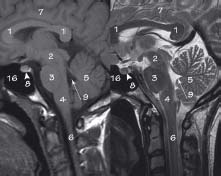
43.1 Sagittal brain MRI : T1 (left) and T2 (right)
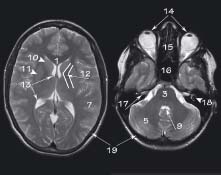
43.2 Axial brain MRI: T2 at level of lateral ventricles (left) and T2 at level of cerebellum (right)
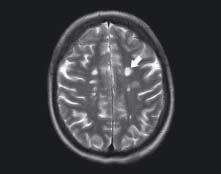
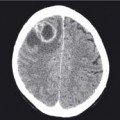
There are multiple bilateral foci of high signal (arrow) present within the white matter (appears dark on T2). These lesions lie immediately above and to the side of the lateral ventricles. The periventricular white matter is a typical location for multiple sclerosis lesions
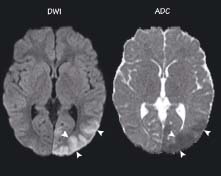
The DWI shows bright signal (arrowheads) in the distribution of the left posterior cerebral artery. The ADC image shows this area as low signal and therefore it is not due to T2 signal (note the bright ventricles). This is evidence of restricted diffusion which is a sign of infarction. DWI is the most sensitive investigation for acute cerebral infarction
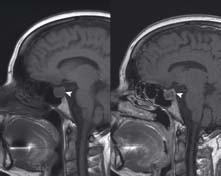
This patient presented with headaches and visual field disturbance (bitemporal hemianopia). The pre-contrast image (left) shows a pituitary adenoma (arrowhead) which demonstrates abnormal enhancement on the post-contrast scan (right). This is classified as a macroadenoma (>1 cm). The bigger a pituitary lesion becomes the more likely it is to cause visual disturbance due to compression of the optic chiasm which lies immediately above the pituitary gland
key
1 Corpus callosum
2 Midbrain
3 Pons
4 Medulla oblongata
5 Cerebellum
6 Spinal cord
7 Cerebrum
8 Pituitary gland
9 Fourth ventricle
10 Caudate nucleus
11 Lentiform nucleus
12 Internal capsule
13 Lateral ventricle
14 Eyes
15 Ethmoid air cells
16 Sphenoid sinus
17 Internal auditory meatus
18 Cochlea
19 Skull
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree