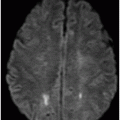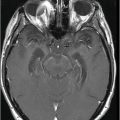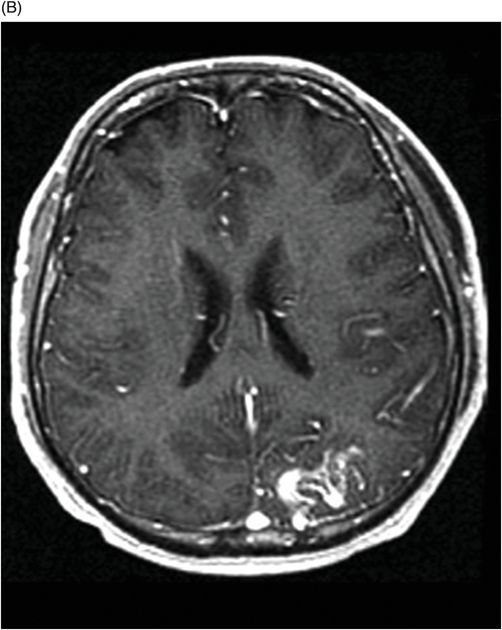
(A) Axial T2WI and (B) Axial enhanced T1WI (two-year follow-up) through the level of the lateral ventricles.

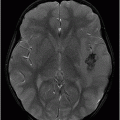
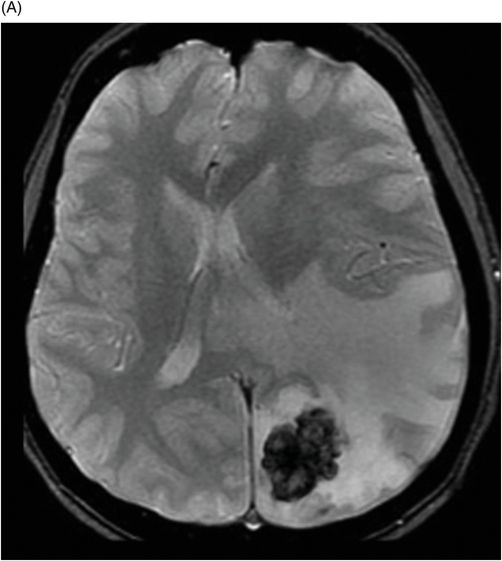
(A) Axial T2* (MPGR), and (B) Axial T1WI postgadolinium images (six-year follow-up) through the level of the lateral ventricles.

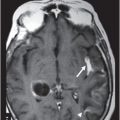
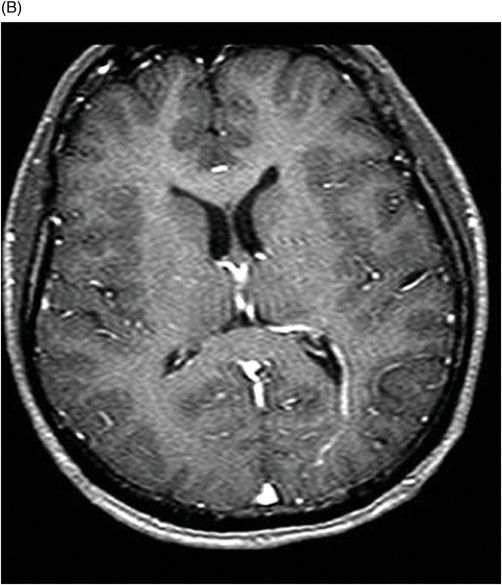
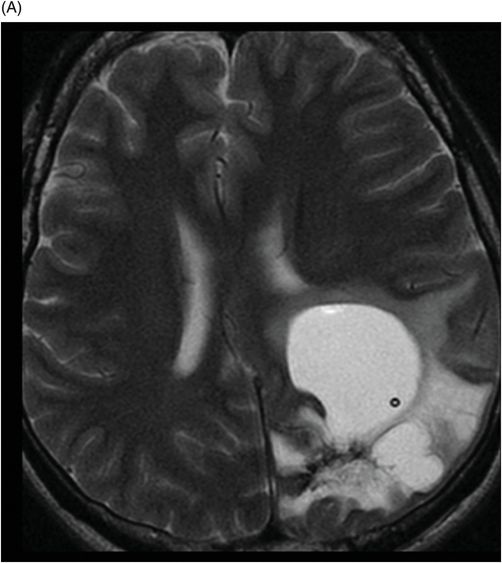
(A) Axial T2WI and (B) Axial T1WI postgadolinium images (eight-year follow-up) through the level of the lateral ventricles and the centrum semiovale.
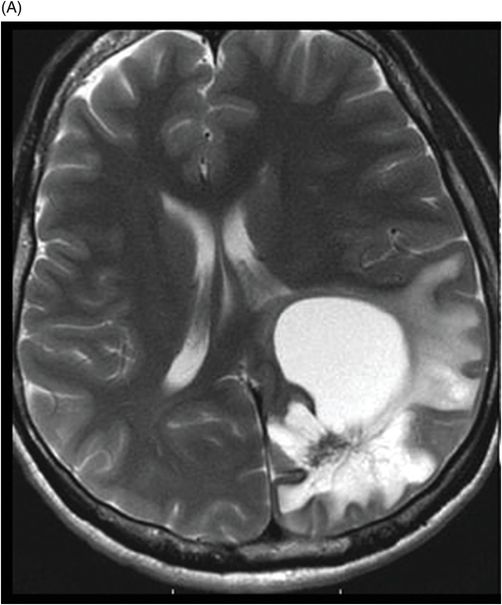

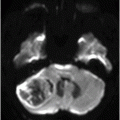
(A) Axial T2WI and (B) Axial T1WI postgadolinium images (14-year follow-up) post-aspiration through the level of the lateral ventricles.

Radiation-Induced Tumefactive Cyst
Primary Diagnosis
Radiation-induced tumefactive cyst
Differential Diagnoses
Radiation necrosis
Radiation-induced tumor (glioma)
Glioblastoma
Gliosarcoma
Imaging Findings
Fig. 32.1: (A–B): Axial T2WI and axial enhanced T1WI showed an arteriovenous malformation (AVM) in the left occipital region. Fig. 32.2: (A–B): Axial T2WI and axial enhanced T1WI (performed two years after radiotherapy) showed a decrease in the AVM nidus size. Fig. 32.3: (A–B) Axial T2* (MPGR) and axial T1WI postgadolinium and post-subtraction images (performed six years after radiotherapy) showed a heterogeneous lesion in the left occipital lobe, with hypersignal on SWI and a fluid level compatible with hematoma. Fig. 32.4: (A–B): Axial T2WI and axial T1WI postgadolinium (performed eight years after radiotherapy) showed a large cyst with mass effect, surrounded by vasogenic edema adjacent to the nodular area of enhancement. Fig. 32.5: (A–B): Axial T2WI and axial T1WI obtained after cyst aspiration shows reduction in cyst size.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree