Emerging Technologies
This chapter is a brief introduction to some of the significant emerging technologies in breast imaging. Listed under each technology are some basic definitions, strengths and weaknesses, data, tips, and guidelines regarding their use.
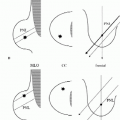
DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY
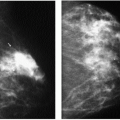
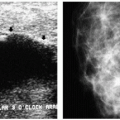
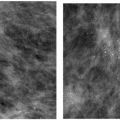
Image is acquired as an electronic signal that can be displayed on a monitor (soft copy display) or printed on film (hard copy display) (1, 2, 3).
Different technologies are being evaluated for the acquisition of digital images, including scintillators with an array of charge-coupled devices (CCDs) and fiberoptic tapers, slot scanners with CCDs, photostimulable phosphor plates, and flat-panel amorphous silicone plates with scintillators (1, 2, 3).
Status of workstation technology is not optimal; difficulties include resolution of monitors, how to compare current digital images to prior film-screen images, how to compare one side to the other and one projection to another, and length of time required to access studies (1, 2, 3).
Most digital systems offer 5 line pairs per millimeter (lp/mm) of resolution (one digital system offers 12.5 lp/mm resolution) compared with 10 to 15 lp/mm that is typical with conventional mammography units. Significance of these resolution differences is not yet clear (1, 2, 3).
Advantages of digital mammography include elimination of artifacts, noise, and variability related to film processing; postexposure processing of images that allows optimization of brightness and contrast; elimination of film and film storage costs; increased efficiency of technologist (no time spent developing films, reduced number of retakes); telemammography; easier application of computer-aided detection (CAD) and diagnosis; and application of new concepts such as tomosynthesis to eliminate superimposition of dense tissue (1, 2, 3).
Disadvantages include availability of only one size of the image receptor, prohibitive costs of units given low reimbursement rates for mammography (mammography is already considered a “lost leader” in radiology); and suboptimal workstation technology. Although not yet clear, lower resolution of digital units may also be a disadvantage (1, 2, 3).
Because the mammographic images are large, image storage can be an issue, particularly if the facility is not working in a PACs environment.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree