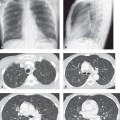
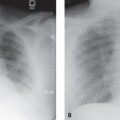
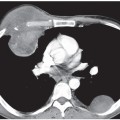
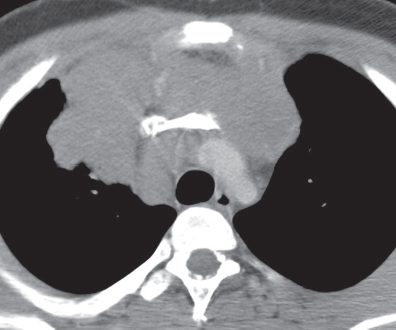
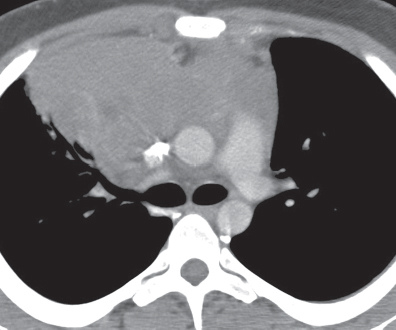
CASE 159 26-year-old man with chest discomfort PA (Fig. 159.1) and lateral (Fig. 159.2) chest radiographs demonstrate a large lobular anterior mediastinal mass that extends to both sides of midline, but predominantly to the right. Contrast-enhanced chest CT (mediastinal window) (Figs. 159.3, 159.4) reveals a large mediastinal soft-tissue mass of irregular lobular borders, which occupies the anterior mediastinum; encases the left brachiocephalic vein, superior vena cava, and ascending aorta; partially encases the right upper lobe bronchus; and produces an irregular margin with the adjacent right upper lobe. Note associated right paratracheal lymphadenopathy (Fig. 159.3). Hodgkin Lymphoma • Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma • Metastatic Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy; Lung Cancer, Extrathoracic Malignancy • Thymoma, Invasive • Thymic Malignancy Fig. 159.1 Fig. 159.2 Fig. 159.3 Fig. 159.4 The lymphomas are a heterogeneous group of malignant neoplasms of the cells of the immune system characterized by proliferation and enlargement of lymph nodes and secondary lymphoid tissues. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is the most frequent lymphoma and accounts for approximately 75% of cases, while Hodgkin lymphoma accounts for approximately 25% of lymphomas. However, mediastinal involvement by lymphoma is much more common in patients Hodgkin lymphoma than in those with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The most common cell type of mediastinal Hodgkin lymphoma is nodular sclerosis. The most common mediastinal non-Hodgkin lymphoma is diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (which, together with follicular lymphoma, accounts for over 50% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas), although lymphoblastic lymphoma and adult T-cell lymphoma characteristically manifest as large mediastinal masses. The latest WHO classification of lymphoma is complex and consists of over 20 subtypes based on cell of origin (B or T cell), morphologic features, and immunophenotypic characteristics. The etiology of lymphoma is unknown. The increasing incidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma has been in part attributed to the growing elderly population and the HIV epidemic. Various forms of immunosuppression have been linked to extranodal lymphoma.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis

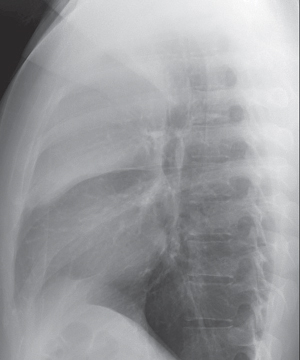
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Clinical Findings
Hodgkin Lymphoma
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine