26 Development of the Arteries of the Lower Limb
T. Rodt, M. Lee
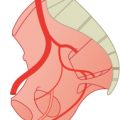
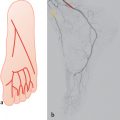
The arteries of the lower limbs derive from the fifth lumbar artery (Chapter 8), which forms the umbilical artery in the embryo. At the embryo stage of a crown-to-heal length of 10 mm, several side branches can already be identified: the external iliac, sciatic, superior gluteal, and internal pudendal arteries. The sciatic artery passes through the sciatic plexus and forms the main artery of the leg. It persists in most vertebrates. By contrast, in mammals the femoral artery, as the continuation of the external iliac artery, becomes the main artery for the lower limbs. Very early, anastomoses are formed between the posterior sciatic artery and the anterior femoral artery. When the main supply to the popliteal artery comes from the femoral artery, the sciatic artery regresses. Other parts of this anastomotic network are the precursor or the profunda femoris artery. The initial part of the sciatic artery remains as the inferior gluteal artery with a minute branch supplying the sciatic nerve.1–4
Another branch of the femoral artery is the saphenous artery, the name indicating that it follows the same course as the saphenous nerve and the great saphenous vein. This artery is connected to the arteries of the foot; its connections to the sciatic artery disappear. As some parts atrophy while others grow, the descending genicular artery and the posterior tibial artery are finally the only remnants of the saphenous artery. Whereas the peroneal artery is a remnant of the sciatic artery, the anterior tibial artery is a new branch. This complicated pattern of embryological development in the arteries of the leg explains the large number of anomalies.1–3,5,6
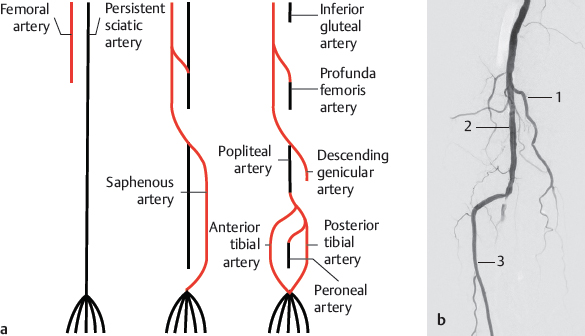
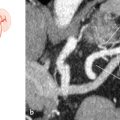
Fig. 26.1 Development of the arteries of the lower limb. Schematics (a) and DSA (b). The schematic drawings show the development of the arteries of the lower limb as described above. The DSA (b) shows a descending genicular artery, a remnant of the saphenous artery, popliteal artery, and anterior tibial artery. The tibioperoneal trunk is occluded. 1 Descending genicular artery;
2 popliteal artery; 3 anterior tibial artery.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree