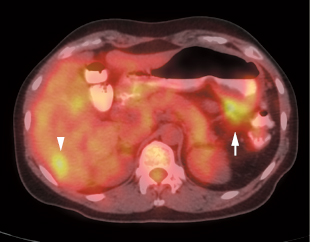
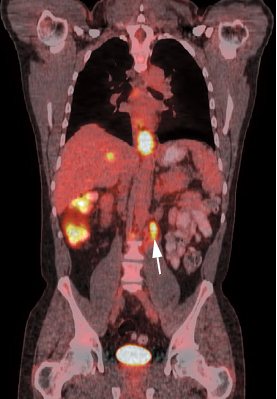
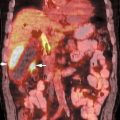
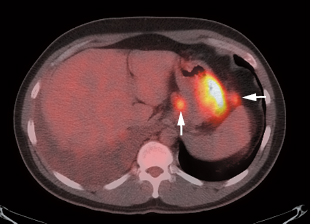
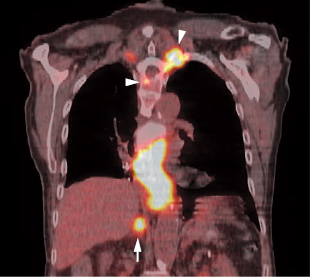
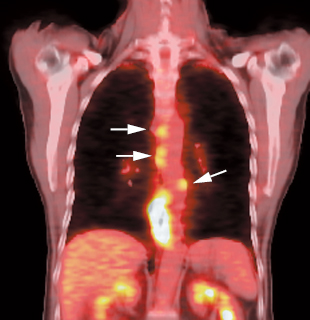
17 Fig. 17.1 Gastric cancer. Axial positron emission tomography/computed tomography scan demonstrates uptake in a primary gastric cancer with two local nodal metastases (arrows). PET has a limited role in evaluating primary esophageal tumors. Fig. 17.4 Metastatic esophageal cancer. Coronal positron emission tomography/computed tomography scan in a patient with esophageal carcinoma demonstrates intense uptake in the primary tumor and adrenal (arrow) and bone (arrowheads) metastases. Fig. 17.5 Esophageal cancer with locoregional nodal metastases. Coronal positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) scan demonstrates multiple metastases to locoregional paraesophageal nodes (arrows) from a distal esophageal cancer. Although endoscopic ultrasound would usually be more sensitive for detection of these nodes, a positive PET study is more specific for metastatic disease.
Gastric, Esophageal, and
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
Eugene C. Lin and Abass Alavi
 Gastric Cancer
Gastric Cancer
Clinical Indication: C
Accuracy and Comparison with Other Modalities
Pearls and Pitfalls
 Detection of Primary Esophageal Cancer
Detection of Primary Esophageal Cancer
Clinical Indication: D
Pitfalls
| Sensitivity % | Specificity % | |
| PET | 77 | 90 |
| CT/EUS | 46 | 69 |
 Staging of Esophageal Cancer
Staging of Esophageal Cancer
Clinical Indication: A
- The combination of PET and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) can be the most cost-effective method of staging esophageal cancer.19
- The primary value of PET is in20
- Detecting distant metastases (Figs. 17.3 and 17.4)
- Improving the specificity of lymph node staging
- Detecting distant metastases (Figs. 17.3 and 17.4)
- However, PET may not be routinely useful in patients with early-stage esophageal cancer (T ≥ 2), as these patients have a low incidence of lymphatic metastases.21
- The overall incremental benefit in staging accuracy of PET compared with CT is 14%.12 PET will identify unsuspected distant metastatic disease in 5 to 8%22 of patients without evidence of metastases after conventional work-up.
- Prognosis. Greater tumor length on PET and increased number of PET positive lymph nodes predict low survival rate.23
| Sensitivity % | Specificity % | |
| PET | 69 | 93 |
| CT | 46 | 74 |
| Sensitivity % | Specificity % | |
| PET | 92 | 94 |
| Bone scan | 77 | 84 |
Accuracy24
- PET: locoregional. Sensitivity 51%, specificity 94%
- PET: distant metastases. Sensitivity 67%, specificity 97%
- PET/CT: locoregional. Sensitivity 94%, specificity 92%25
- Significantly more accurate than PET alone
Comparison with Other Modalities
- Locoregional nodes.21 PET is insensitive for locoregional disease and cannot replace CT/EUS for locoregional staging, but a positive result is more specific than CT/EUS for nodal disease (Fig. 17.5). A large percentage of false-negative nodal groups on PET are in the immediate vicinity of the primary tumor.12 EUS will detect more pathologic periesophageal and celiac axis nodes than PET or CT (Table 17.1).26
- Distant nodes (Table 17.2).21
- Distant metastases (nodal and other) (Table 17.3)27
- Bone metastases. PET may be more accurate than bone scintigraphy for bone metas-tases (Table 17.4).28
- Anatomical region. PET has the highest accuracy in the neck, upper thoracic, and abdominal regions but low sensitivity in the mid- and lower thoracic regions.13
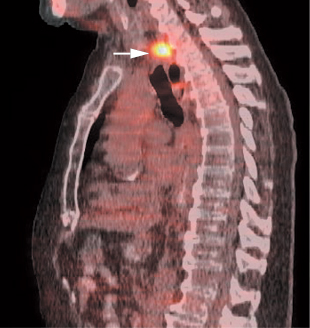
Fig. 17.6 Esophageal cancer recurrence. Sagittal positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) in an esophageal cancer patient status postesophagectomy and gastric pull-through demonstrates recurrence at the proximal anastomosis (arrow).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree