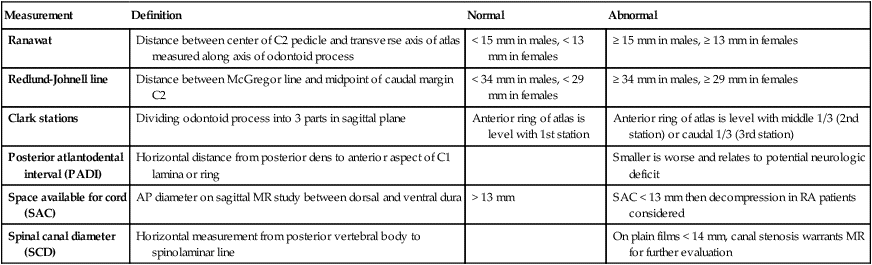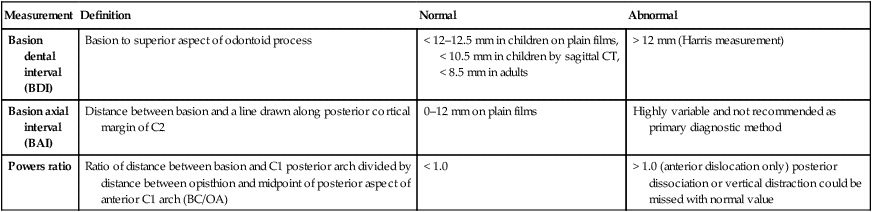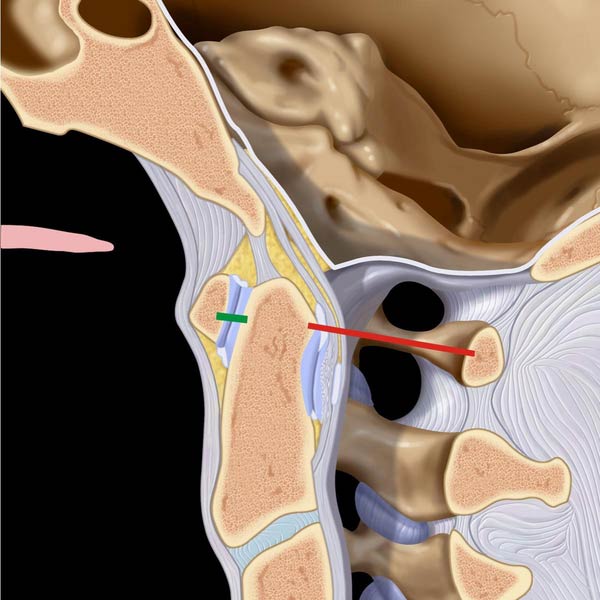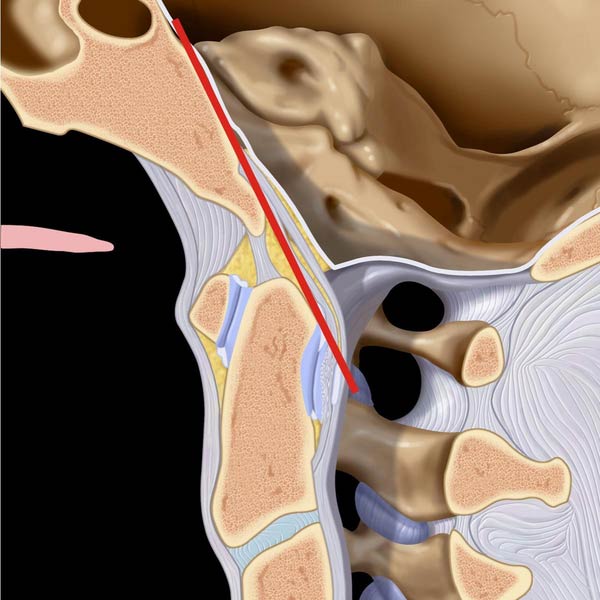
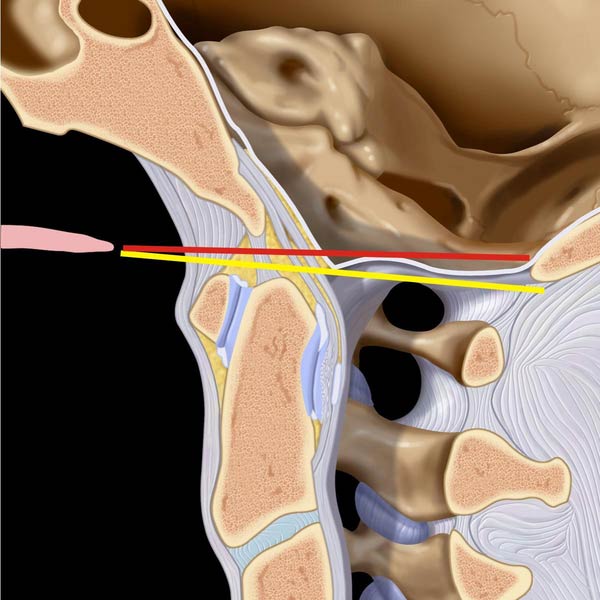
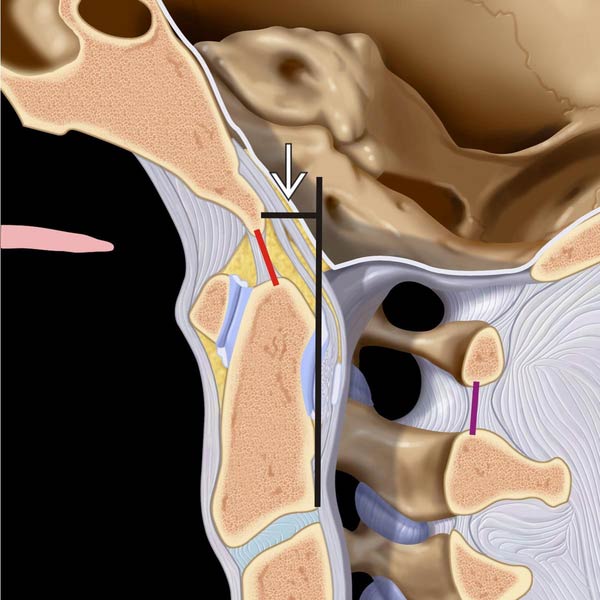
 extending from basion to line extended along posterior margin of C2, which should be < 12 mm on plain films. C1-C2 spinolaminar line is shown in purple (< 8 mm in adults).
extending from basion to line extended along posterior margin of C2, which should be < 12 mm on plain films. C1-C2 spinolaminar line is shown in purple (< 8 mm in adults).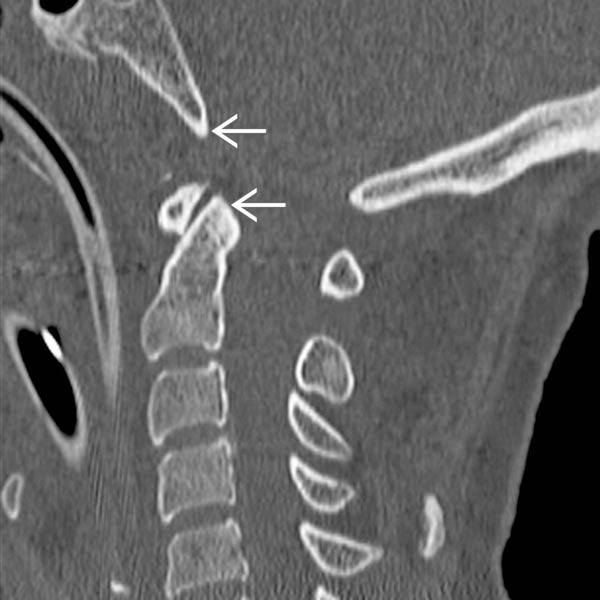
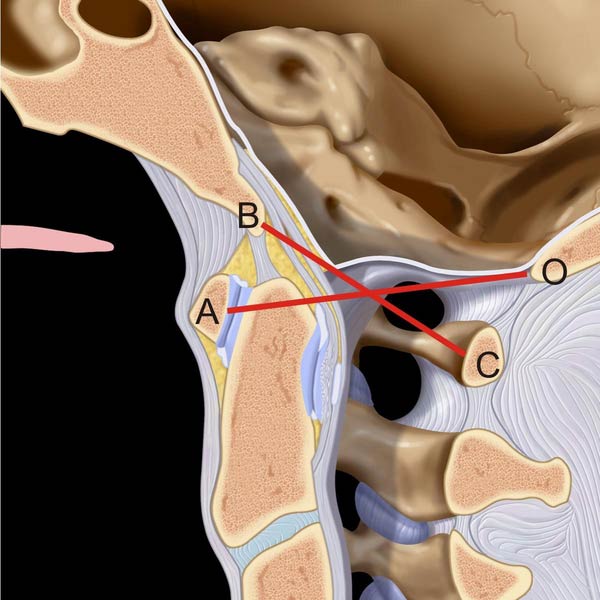
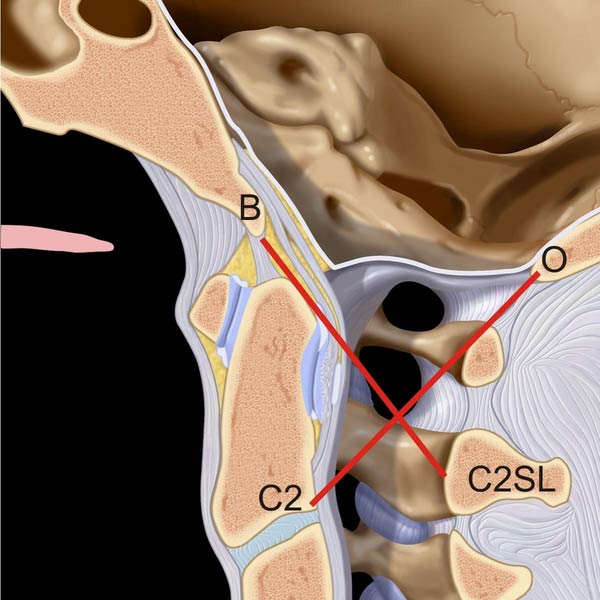
 of the BDI > 8.5 mm in this adult. Note the normal Wackenheim line relationship.
of the BDI > 8.5 mm in this adult. Note the normal Wackenheim line relationship.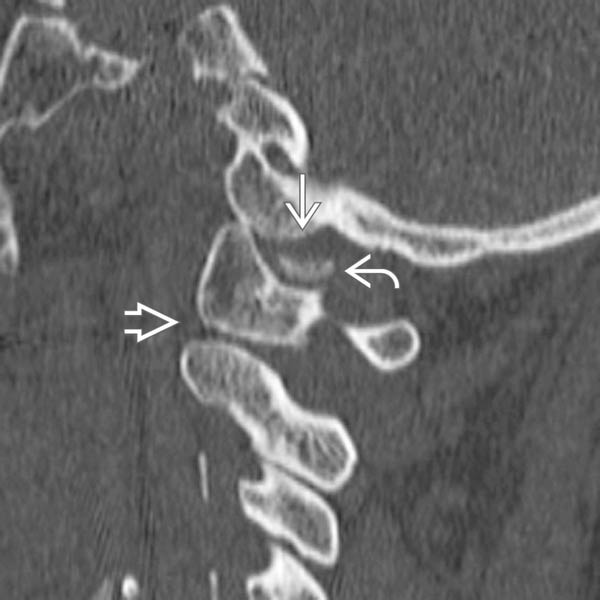
 with anterior subluxation of the condyle. Condylar fragment is present in the joint space
with anterior subluxation of the condyle. Condylar fragment is present in the joint space  . Note the normal C1-C2 relationship
. Note the normal C1-C2 relationship  .
.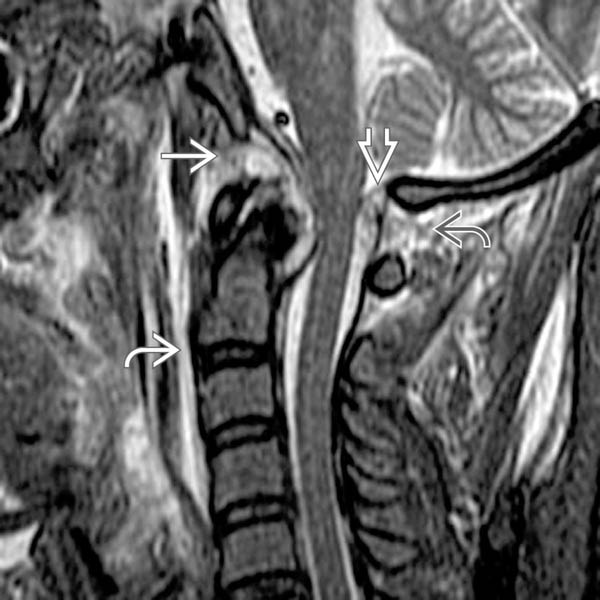
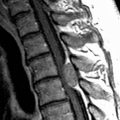
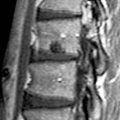
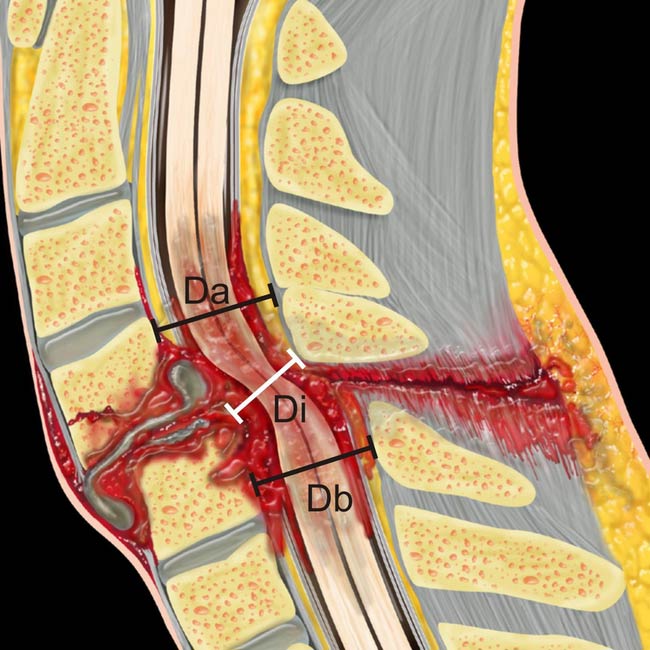
 from alar and apical ligament rupture. Note also prevertebral edema
from alar and apical ligament rupture. Note also prevertebral edema  and posterior interspinous ligament disruption
and posterior interspinous ligament disruption  . Posterior epidural hemorrhage
. Posterior epidural hemorrhage  contributes to subarachnoid space narrowing.
contributes to subarachnoid space narrowing.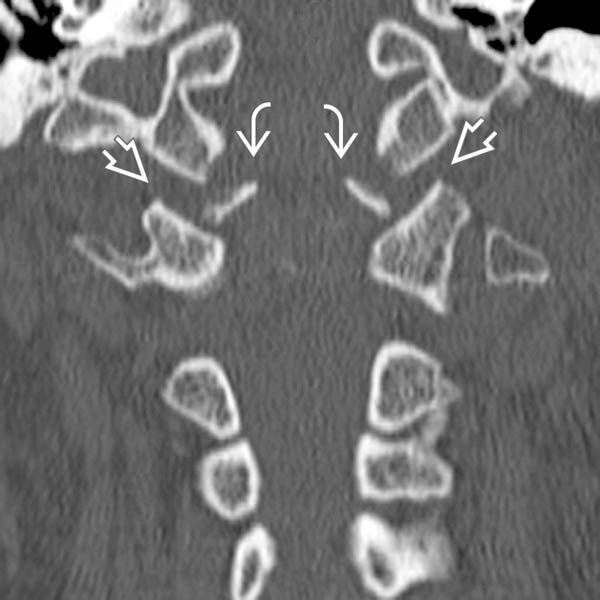
 , which should be approximately 2 mm. Bilateral symmetric avulsion fractures off of the condyles are present
, which should be approximately 2 mm. Bilateral symmetric avulsion fractures off of the condyles are present  .
.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree