FANCONI SYNDROME
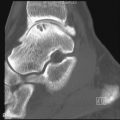
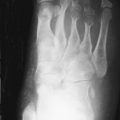
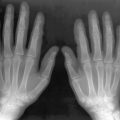
Fanconi syndrome includes a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by a defect in transport capacity of the proximal tubules that results in impaired reabsorption of glucose, calcium, phosphate, amino acids, bicarbonate, uric acid, and organic acids. Excretion of low-molecular-weight proteins (< 50,000 Da), magnesium, sodium, and potassium are also increased. Various familial and acquired disorders contribute to the pathogenesis of this syndrome, ultimately resulting in injury to the proximal tubules. The most common causes of Fanconi syndrome in adults and children are light-chain myeloma and cystinosis (autosomal-recessive cystine storage disease), respectively. This syndrome has also been seen in vitamin D deficiency. Box 38-1 presents selected causes of Fanconi syndrome.
INHERITED
Galactosemia
Cystinosis
Hereditary fructose intolerance
Glycogen storage disease
Wilson’s disease
Tyrosinosis (tyrosinemia, type I)
ACQUIRED
Amyloidosis
Multiple myeloma
Nephrotic syndrome
Heavy metal exposure (lead, mercury)
Malignancy
Vitamin D deficiency
Medications (aminoglycosides, valproic acid, ifosfamide, outdated tetracycline, cis-platinum)
Glue sniffing (toluene inhalation)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree