusion of infratibial arteries and long thrombus in popliteal artery (arrows). (B, C) Final angiograms after thrombolysis show complete resolution of clot and straight line flow into the foot. The left common femoral artery was punctured using the Seldinger technique and a pigtail catheter was advanced into the abdominal aorta. A pelvic arteriogram revealed no abnormalities. The pigtail catheter was used to catheterize the contralateral common iliac artery, and the catheter was then exchanged for a 6-French (F) Balkan sheath (Cook, Bloomington, Indiana) over the guidewire. A 5F Multipurpose angled (MPA) catheter was then advanced into the common femoral artery, and angiography was performed, revealing acute thrombus in the distal superficial femoral artery (Fig. 10-1A) and complete occlusion of the arteries distal to the thrombus. Acute arterial thrombosis due to uncorrected hypercoagulability. The left common femoral artery had already been catheterized for arteriography. The contralateral common iliac artery was catheterized over the aortic bifurcation and an endhole catheter was advanced down the superficial femoral artery. A guidewire was used to gently probe the thrombus. The guidewire advanced easily through the occlusion. The endhole catheter was then exchanged for a multiside-hole infusion catheter. The multiside-hole infusion catheter was positioned with most of the side-holes in the clot and a few side-holes proximal to the thrombus. Tissue plasminogen activator (TPA, alteplase, Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, California) was infused at a rate of 0.5 mg per hour overnight. Heparin was infused at a rate of 100 units per hour through the femoral artery sheath. Follow-up arteriography showed complete thrombolysis with rapid antegrade flow to the foot (Figs. 10-1B, C). The patient had strong pulses, and the foot was warm.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Studies
Arteriogram
Diagnosis
Treatment
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree