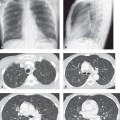
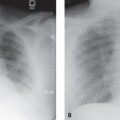
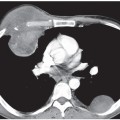
CASE 121 34-year-old woman with dyspnea PA chest radiograph (Fig. 121.1) demonstrates increased lung volumes without other radiographic abnormality or evidence of interstitial lung disease. HRCT (Figs. 121.2, 121.3) reveals profuse, uniform, bilateral, small thin-walled cysts affecting both lungs. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis • Pulmonary Langerhans’ Cell Histiocytosis (PLCH) • Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia • Emphysema Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare idiopathic disease that affects women of childbearing age and is characterized by abnormal proliferation of smooth muscle cells (LAM cells) along lymphatics in the chest and abdomen but also along vessels and bronchi in the lung. Lymphatic involvement can lead to chylous pleural effusions and/or ascites. Fig. 121.1 Fig. 121.2 Fig. 121.3 Unknown
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
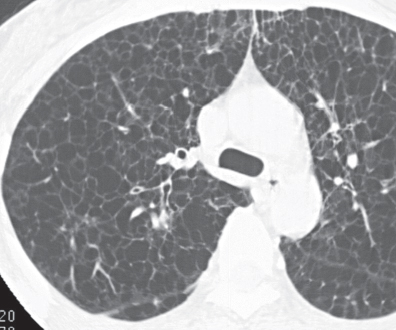
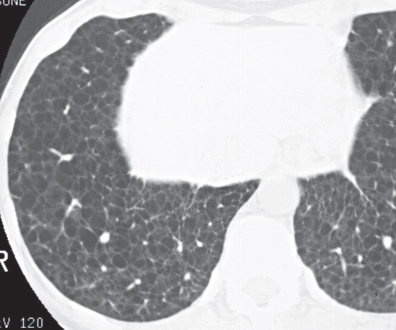
Etiology
Clinical Findings
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine