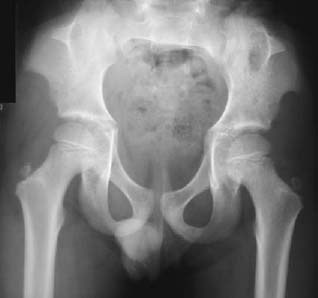
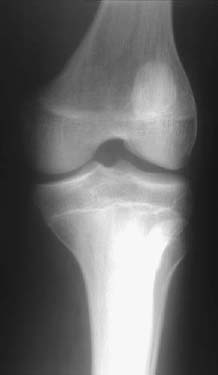
CASE 33 Hema N. Choudur, Anthony G. Ryan, Peter L. Munk A family practitioner incidentally noted the absence of fingernails in a female patient. This raised suspicions of possible nail-patella syndrome, and the patient was investigated further. On clinical examination, her knees were noted to have a squared appearance but no other discernible skeletal abnormality. Figure 33A Figure 33B The plain radiographs of the pelvis (Fig. 33A) reveal pathognomonic iliac horns bilaterally. Hypoplastic patellae were noted in the knee radiographs (Fig. 33B). Nail-patella (Fong’s) syndrome (NPS). None. Iliac horns are pathognomonic. NPS (Fong’s disease or hereditary osteo-onychodysplasia (HOOD) iliac horn syndrome, Turner-Kieser syndrome) is characterized by typical skeletal abnormalities with frequently coexisting glaucoma and kidney disease. NPS has been recognized as a hereditary condition, with an autosomal dominant inheritance in the ABO blood group. The risk of transmission is 50% per pregnancy, irrespective of gender, females being affected ~10% more often than males. About 20% of cases are sporadic, as a result of a new mutation. The incidence is ~1 in 50,000, and the condition occurs in all ethnic groups. The gene for NPS, recently discovered and named LMX1B, is located on chromosome 9q34. The pathophysiology underlying NPS is not yet known, but it is clear that the musculoskeletal abnormalities arise from a disorder of collagen synthesis, assembly, or degradation. Deformity of the nails is the most noticeable abnormality. The nails are either absent or underdeveloped, especially those of the thumbs, or may be brittle, cracked, concave, or ridged. Often, the lunalae (which are the light parts of the nail near the cuticle) are pointed instead of the usual rounded shape. Abnormality of the nails is seen in 80 to 90% of patients with NPS. The skin may be wrinkled and loose, although there are often no creases over the distal joints of the fingers, resulting in decreased mobility.
Fong’s Disease/Nail Patella Syndrome
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Clinical Findings
NAILS
SKIN
KNEES
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


