8 Hematologic Diseases
Anemia(s)
Sickle-cell Anemia
Definition
Sickle-cell anemia is a form of chronic hemolytic anemia with abnormally sickleshaped red blood cells.
Pathology
 hereditary hemoglobinopathy (HbS) occurring predominantly in people of African descent
hereditary hemoglobinopathy (HbS) occurring predominantly in people of African descent
 erythrocytes have a sickle shape
erythrocytes have a sickle shape
 due to decreased deformability sickle cells are occluding peripheral vessels, thus disturbing microcirculation and causing organ infarction
due to decreased deformability sickle cells are occluding peripheral vessels, thus disturbing microcirculation and causing organ infarction
– bone marrow hyperplasia due to longstanding anemia
Clinical Signs
 anemia
anemia
 severe pain episodes with infarction and bone marrow necrosis from vessel occlusion
severe pain episodes with infarction and bone marrow necrosis from vessel occlusion
 vulnerability to infection caused by functional asplenia as a result of repeated splenic infarction
vulnerability to infection caused by functional asplenia as a result of repeated splenic infarction
 osteomyelitis, arthritis (pathogen in more than 50% is Salmonella)
osteomyelitis, arthritis (pathogen in more than 50% is Salmonella)
 chronic synovitis
chronic synovitis
 chronic leg ulcers
chronic leg ulcers
Diagnostic Evaluation
 (→ primary method of choice)
(→ primary method of choice)
Recommended Radiography Projections
 standard projections
standard projections
Findings (Fig. 8.1)
 coarse bands of osteoporosis and thinning of compact bone
coarse bands of osteoporosis and thinning of compact bone
 irregular widening of the marrow cavity
irregular widening of the marrow cavity
 cortical destruction and periosteal new bone formation
cortical destruction and periosteal new bone formation
 patchy areas of radiolucency and sclerosis from bone infarction
patchy areas of radiolucency and sclerosis from bone infarction
 epiphyseal/metaphyseal growth disturbance
epiphyseal/metaphyseal growth disturbance
Role of Imaging
 detection of osseous deformity and abnormal bone density
detection of osseous deformity and abnormal bone density
 detection of inflammatory changes involving bones and joints
detection of inflammatory changes involving bones and joints
 detection of abnormal marrow signal on MRI
detection of abnormal marrow signal on MRI
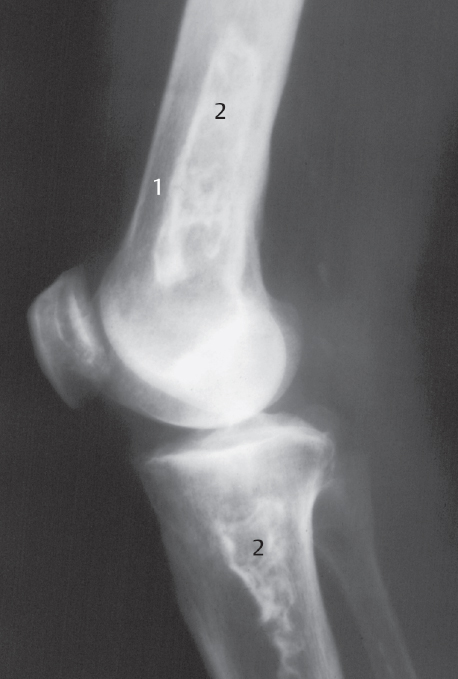
Fig. 8.1  Sickle-cell anemia.
Sickle-cell anemia.
Radiograph: osteoporosis and cortical thinning (1), infarctions with areas of radiolucency and sclerosis (2).
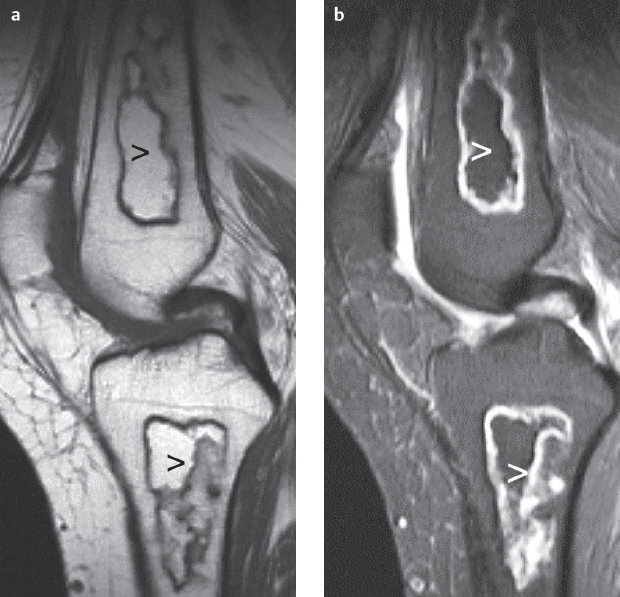
Fig. 8.2a,b  Infarctions.
Infarctions.
MRI, bone marrow infarction (open arrow) demarcated by garlandshaped zones appearing with low signal on T1 and high signal on STIR (same patient as in Fig. 7.4).
a Sagittal T1 SE image.
b Sagittal STIR image.
Basic Treatment Strategies
 symptomatic therapy
symptomatic therapy
 possibly bone marrow transplantation
possibly bone marrow transplantation
 (→ complementary method)
(→ complementary method)
Recommended Imaging Mode
 standard parameter settings, plain and contrast-enhanced images of the knee
standard parameter settings, plain and contrast-enhanced images of the knee
Findings
 especially with inflammatory changes very early detection of subperiosteal abscesses
especially with inflammatory changes very early detection of subperiosteal abscesses
 (→ complementary method)
(→ complementary method)
Findings
 increased uptake due to increased blood flow in expanded marrow
increased uptake due to increased blood flow in expanded marrow
 bone infarction:
bone infarction:
– decreased or absent uptake with acute bone infarction
– increased activity one to two weeks after infarction due to reactive new bone formation around the infracted area
 scans with bone-specific and bone-marrow-specific radionuclides enable differentiation between osteomyelitis and osteonecrosis
scans with bone-specific and bone-marrow-specific radionuclides enable differentiation between osteomyelitis and osteonecrosis
 (→ complementary method)
(→ complementary method)
Recommended Sequences
 plain T1-weighted spin-echo (T1 SE)
plain T1-weighted spin-echo (T1 SE)
 short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequence
short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequence
Findings (Fig. 8.2)
 bone marrow reconversion:
bone marrow reconversion:
– diffuse or focal decreased signal intensity on T1 SE caused by transformation of fatty marrow to hematopoietic marrow (hematopoiesis)
 bone marrow ischemia and infarction:
bone marrow ischemia and infarction:
– reduced fatty marrow signal on T1 SE (see Chapter 7)
 osteomyelitis:
osteomyelitis:
– bacterial infection leads to rapid increase in water content, which reduces signal on T1 SE and increases signal intensity on STIR sequences
Thalassemia
Definition
Thalassemia involves a synthesis disorder of hemoglobin with mild hypochromic anemia in thalassemia minor (heterozygote) and severe hemolytic anemia in thalassemia major (homozygote).
Pathology
 autosomal dominant hemoglobinopathy with typical target cells
autosomal dominant hemoglobinopathy with typical target cells
 bone marrow hyperplasia and hemochromatosis with sideroblast formation in bone marrow
bone marrow hyperplasia and hemochromatosis with sideroblast formation in bone marrow
 occurring in Mediterranean countries, Southeast Asia, Iran
occurring in Mediterranean countries, Southeast Asia, Iran
Clinical Signs
 anemia, fatigue, jaundice
anemia, fatigue, jaundice
 “hair-on-end” appearance of the skull
“hair-on-end” appearance of the skull
 malalignment of teeth
malalignment of teeth
 dwarfism caused by premature closure of the epiphyseal growth plate
dwarfism caused by premature closure of the epiphyseal growth plate
Diagnostic Evaluation
 (→ method of choice)
(→ method of choice)
Recommended Radiography Projections
 standard projections
standard projections
Findings (Fig. 8.3)
 severe osteoporosis with small cystic lesions and cortical thinning
severe osteoporosis with small cystic lesions and cortical thinning
 Erlenmeyer-flask deformity with loss of concavity and flaring of bone contour especially on the medial aspect of the diaphyses
Erlenmeyer-flask deformity with loss of concavity and flaring of bone contour especially on the medial aspect of the diaphyses
 premature closure of the epiphyseal plate at the distal end of the femur
premature closure of the epiphyseal plate at the distal end of the femur
 fractures with prolonged healing and deformity
fractures with prolonged healing and deformity
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


