© The Author(s) 2016
Amit Kumar and Fahimuddin ShaikImage Processing in Diabetic Related CausesSpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology10.1007/978-981-287-624-9_11. Introduction to Diabetes Related Causes and Overview of Image Processing Methods
(1)
BioAxis DNA Research Centre (P) Limited, Hyderabad, India
(2)
SJB Research Foundation, Bangalore, India
(3)
Annamacharya Institute of Technology and Science, Rajampet, India
1.1 Diabetes and Related Causes
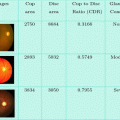
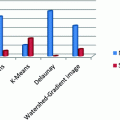
Diabetes mellitus (DM) often simply known as diabetes—is a group of metabolic diseases. The most burning problem in India is ‘Metabolic Syndrome’. One of these is the DM, calling India the diabetes Capital of the world as there is an alarming rise in prevalence of diabetes, which has gone beyond epidemic to the pandemic one. For every 10 s a person dies from diabetic related causes in the world. DM is a metabolic disorder which characterizes the inability of the pancreas to control blood glucose concentration. This problem results in blood glucose levels moving out of normal range [1].
The classification of diabetes falls under 3 categories:
DM type 1 results from the failure of body to produce insulin, and requires the injection of insulin. (Most preferably called as insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, in short IDDM, and juvenile diabetes.)
DM type 2 results from insulin resistance, a simple condition in which cells fail to properly utilize insulin, sometimes it may be assumed as absolute insulin deficiency. (Referred to as Non insulin dependent DM, NIDDM for short, also called adult onset diabetes.)
Other forms of DM include congenital diabetes occurs due to genetic defects of insulin secretion, cystic fibrosis-related diabetes, diabetes (steroidal) induced by high doses of glucocorticoids, and other forms of monogenic diabetes.
All forms of diabetes are treatable to an extent since insulin became available in 1921, and type 2 diabetes may be controlled with proper timely medications. Both type 1 and 2 DM are chronic conditions that usually cannot be cured but prevented to some extent. The transplantations of Pancreas have been tried with limited success in type 1 DM but gastric bypass surgery has been successful in many with morbid obesity and type 2 DM. Gestational type of DM usually resolves after delivery. Diabetes without proper treatments can cause many complications. Acute complications include hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, or nonketotic hyperosmolar coma. Serious long-term complications in DM include more chances of cardiovascular disease, chronic renal failure, and retinal damage. Adequate treatment of diabetes is thus very much of important, as well as blood pressure control and lifestyle factors such as smoking and maintaining a healthy body weight [2, 3].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree