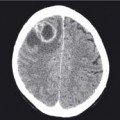
41.1 CT Pulmonary angiogram: pulmonary embolus
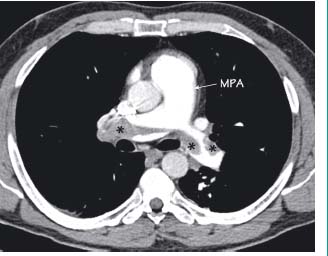
This patient presented with shortness of breath and chest pain 10 days after a gynaecological operation. The main pulmonary artery (MPA) is dilated and within the right and left pulmonary arteries there are filling defects (*) of soft tissue density due to a large pulmonary embolus. This crosses the midline forming a ‘saddle’
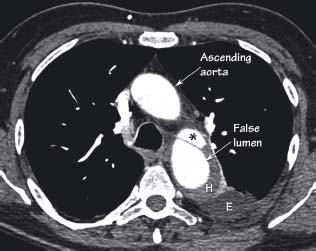
There is a large ‘false lumen’ of the descending aorta. This arises distal to the left subclavian artery (not shown). The ‘true lumen’ (*) remains patent but it is compressed by the false lumen. Other features that often accompany aortic dissections are the unopacified mural/wall haematoma (H) and a left-sided pleural effusion (E). This patient presented with tearing interscapular pain typical of an aortic dissection
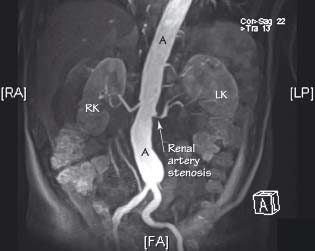
MR angiography of this patient with hypertension revealed a stenosis at the origin of the left renal artery. This type of lesion is often treated radiologically with balloon dilatation or stent insertion under imaging guidance. A aorta, LK left kidney, RK right kidney
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree