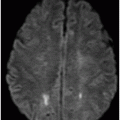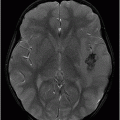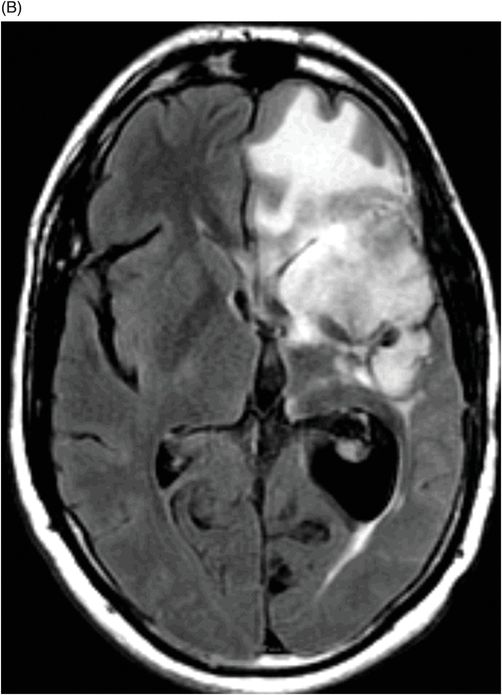
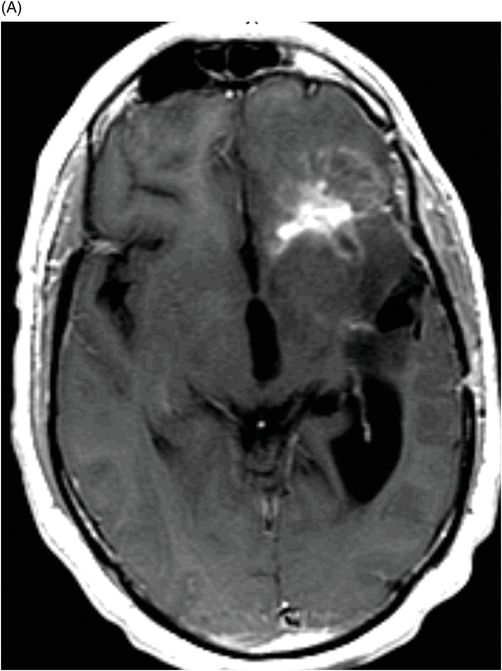
(A) Axial postcontrast T1WI and (B) Axial FLAIR image through the frontal lobe (two months after initiation of bevacizumab).

(A) Axial postcontrast T1WI and (B) Axial FLAIR image through the frontal lobe (three months after initiation of bevacizumab).


Pseudoresponse Associated with Antiangiogenic Therapy
Primary Diagnosis
Pseudoresponse associated with antiangiogenic therapy
Differential Diagnosis
True tumor response
Imaging Findings
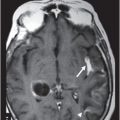
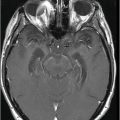
Fig. 94.1: (A) Axial postcontrast T1WI through the frontal lobe (obtained before initiation of bevacizumab) demonstrated a heterogeneously enhancing mass centered in the left frontal lobe. Postsurgical changes are evident in the left frontotemporal regions. (B) Axial FLAIR image through the same level demonstrates FLAIR hyperintensity diffusely involving the left frontal lobe that also extends to the anterior temporal lobe. It can be noted that there is mass effect to the third ventricle, as well as the anterior interhemispheric fissure. Fig. 94.2: (A) Axial postcontrast T1WI through the frontal lobe (two months after initiation of bevacizumab) demonstrates significant improvement of the left frontal lobe heterogeneous enhancement. (B) Axial FLAIR image through the same level demonstrates minimal, if any, improvement of the FLAIR hyperintense area. The mass effect to the third ventricle, as well as the anterior interhemispheric fissure, is not evident on this scan. Fig. 94.3: (A) Axial postcontrast T1WI through the frontal lobe (three months after initiation of bevacizumab) demonstrates further enlargement of the tumor’s enhancing component as compared to both the pretreatment and two-month follow-up. (B) Axial FLAIR shows there is also interval worsening of the FLAIR hyperintense areas. Mass effect to the third ventricle is noticeable.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree