10.1055/b-0039-166443
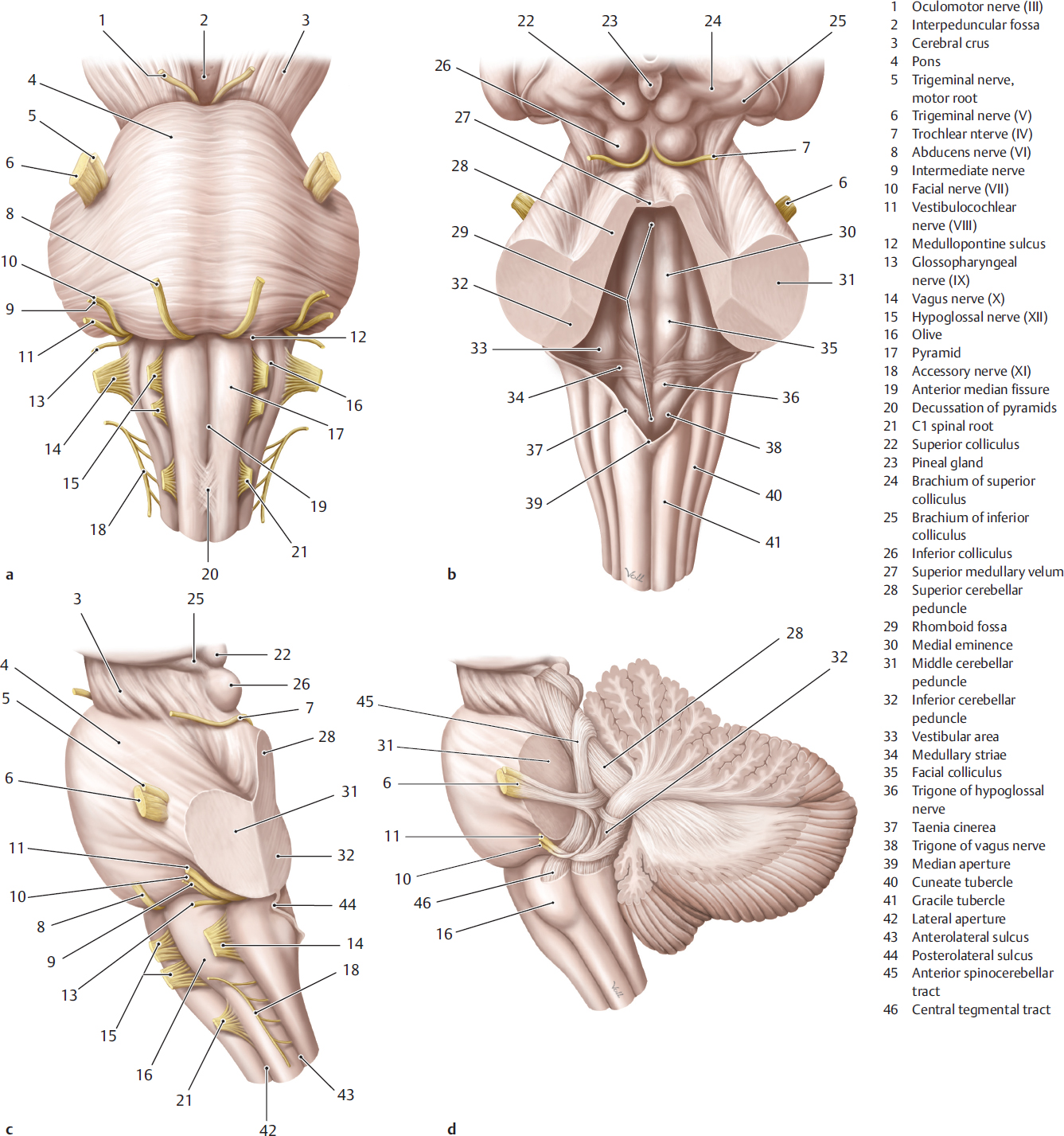
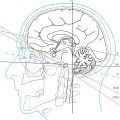
Fig. 6.1 Brainstem views of external appearance and depiction of cerebellar tracts. (Reproduced from Schuenke, Schulte, and Schumacher, Atlas of Anatomy, 2nd and 3rd editions. ©2009, 2012, Thieme Publishers, Stuttgart. Illustration by Karl Wesker/Markus Voll.) Fig. 6.1a Anterior view. Fig. 6.1b Posterior view. Fig. 6.1c View from the left. Fig. 6.1d View from the left with cerebellum. 
Fig. 6.2 Arrangement of cranial nerve nuclei in the brainstem. (Reproduced from Schuenke, Schulte, and Schumacher, Atlas of Anatomy, 3rd edition, ©2012, Thieme Publishers, Stuttgart. Illustration by Karl Wesker/Markus Voll.) Fig. 6.2a Posterior view with cerebellum removed and view of the rhomboid fossa. Depiction of nuclei of origin to the left of midline with emerging efferent or motor fibers (red = somatic efferent or somatic motor nuclei; light blue = parasympathetic nuclei; dark blue = nuclei of branchial nerves). Nuclei of termination are depicted to the right of the midline (dark green = general viscero-afferent fibers, light green = special viscero-afferent fibers, yellow = somato-afferent or somatosensory nuclei). Fig. 6.2b Lateral view. Afferent and efferent tracts have been illustrated in addition to nuclei. 
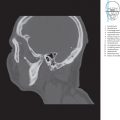
Fig. 6.3 Brainstem sections. Illustration based on a cephalogram and an MR image (see Chapter 12 for specimens). The 5-mm-thick slices of the brainstem series have been sectioned perpendicular to the Meynert axis, assembled and displayed. The Meynert axis runs tangentially through the floor of the rhomboid fossa and in the median plane. Sections have been contiguously numbered with encircled digits from inferior to superior (for details see Section 1.2). The illustrated section always corresponds to the line lying above the encircled number of the slice concerned. MA = Meynert axis. 
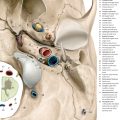
Fig. 6.4 Brainstem series. M = median plane ME = Meynert plane Fig. 6.4a View of the superior surface of the first anatomical section of the brainstem series, oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis and to the median plane (see ▶Fig. 6.3). The blue line at the top left signet indicates the position of the sectional plane at the level of the coronoid and condyloid processes of the mandible as well as the inferior part of the posterior cranial fossa. The maxillary sinus, the nasopharynx, and the posterior cranial fossa, the inferior aspect of the medulla oblongata and the cerebellar tonsils, about 1 cm above the foramen magnum, are visualized in this section (see ▶Fig. 6.3). 
Fig. 6.4b Detail section enlarged from a, depicting the opening of the left auditory tube in the nasopharynx. The inferior part of the medulla oblongata, the roots of the hypoglossal nerve, and the hypoglossal canal have been sectioned. 
Fig. 6.4c MR images oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis, corresponding approximately to a and b. This MR series (see ▶Fig. 6.4c, ▶Fig. 6.5, ▶Fig. 6.6, ▶Fig. 6.7, ▶Fig. 6.8, ▶Fig. 6.9, ▶Fig. 6.10, ▶Fig. 6.11, ▶Fig. 6.12, and ▶Fig. 6.13c) has been obtained from 33- and 34-year-old men. T1w and T2w image pairs (see ▶Fig. 6.4c, ▶Fig. 6.5, ▶Fig. 6.6, ▶Fig. 6.7, ▶Fig. 6.8, ▶Fig. 6.9, ▶Fig. 6.10, ▶Fig. 6.11, ▶Fig. 6.12, and ▶Fig. 6.13c) have been described by a common legend. If a structure is only seen in one of the MR image pairs, this has been indicated by “left” for “left image” or “right” for “right image” at the end. The T1w MR image (on the left) is a gradient echo FLASH sequence. Structures of the brain have been accentuated by the selected sequence. The T2w MR image (on the right) was obtained using a T2w MEDIC sequence. Fiber tracts appear hypointense against gray matter in the employed T2w sequence. For technical data see Chapter 12. 
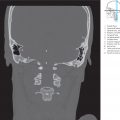
Fig. 6.5 Brainstem series. M = median plane ME = Meynert plane Fig. 6.5a View of the superior surface of the second anatomical section of the brainstem series (see ▶Fig. 6.3). The sectional plane passes through the inferior nasal turbinates, the temporomandibular joint, head of the mandible, and the jugular foramen. The medulla oblongata has been sectioned in the posterior cranial fossa at the level of the dural opening for the accessory nerve. 
Fig. 6.5b Detail section enlarged from a. The cartilaginous part of the auditory tube, the inferior part of the inferior olivary nucleus, and the origin of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery from the vertebral artery have been sectioned. The two internal jugular veins are symmetrically visualized; the right jugular foramen is widened with an enlarged superior bulb of the internal jugular vein (variant). 
Fig. 6.5c MR images oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis corresponding approximately to a and b. T1w MR image on the left, with a T2w MEDIC MR image on the right. For technical data see Chapter 12. 
Fig. 6.6 Brainstem series. M = median plane ME = Meynert plane Fig. 6.6a View of the superior surface of the third anatomical section of the brainstem series. The sectional plane lies at the level of the external auditory canal and the attachment of the inferior nasal turbinate to the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. The medulla oblongata has been sectioned in the posterior cranial fossa at the inferior end of the rhomboid fossa. 
Fig. 6.6b Detail section enlarged from a. The mandibular nerve lies just below the foramen ovale. The roots of the vagus nerve arise from the medulla oblongata. 
Fig. 6.6c MR images oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis, corresponding approximately to a and b. T1w MR image on the left, with a T2w MEDIC MR image on the right. For technical data see Chapter 12. 
Fig. 6.7 Brainstem series. M = median plane ME = Meynert plane Fig. 6.7a View of the superior surface of the fourth anatomical section of the brainstem series. The middle turbinate has been sectioned in the nasal cavity. The sectional plane passes through the floor of the middle cranial fossa through the tympanic cavity of the temporal bone and the superior part of the medulla oblongata at the level of the lateral aperture of the fourth ventricle in the posterior cranial fossa. 
Fig. 6.7b The detail section from a displays the confluence of the vertebral arteries with the basilar artery. The roots of the abducens nerve arise at the junction of the medulla oblongata and pons. The superior part of the inferior olivary nucleus lies in the medulla oblongata. 
Fig. 6.7c MR images oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis, corresponding approximately to a and b. T1w MR image on the left, with a T2w MEDIC MR image on the right. For technical data see Chapter 12. 
Fig. 6.8 Brainstem series. M = median plane ME = Meynert plane Fig. 6.8a View of the superior surface of the fifth anatomical section of the brainstem series. The sectional plane runs just above the floor of the orbital cavity. The base of the temporal lobe lies in the middle cranial fossa. The hammer and the incus can be identified in the tympanic cavity. The posterior cranial fossa has been sectioned at the level of the inner auditory canal, pons, dentate nucleus, and the internal occipital protuberance. The pole of the left occipital lobe is seen on the left. 
Fig. 6.8b The detail section from a shows the sphenoid sinus with the adjoining trigeminal ganglion (left) and the trigeminal nerve (right). The cross-section through the inferior part of the pons shows the middle cerebellar peduncle. The seventh and eighth cranial nerves enter the internal auditory canal. 
Fig. 6.8c MR images oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis, lying somewhat further superiorly than a and b. T1w MR image on the left, with a T2w MEDIC MR image on the right. For technical data see Chapter 12. 
Fig. 6.9 Brainstem series. M = median plane ME = Meynert plane Fig. 6.9a View of the superior surface of the sixth anatomical section of the brainstem series. The sectional plane lies at the level of the ethmoidal air cells, sphenoid sinus, and the upper part of the petrous bone. The pons and cerebellum lie in the infratentorial region of this section, while the bases of the occipital lobes lie in the supratentorial region. The two regions are separated by the cerebellar tentorium. 
Fig. 6.9b The detail section from a shows the triangular part of the fifth cranial nerve with the sixth cranial nerve at the dural opening. The pons has been sectioned approximately in its center. 
Fig. 6.9c MR images oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis, corresponding approximately to a and b. T1w MR image on the left, with a T2w MEDIC MR image on the right. For technical data see Chapter 12. 
Fig. 6.10 Brainstem series. M = median plane ME = Meynert plane Fig. 6.10a View of the superior surface of the seventh anatomical section of the brainstem series. The sectional plane runs through the superior orbital fissure, the sella turcica with the pituitary gland as well as through the basal parts of the temporal and occipital lobes. The pons has been sectioned at the level of the exit of the trigeminal nerve. 
Fig. 6.10d High-resolution T2w image of the trigeminal nerve and its entry into Meckel’s cave. 
Fig. 6.10b The detail section from a shows the adeno- and the neurohypophysis with the laterally situated segments of the internal carotid arteries. The superior cerebellar peduncle lies lateral to the fourth ventricle. 
Fig. 6.10c MR images oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis, corresponding approximately to a and b. T1w MR image on the left, with a T2w MEDIC MR image on the right. For technical data see Chapter 12. 
Fig. 6.11 Brainstem series. M = median plane ME = Meynert plane Fig. 6.11a View of the superior surface of the eighth anatomical section of the brainstem series. The olfactory bulb and tract have been sectioned in the depths of the anterior cranial fossa. The optic nerve enters the optic canal. The supratentorial region with the temporal and occipital lobes is significantly larger in this section than the infratentorial region with the pons and cerebellum. 
Fig. 6.11b The detail section from a displays a nearly horizontal stretch of the third and fourth cranial nerves. The infundibulum pierces the roof of the sella turcica. The fourth ventricle tapers in the upper part of the pons in the direction of the aqueduct of the midbrain. 
Fig. 6.11c MR images oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis, lying somewhat further inferiorly than a and b. T1w MR image on the left, with a T2w MEDIC MR image on the right. For technical data see Chapter 12. 
Fig. 6.12 Brainstem series. M = median plane ME = Meynert plane Fig. 6.12a View of the superior surface of the ninth anatomical section of the brainstem series. The sectional plane lies anteriorly just below the roof of orbit and medially behind it in the region of the straight gyrus above the anterior cranial fossa. The mammillary bodies and the midbrain at the level of the inferior colliculi are seen in this section. 
Fig. 6.12b The detail section from a shows the optic tract. The optic chiasm lies within this ninth section (interrupted yellow), posterior to which lies the hypothalamus with the mammillary bodies. The trochlear nerve is seen exiting the midbrain in this section behind the inferior colliculus. 
Fig. 6.12c MR images oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis, corresponding approximately to a and b. T1w MR image on the left, with a T2w MEDIC MR image on the right. For technical data see Chapter 12. 
Fig. 6.13 Brainstem series. M = median plane ME = Meynert plane Fig. 6.13a View of the superior surface of the tenth anatomical section of the brainstem series. Sections of the frontal and temporal lobes, hypothalamus, and midbrain have been sectioned in this plane at the level of the superior colliculi. 
Fig. 6.13b The detail section from a portrays structures adjoining the optic tract-hypothalamus, midbrain at the level of the superior colliculi, and the hippocampus. 
Fig. 6.13c MR images oriented perpendicular to the Meynert axis, lying somewhat further inferiorly than a and b. T1w MR image on the left, with a T2w MEDIC MR image on the right. For technical data see Chapter 12.
6 Brainstem
3D views of the brainstem, its nuclei, and 10 brainstem sections, from inferior to superior, have been described in this section of the book. ▶Fig. 6.1 illustrates the brainstem and cerebellar tracts and ▶Fig. 6.2 shows the cranial nerve nuclei, while ▶Fig. 6.3 depicts the position of brainstem sections. Individual brainstem sections have been reproduced in ▶Fig. 6.4, ▶Fig. 6.5, ▶Fig. 6.6, ▶Fig. 6.7, ▶Fig. 6.8, ▶Fig. 6.9, ▶Fig. 6.10, ▶Fig. 6.11, ▶Fig. 6.12, and ▶Fig. 6.13.


































Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree