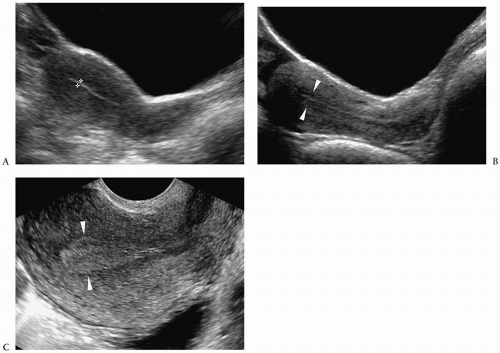
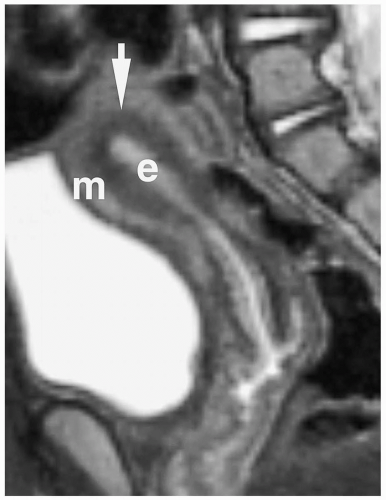
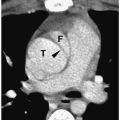
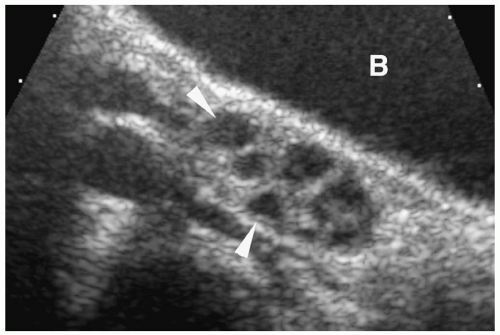
 Figure 10.1 Normal prepubertal ovary. Longitudinal sonogram of the right ovary of a 2-year-old girl shows multiple small follicles (arrowheads), measuring less than 9 mm in diameter (B, bladder). |
Table 10.1: Ovarian Volume Measurements | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
stimulated follicle can attain a size of 20 to 30 cm, before it ruptures and releases its ovum. The ruptured follicle involutes and becomes a corpus luteum, unless the ovum is fertilized. Corpus luteum follicles range between 10 and 30 mm in diameter. Of note, the diameter of a physiologic cyst should be 3 cm or less.
Table 10.2: Normal Uterine Diameters and Volume | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
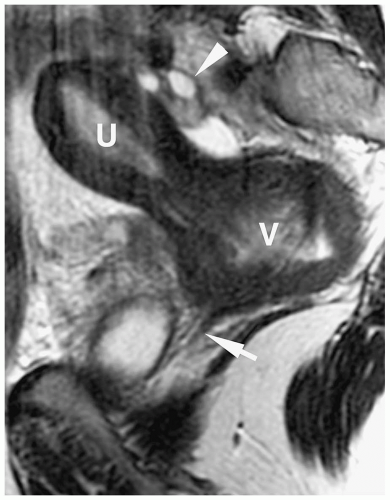
myometrium and endometrium cannot be differentiated from each other (Fig. 10.9). Three distinct zones can be seen within the fundus on T2-weighted MR images: the high signal intensity endometrium, low signal intensity inner myometrium, and intermediate signal intensity outer myometrium (Fig. 10.10).
of the female reproductive tract, the lower segments of the paired müllerian ducts fuse to form the uterus, cervix, and upper vagina. After the lower müllerian ducts fuse, a central septum is present, which eventually resorbs to form a single uterine cavity and cervix. Uterine anomies result when there is an error in development or fusion of the ducts or resorption of the midline septum. Patients may present with primary amenorrhea, mass (hematocolpos), or delayed onset of menarche. Coexistent renal ectopia or agenesis occurs in 20% to 30% of patients. Ultrasonography and MRI are the studies of choice to detect and characterize müllerian duct anomalies (11,12). The most common anomalies are discussed below.
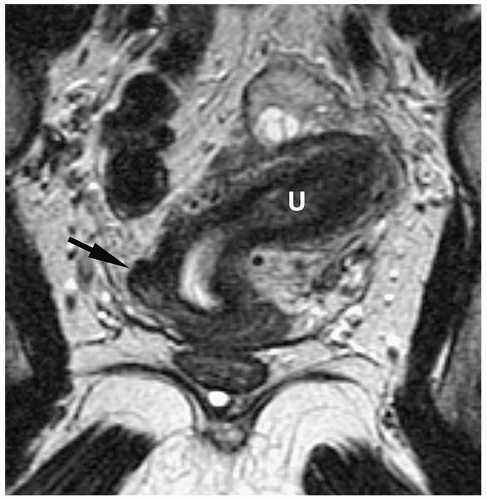
banana-shaped uterus (fusiform uterine cavity with lateral deviation) with normal zonal anatomy. Partial arrest in development of one duct results in a rudimentary uterine horn, which may or may not connect to the opposite cornua (Fig. 10.12). If the rudimentary horn is obstructed and contains functioning endometrium, it may be distended by blood or blood products. Unicornuate uterus does not require treatment unless there is hematometra.
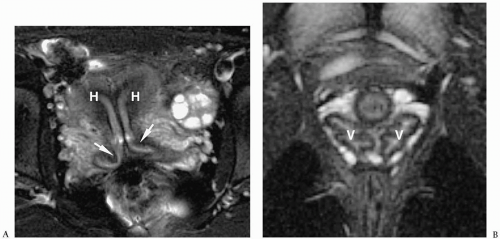
bicornuate uterus from septate uterus is the fundal contour. Differentiation is important because septate uteri are treated with transvaginal hysteroscopic resection of the septum, while an abdominal approach is required for the bicornuate uterus.
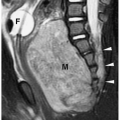
 Figure 10.15 Bicornuate uterus. Fat-saturated T2-weighted MR image shows two uterine bodies (arrows). There is a deep cleft (> 1 cm) in the uterine fundus. Each uterine horn is of similar size and has differentiated zonal anatomy. The two bodies fused just above a single cervix.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|